| CPC H04W 40/16 (2013.01) [H04L 1/1607 (2013.01); H04L 45/74 (2013.01); H04W 4/06 (2013.01); H04W 40/125 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
1. A method for mobility management of nodes in an IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Network based on RPL, wherein, the method comprises following steps:
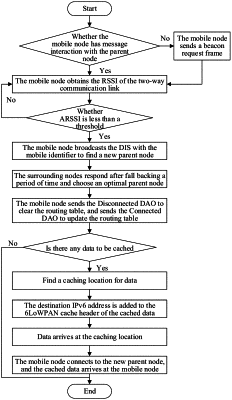
S1: in the IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Network with a mobile node, obtaining, by the mobile node, a received signal strength indication (RSSI) of two-way communication link after the mobile node sends a message to the mobile node's parent node and the parent node receives the message, records an RSSI of a corresponding link, and puts the recorded RSSI into a corresponding acknowledge character (ACK) frame load to reply to the mobile node; sending actively, by the mobile node, a beacon request frame to obtain the RSSI if the mobile node does not perform message interaction with the parent node for a period of time;
S2: obtaining, by the mobile node using an average filtering method, an average RSSI (ARSSI) after the mobile node obtains the RSSI of the two-way communication link with the parent node, and comparing the ARSSI with a set threshold; if the ARSSI is less than the threshold, determining that the node is moving and is moving away from the parent node, and not immediately disconnecting a current link of the mobile node; if the ARSSI is not less than the threshold, turning to step S1;
S3: multicasting, by the mobile node, a directed acyclic graph information solicitation (DIS) message with a mobile identifier, to search for a new parent node around, after the mobile node detects that it is moving away from the parent node;
S4: after non-leaf nodes around the mobile node receive the DIS message with the mobile identifier, calculating, by each of the nodes, fallback time according to the RSSI of the request message and a distributed competition algorithm, and replying to the mobile node a directed acyclic graph information object (DIO) message with an identifier according to the fallback time;
S5: after the mobile node finds out the new parent node, sending, by the mobile node, a disconnected destination advertisement object (DAO) message to the original parent node to request to disconnect the original link and clear an old routing table, and forward the DAO message to an upper-level node to delete all routing entries related to the mobile node; and sending, by the mobile node, a Connected DAO message to the new parent node to request to connect to the new parent node and update the routing table, and forward the Connected DAO message to an upper-level node until a complete communication path is established;
S6: confirming data to be cached; after the mobile node disconnects the original link, if there is no data to be sent to the mobile node during the disconnection process, ending the mobility management; if there is data to be sent to the mobile node during the disconnection process, finding, by the original parent node, a cache node for the data to be sent to the mobile node: if the original parent node receives the Disconnected DAO message, caching the data to be sent to the mobile node to the new parent node; if the original parent node does not receive the Disconnected DAO message due to some reasons, caching the data to a root node of the network;
S7: after the original parent node confirms the cache node, that is, finds out a cache location for the data, putting, by the original parent node, an IPv6 address of the cache node in a cache header of a 6LoWPAN message of the data to be cached, and then forwarding the data to the cache node for caching; and
S8: after the mobile node connects to the new parent node and updates the network routing table, sending, by the cache node, the cached data to the mobile node, and ending the mobility management.
|