| CPC G06F 30/367 (2020.01) | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
providing a frequency error margin value and a duty cycle error margin value associated with processing a digital signal having a transient waveform that comprises a sequence of pulses, each pulse having a pulse frequency, a pulse duty cycle, and a pulse duration;
identifying a buffer frequency, a buffer duty cycle, and a buffer duration of one of a plurality of sub-sequences of pulses, wherein each sub-sequence of pulses comprises one or more pulses, and wherein for the one of the sub-sequences of pulses:
the buffer frequency is a first function of the pulse frequencies of the sub-sequence of pulses, such that the buffer frequency and each of the pulse frequencies of the sub-sequence of pulses differ by less than the frequency error margin,
the buffer duty cycle is a second function of the pulse duty cycles of the sub-sequence of pulses, such that the buffer duty cycle and each of the pulse duty cycles of the sub-sequence of pulses differ by less than the duty cycle error margin, and
the buffer duration is the sum of the pulse durations over the sub-sequence of pulses;
representing the sub-sequence of pulses as a point comprising the buffer frequency, the buffer duty cycle, and the buffer duration;
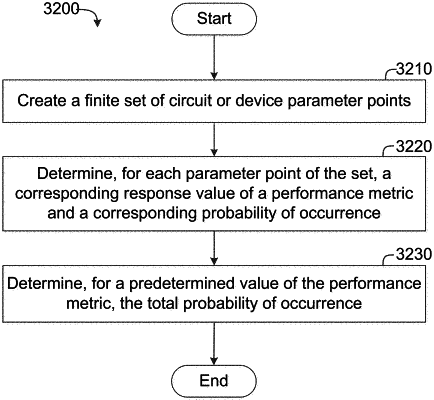
determining a response value of a performance metric and a probability of occurrence corresponding to the response value, based on the point; and
designing an electronic circuit based on the probability of occurrence, or driving an electronic circuit with a workload selected based on the probability of occurrence.
|