| CPC G21D 3/10 (2013.01) [G21D 3/001 (2013.01); G21C 7/36 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A method of regulating operating parameters of a nuclear reactor, the nuclear reactor comprising:
a tank;
a core comprising a plurality of nuclear fuel assemblies placed in the tank;
control clusters for controlling the reactivity of the core, and drive mechanisms configured to move each control cluster in the direction of insertion into the core or in the direction of extraction out of the core;
a primary circuit for cooling the core in which circulates a primary coolant fluid, comprising cold and hot branches pierced in the tank and through which the primary coolant respectively enters into the tank and leaves the tank; and
an injection circuit configured to selectively inject into the primary coolant fluid a neutron poison or diluent fluid without neutron poison, the operating parameters comprising at least a mean core temperature and an axial power imbalance, the method comprising the following steps:
acquiring a current value of at least one input;
acquiring a current value of a vector of outputs, with outputs comprising at least the operating parameters;
developing a reference value of the vector of outputs, using the current value of the at least one input;
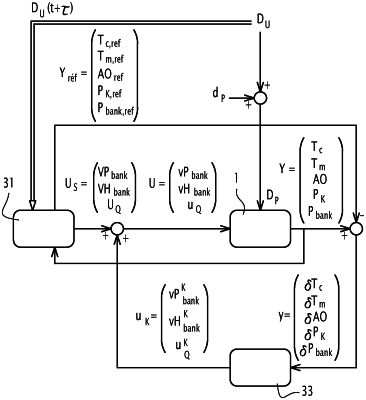
developing of a vector of control values of nuclear reactor controls by a supervisor implementing a predictive control algorithm, using at least said current value of the at least one input and the current value of the vector of outputs;
developing of a vector of corrective values of the nuclear reactor controls by a regulator implementing a sequenced gain control algorithm, using the current value of the vector of outputs and the reference value of the vector of outputs, the sequenced gain control algorithm comprising a plurality of linear regulators, each determined for regulating the operating parameters around a determined operating point of the nuclear reactor, said operating points being scaled to cover a nuclear reactor power range of 25% to 100% of a rated nuclear reactor power;
developing of a vector of corrected values of the controls of the nuclear reactor, by using the vector of control values of the controls developed by the supervisor and the vector of the corrective values of the controls developed by the regulator;
regulating the operating parameters of the nuclear reactor, by controlling the drive mechanisms to move the control cluster and by controlling the injection circuit to selectively inject into the primary coolant fluid the neutron poison or diluent fluid, using the vector of the corrected values of the nuclear reactor controls, the nuclear reactor controls comprising at least one rate of movement of the control clusters and at least one rate of injection of the neutron poison or of diluent fluid.
|