| CPC G01N 21/211 (2013.01) [G01N 2021/213 (2013.01); G01N 2201/021 (2013.01); G01N 2201/06113 (2013.01); G01N 2201/12 (2013.01)] | 27 Claims |
|
1. A method of investigating a sample with electromagnetic radiation in the mid-infrared spectral range, which reduces the effects of speckle and standing waves, comprising the steps of:
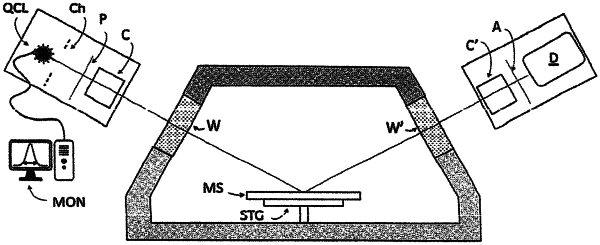
a) providing an ellipsometer or polarimeter system comprising:
a′) a quantum cascade laser source of high-brilliance, tunable electromagnetic radiation with emission wavelengths in the mid-infrared spectral range, said quantum cascade laser source comprising means for dithering the electromagnetic radiation output;
b′) a beam polarizing optical element;
c′) a first rotatable optical retarder or polarizer element;
d′) a stage for supporting a sample;
e′) a second rotatable optical retarder or polarizer element;
f′) a beam analyzing polarizer optical element;
g′) a single-point detector for infrared radiation which is not capable of resolving individual pulses of quantum cascade laser electromagnetic radiation;
said method being characterized in that:
during use said quantum cascade laser source of electromagnetic radiation operates in a continuous or quasi-continuous wave, so that individual pulses are not detected; and
during use the wavelength content of said continuous or quasi-continuous wave is dithered so that cyclically or randomly a sequential plurality of different wavelengths around a central wavelength is output; and
during use said detector provides output data based on an average of a multiplicity of pulses in said continuous or quasi-continuous dithered electromagnetic radiation input thereto; and
during use said rotatable optical retarder or polarizing elements continuously rotate at different frequencies of fixed ratio;
said method further comprising:
b) placing a sample on said stage for supporting a sample;
c) while causing said rotatable optical retarder or polarizing elements continuously rotate at different frequencies of fixed ratio, causing said quantum cascade laser source to provide a dithered continuous or quasi-continuous beam of electromagnetic radiation directed so that it passes through said:
beam polarizing optical element; and
first rotatable optical retarder or polarizer element;
interacts with said sample on said stage for supporting a sample;
then passes through said:
second rotatable optical retarder or polarizer element; and
beam analyzing polarizer optical element; and
enters said single-point detector for infrared radiation;
d) causing said single-point detector for infrared radiation to provide sample characterizing output data based upon said received dithered continuous or quasi-continuous beam of electromagnetic radiation; and
e) analyzing the data output by said single-point detector to provide sample characterizing information.
|