| CPC C12Q 1/686 (2013.01) [G16B 30/00 (2019.02); G16B 40/00 (2019.02); Y10S 707/964 (2013.01); Y10S 707/99931 (2013.01); Y10S 707/99941 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method of storing and retrieving digital data in polynucleotides:
encoding digital data in a payload sequence;
associating the payload sequence with a unique primer;
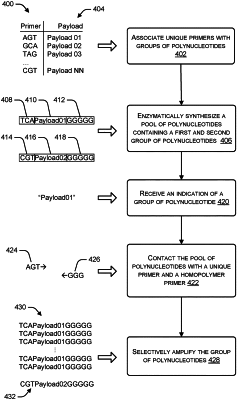
enzymatically synthesizing a polynucleotide having a sequence that includes a unique primer binding site that hybridizes with the unique primer, the payload sequence, and a homopolymer primer binding site;
contacting the polynucleotide with the unique primer, a homopolymer primer that hybridizes to the homopolymer primer binding site, and a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction mixture;
selectively amplifying, by PCR, the polynucleotide;
sequencing the polynucleotide to generate sequence data; and
decoding the sequence data to retrieve the digital data.
|
|
7. A method of performing random access to obtain specific polynucleotides from a pool of polynucleotides, the method comprising:
enzymatically synthesizing a pool of polynucleotides containing:
a first group of polynucleotides each comprising a first payload region encoding a portion of a first digital data file, a first unique primer binding site, and a homopolymer primer binding site, and
a second group of polynucleotides each comprising a second payload region encoding a portion of a second digital data file, a second unique primer binding site, and a same or different homopolymer primer binding site;
receiving an indication of the first group of polynucleotides;
contacting at least a portion of the pool of polynucleotides with a first unique primer complementary to the first unique primer binding site, a homopolymer primer complementary to at least a portion of the homopolymer primer binding site, and a PCR reaction mixture; and
selectively amplifying, by PCR, the first group of polynucleotides.
|
|
14. A method comprising:
contacting a polynucleotide comprising a first unique primer binding site, a payload region, and a homopolymer primer binding site with:
a unique primer having a sequence that hybridizes to the first unique primer binding site,
an overhang primer that hybridizes to the homopolymer primer binding site and that includes a unique nucleotide sequence which overhangs an end of the polynucleotide, and
a PCR reaction mixture; and
selectively amplifying, by PCR, the polynucleotide to create a first amplification product having a second unique primer binding site formed from the unique nucleotide sequence of the overhang primer.
|