| CPC H04L 41/06 (2013.01) [H04L 41/0677 (2013.01); H04L 41/12 (2013.01); H04L 43/50 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
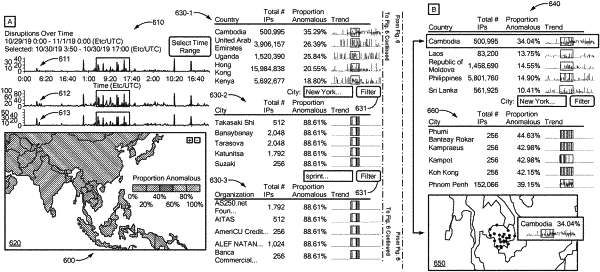
|
1. A method of identifying and reporting network anomalies, comprising:
receiving a plurality of routing path messages of advertised routes in a network, the routing path messages indicative of available network paths between network entities;
identifying an anomaly in an available network path indicative of a change to an advertised route, the anomaly causing network traffic between autonomous systems (AS) to follow a different path;
aggregating the plurality of routing path messages defining an anomaly received during a plurality of time intervals;
comparing the anomalies in each time interval of the plurality of time intervals to the anomaly in the others of the plurality of time intervals by:
building a node structure defining an isolation forest representative of the paths depicted in the routing path messages;
traversing the node structure; and
concluding, based on the comparison, whether a difference in the anomalies is indicative of a network disruption by:
defining a plurality of decision trees based on routing paths indicative of a sequence of autonomous systems for satisfying a plurality of routes to a destination;
splitting the decision trees until each respective decision tree has a terminal leaf node; and
identifying, based on an average number of splits until a terminal leaf node is attained, whether the decision tree is indicative of an anomaly.
|