| CPC F24F 11/65 (2018.01) [F24F 11/47 (2018.01); F24F 11/48 (2018.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
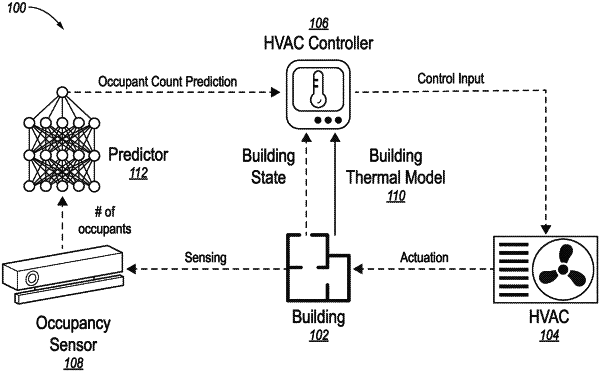
1. A method for controlling heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) operation of a building to minimize energy consumption using predicted occupant-counts and accounting for misprediction cost, comprising:
updating a thermal state of a plurality of zones of the building according to a building thermal model and information received from temperature sensors of the building;
updating predicted occupant counts for an upcoming plurality of time slots for each of the plurality of zones using actual occupancy counts for each of the plurality of zones;
updating a misprediction type distribution for the upcoming plurality of time slots for each of the plurality of zones, the misprediction type distribution indicating misprediction for true negatives, false positives, false negatives, and true positives;
updating a total misprediction cost expectation according to the predicted occupant counts and the misprediction type distribution;
determining HVAC power for each of the plurality of zones to optimize occupant thermal comfort weighted according to the predicted occupant counts while minimizing the total misprediction cost expectation, the determining being constrained to a heat exchange configuration of the building and minimum and maximum HVAC power available to each of the plurality of zones; and
controlling HVAC operation of the building according to the HVAC power determined for each of the plurality of zones.
|