| CPC G06T 7/0012 (2013.01) [G01N 1/30 (2013.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); G01N 2001/302 (2013.01); G01N 2001/305 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
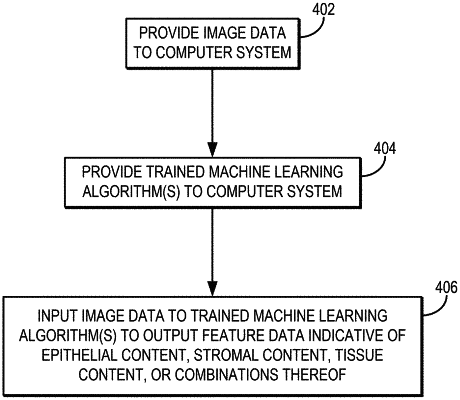
1. A method of detecting and optionally treating prostate cancer in a human subject, the method comprising:
obtaining histologically normal prostate tissue from the subject; and
quantifying, comprising one or more of:
quantifying an increase in epithelial thickness in the tissue of at least 6% relative to the epithelial thickness measured in a sample from a healthy, prostate tumor-free subject; and
quantifying a decrease in gland lumen roundness in the tissue of at least 10% relative to the gland lumen roundness measured in a sample from a healthy, prostate tumor-free subject; and then
performing a prostate cancer detection procedure on the subject.
|