| CPC A61B 17/22004 (2013.01) [A61B 17/2258 (2013.01); A61M 37/0092 (2013.01); A61B 5/055 (2013.01); A61B 5/0536 (2013.01); A61B 8/00 (2013.01); A61B 8/08 (2013.01); A61B 8/485 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00154 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00172 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00778 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22001 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22008 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22088 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22089 (2013.01); A61B 2090/378 (2016.02)] | 6 Claims |
|
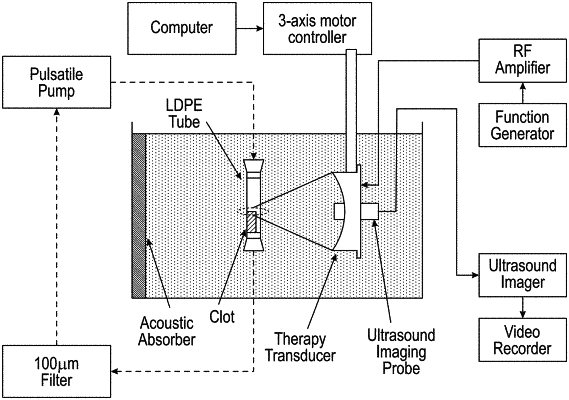
1. A method for controlled mechanical fractionation of a target tissue, comprising:
outputting an ultrasound pulse sequence from a transducer array resulting in cavitation forming a bubble cloud;
detecting a location of the bubble cloud;
actuating the transducer array such that the bubble cloud is spatially positioned within the target tissue in response to the location of the bubble cloud;
monitoring backscatter from the bubble cloud with the transducer array; and
adjusting one or more parameters of the ultrasound pulse sequence based on the monitored backscatter from the bubble cloud.
|