| CPC B60L 58/12 (2019.02) [B60L 50/60 (2019.02); B60L 58/15 (2019.02); B60L 58/16 (2019.02); G06N 5/02 (2013.01); B60L 2240/545 (2013.01); B60L 2240/547 (2013.01); B60L 2240/549 (2013.01); B60L 2260/44 (2013.01); B60L 2260/50 (2013.01); Y02T 10/70 (2013.01); Y02T 90/16 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
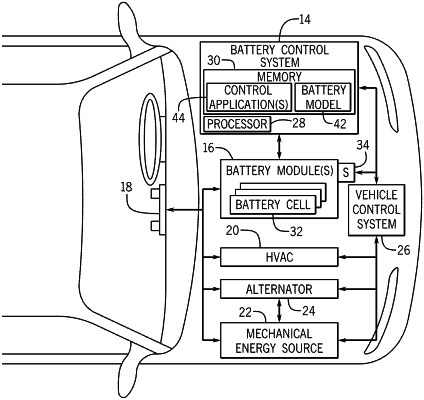
1. An automotive electrical system comprising a battery system, wherein the battery system comprises:
a battery comprising terminals configured to be electrically coupled to a one or more electrical devices in the automotive electrical system;
one or more sensors electrically coupled to the terminals of the battery, wherein the one or more sensors are configured to determine sensor data indicative of measured operational parameters of the battery comprising a measured terminal voltage; and
a battery control system communicatively coupled to the one or more sensors, wherein the battery control system is programmed to:
determine predicted operational parameters of the battery expected to occur during a prediction horizon by projecting the measured operational parameters over the prediction horizon;
determine a predicted internal resistance of the battery expected to occur during the prediction horizon based at least in part on the predicted operational parameters;
determine a charging power limit used to control supply of electrical power to the battery based at least in part on the predicted internal resistance when the measured terminal voltage of the battery is not greater than a lower voltage threshold; and
when the measured terminal voltage of the battery is greater than the lower voltage threshold:
determine a real-time internal resistance of the battery based at least in part the measured terminal voltage of the battery and a battery model that describes relationship between the measured operational parameters and internal resistance of the battery; and
determine the charging power limit based at least in part on the real-time internal resistance to facilitate improving operational reliability of the battery.
|