| CPC C12Q 1/6883 (2013.01) [C12Q 1/6827 (2013.01); C12Q 1/6844 (2013.01); C12Q 2600/156 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
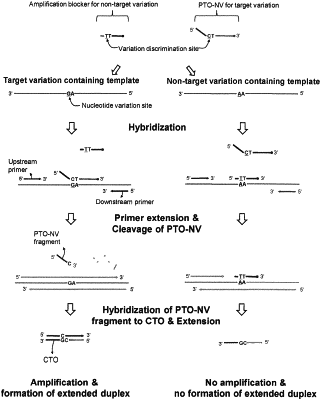
1. A method for detecting a target nucleotide variation on a target nucleic acid sequence using an amplification blocker and a VD-PTOCE (Variation Detection by Probing and Tagging Oligonucleotide Cleavage and Extension) assay, comprising:
(a) hybridizing the target nucleic acid sequence with a primer pair comprising an upstream primer and a downstream primer for amplification of the target nucleic acid, an amplification blocker having the resistance to 5′ nuclease cleavage and a PTO-NV (Probing and Tagging Oligonucleotide for Nucleotide Variation); wherein each of the upstream primer and the downstream primer comprises a hybridizing nucleotide sequence complementary to the target nucleic acid sequence; the amplification blocker comprises a complementary sequence to a non-target nucleotide variation different from the target nucleotide variation on the target nucleic acid sequence and the PTO-NV comprises
(i) a 3′-targeting portion comprising a hybridizing nucleotide sequence complementary to the target nucleic acid sequence,
(ii) a 5′-tagging portion comprising a nucleotide sequence non-complementary to the target nucleic acid sequence, and
(iii) a nucleotide variation discrimination site comprising a complementary sequence to the target nucleotide variation on the target nucleic acid, positioned on a 5′-end part of the 3′-targeting portion;
wherein the amplification blocker is hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence having the non-target nucleotide variation and not hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence having the target nucleotide variation; wherein the 3′-targeting portion of the PTO-NV is hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence and the 5′-tagging portion of the PTO-NV is not hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence;
wherein the upstream primer is located upstream of the PTO-NV; the amplification blocker is located downstream of the upstream primer or the downstream primer;
(b) contacting the resultant of step (a) with an enzyme having 5′ nuclease activity under conditions for cleavage of the PTO-NV; wherein the upstream primer induces through its extended strand the cleavage of the PTO-NV by the enzyme having 5′ nuclease activity; wherein the hybridization of the amplification blocker with the target nucleic acid sequence having the non-target nucleotide variation inhibits the extension of the primer located upstream of the amplification blocker, thereby blocking the amplification of the target nucleic acid sequence having the non-target nucleotide variation;
wherein when the PTO-NV is hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence having the target nucleotide variation complementary to the nucleotide variation discrimination site, the 5′-end part of the 3′-targeting portion forms a double strand with the target nucleic acid sequence to induce cleavage from a first initial cleavage site and a first fragment is released; wherein when the PTO-NV is hybridized with the target nucleic acid sequence having the non-target nucleotide variation non-complementary to the nucleotide variation discrimination site in spite of the presence of the amplification blocker, the 5′-end part of the 3′-targeting portion does not form a double strand with the target nucleic acid sequence to induce cleavage from a second initial cleavage site located downstream of the first initial cleavage site and a second fragment is released; wherein the second fragment comprises an additional 3′-end portion allowing the second fragment to be different from the first fragment;
(c) hybridizing a fragment released from the PTO-NV with a CTO (Capturing and Templating Oligonucleotide); wherein the CTO comprises in a 3′ to 5′ direction (i) a capturing portion comprising a nucleotide sequence complementary to the 5′-tagging portion or a part of the 5′-tagging portion of the PTO-NV and (ii) a templating portion comprising a nucleotide sequence non-complementary to the 5′-tagging portion and the 3′-targeting portion of the PTO-NV; wherein the CTO has a sequence selected such that the CTO is not hybridized with the additional 3′-end portion of the second fragment to prevent the second fragment from extension when the second fragment is hybridized with the capturing portion of the CTO; wherein the first fragment or the second fragment released from the PTO-NV is hybridized with the capturing portion of the CTO;
(d) performing an extension reaction using the resultant of step (c) and a template-dependent nucleic acid polymerase; wherein when the first fragment is hybridized with the capturing portion of the CTO, it is extended to form an extended strand comprising a extended sequence complementary to the templating portion of the CTO; wherein when the second fragment is hybridized with the capturing portion of the CTO, it is not extended; and
(e) detecting the presence of the extended strand, whereby the presence of the extended strand indicates the presence of the target nucleotide variation.
|