CPC Definition - Subclass H05H
This place covers:
Systems and methods for handling plasma, i.e.:
Generating plasma;
Confining plasma.
These systems are essentially related to experimental plasma systems used for studying the conditions for a controlled thermonuclear fusion.
Methods for investigating plasma, i.e. for measuring plasma parameters;
Systems and methods for generating local plasma to be used in industrial applications, e.g. plasma torches for cutting, welding, spraying or incinerating;
Systems and methods for generating and/or accelerating neutral particle beams, i.e. atomic or molecular beams, neutron beams;
Targets for producing nuclear reactions under irradiation;
Systems and methods for accelerating charged particle beams, i.e electrostatic accelerators, linear accelerators, magnetic induction accelerators, magnetic resonance accelerators.
This place does not cover:
Nuclear fusion reactors | |
Ion beam tubes | |
Gas-filled discharge tubes for surface treatments | |
Mass spectrometers | |
Producing X-rays involving plasma generation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Atomic clocks | |
Obtaining neutrons from radioactive sources | |
Radioactive neutron sources | |
Techniques for handling particles or ionising radiation not otherwise provided for; Irradiation devices; Gamma ray or X-ray microscopes | |
Lasers | |
Magnetohydrodynamic generators | |
Frequency regulation by comparison with a reference frequency determined by energy levels of molecules, atoms, or subatomic particles |
This place covers:
- Methods for investigating plasma, i.e. for measuring plasma parameters;
- Systems and methods for confining a plasma by electric, magnetic or electromagnetic means;
- Systems and methods for heating and sustaining a plasma, in particular for performing nuclear fusion reactions, at laboratory scale;
- Systems and methods for generating plasma for industrial applications.
This place does not cover:
Nuclear fusion reactors | |
Discharge vessels for exposing objects to the discharge |
This place covers:
Methods for measuring different parameters inherently associated with plasma, by using radiation, thermal, electric, magnetic or acoustic means.
This place does not cover:
Investigating by interferrometry | |
Investigating by spectrometry | |
Investigating by using infrared or ultraviolet radiation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating strength properties of solid materials by application of mechanical stress | |
Mass spectrometry |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by particle or neutron radiation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by particle or neutron radiation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by use of microwaves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by use of thermal means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by use of electric or magnetic means | |
Measuring electric or magnetic variables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by use of electric or magnetic means | |
Measuring electric or magnetic variables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating materials by use of ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for confining a plasma; systems and methods for heating and sustaining the confined plasma.
This place does not cover:
Closed discharge vessels for plasma treatment of objects exposed to the discharge |
This place covers:
Laboratory systems in which plasma is confined in closed toroidal or helical loops by externally applied magnetic fields.
Nuclear fusion reactors (operated as prototypes for industrial energy production) based on closed-loop plasma containment systems are classified in G21B.
This place does not cover:
Field Reversed Confinement nuclear reactors | |
Stellarator nuclear reactors | |
Tokamak nuclear reactors |
This place covers:
Laboratory systems in which plasma is generated and confined by application of external magnetic fields and electric fields.
This place does not cover:
Discharge vessels in which objects are exposed to the discharge |
This place covers:
Laboratory systems in which plasma is generated and confined by application of external electromagnetic fields at RF or microwave frequency, often operated in condition of electron-cyclotron resonance or ion-cyclotron resonance.
This place does not cover:
Discharge vessels operated at RF or microwave frequency, in which objects are exposed to the discharge |
This place covers:
Laboratory systems in which the plasma is heated by inducing a current through it. The current is induced by an electromagnetic winding linked with the plasma torus, i.e. the plasma acts as the secondary winding of a transformer.
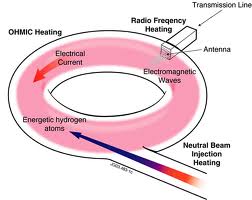
This place does not cover:
Nuclear fusion reactors |
This place covers:
Laboratory systems in which high-energy atoms are injected into the ohmically heated, magnetically confined plasma. The atoms are ionized as they pass through the plasma and are trapped by the magnetic field. The high-energy ions then transfer part of their energy to the plasma particles in repeated collisions, increasing the plasma temperature.

This place does not cover:
Nuclear fusion reactors |
This place covers:
Arrangements for generating plasma to be used in industrial applications, i.e.
- Plasma torches for cutting, welding, surface treatments or spectrometry;
- Plasma systems, other than torches, for treatment of objects or incineration;
- Devices using a plasma discharge for specific applications, e.g. spark gaps, plasma guns;
- Microplasma systems;
- Plasma acceleration systems;
- Power supply systems for the arrangements covered by this group.
Thermonuclear plasma generating and confining systems for use in nuclear fusion reactor plants are dealt with in G21B 1/00. Plasma generating and confining systems for laboratory nuclear fusion studies are dealt with in H05H 1/00 - H05H 1/22. H01J 49/00 covers the particle spectrometer or separator tubes. H05H 1/24 covers the plasma generation and therefore includes the torches used to generate a plasma from a gas. In gas spectrometry, a gas is normally turned into plasma and the electromagnetic emission is analysed. The torches used to turn such gas into plasma are generally classified in the lower subgroup H05H 1/30, because they use an electromagnetic field to activate the plasma gas.
This place does not cover:
Nuclear fusion reactors | |
Gas-filled discharge tubes for surface treatments |
This place covers:
Arrangements for generating plasma using dielectric-barrier discharges, i.e. a dielectric is interposed between the plasma generating electrodes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dielectric-barrier discharges in gas-filled discharge tubes |
This place covers:
Arrangements for generating local plasma by application of pressure waves to a gas or liquid-filled medium, i.e. cavitation, sonoluminescence.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plasma generated by shock-waves |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Cavitation | Collapse of gas bubbles trapped in a liquid medium |
Sonoluminescence | Emission of light by compression and collapse of gas bubbles in a liquid medium |
This place covers:
Plasma torches, whereby a plasma torch is meant as a device for generating a directed flow of plasma, e.g. used for cutting or welding metals, for localized surface treatment of objects or spectroscopic analysis. In particular, this group covers:
- Torches in which plasma is generated by applied electromagnetic fields, e.g. torches for spectrometry;
- Torches in which plasma is generated by establishment of an arc, e.g. non-transferred arc, transferred arc or both.
Systems for metal working which include a plasma generating torch are dealt with in B23K 9/00 and B23K 10/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Generation of plasma by RF or microwaves | |
Metal spraying | |
Metal working with constricted arc | |
Devices external to, and connected to, the plasma generating torch | |
Generation of plasma in a gas-filled tube |
This place covers:
Arrangements within a plasma torch for cooling the components of the torch and evacuating the heat produced during the torch service.
This place covers:
Torches in which plasma is generated by high-frequency electromagnetic fields (e.g. inductive coils enveloping the torch), in particular used for spectroscopic analysis.
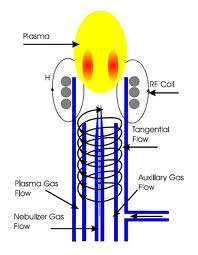
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for arc stabilization by means of externally applied magnetic fields | |
Mass spectrometry |
This place covers:
Torches in which plasma is generated by establishing an arc discharge between two electrodes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Generation of plasma by RF or microwaves | |
Metal spraying | |
Devices external to, and connected to, the plasma generating torch | |
Generation of plasma in a gas-filled tube |
This place covers:
Details related to the electrical and mechanical components of a plasma arc torch.
This place covers:
Arrangements for controlling the discharge generating arc, e.g. shaped nozzles, secondary gas circuits.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements providing protecting fluids coaxial with the plasma jet | |
Arrangements for arc stabilization by means of externally applied magnetic fields |
This place covers:
Arrangements for protecting the plasma jet exiting from the torch, e.g. from mixing with and/or cooling by the surrounding atmosphere.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for controlling the plasma jet |
This place covers:
Circuits arrangements for supplying electric power to the torch, and arrangements for supplying gases to the torch.
The arc welding or cutting systems, in which a plasma arc torch is inserted, are dealt with in B23K 10/00 and B23K 9/00.
This place covers:
Arrangements for controlling the discharge generating arc with magnetic means.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for controlling the discharge generating arc with mechanical means | |
Circuits for magnetic control of the arc in arc welding systems |
This place covers:
Torches provided with arrangements for introducing materials into the plasma, e.g. precursors for material treatment, either within the torch or at the torch plasma jet exit.
This place does not cover:
Electrostatic spraying apparatuses | |
Devices for supplying a welding powder |
This place covers:
- Plasma systems, other than torches, for treatment of objects, wherein plasma is generated by applied electromagnetic fields, e.g. microwaves, radiofrequency;
- Microplasma systems.
Discharge tubes or vessels for plasma treatment of objects under controlled pressure are dealt with in H01J 37/32.
This place does not cover:
Plasma torches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dielectric barrier discharge devices | |
Plasma devices using an arc | |
Discharge tubes with provision for introducing objects or material to be exposed to the discharge |
This place covers:
Plasma systems, other than torches, for treatment of object surfaces, wherein plasma is generated by a corona discharge (i.e. the discharge occurs when the strength of the electric field around the electrode is high enough to form a conductive region, but not high enough to cause electrical breakdown or arcing to the object).
This place does not cover:
Dielectric barrier discharge devices |
This place covers:
Plasma systems, other than torches, for treatment of objects, wherein plasma is generated by establishment of an arc, e.g. incinerators.
This place does not cover:
Plasma torches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Systems with plasma generated by EM fields |
This place covers:
Systems using local plasma generation for specific applications.
This place does not cover:
Plasma torches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Spark gaps in general |
This place covers:
System and methods for accelerating ions and/or electrons out of a plasma.
This place does not cover:
Ion thrusters | |
Ion sources for ion beam tubes | |
Electron sources for spectroscopy | |
Ion sources for spectroscopy |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for generating atomic beams, molecular beams and neutron beams, as well as systems and methods for generating electromagnetic radiation.
This place does not cover:
X-ray or gamma detectors | |
Neutron detectors | |
Manipulation of neutral molecules by optical means | |
Charge exchange devices | |
Irradiation devices |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for generating a beam of molecular or atomic particles, e.g. by irradiation of a target or by neutralization of charged particles.
This place does not cover:
Neutron generation | |
Molecular beams for analysing or investigating materials | |
Optical traps | |
Atomic clocks | |
Charge exchange devices | |
Polarising devices | |
Cathodic sputtering | |
Beam masers |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for accelerating electrically neutral particules by means of electromagnetic fields (e.g. by exploiting their dipolar electric moment, levitation devices) and for accelerating or cooling atom beams (e.g. atom traps, atom chips).
This place does not cover:
Use of photons for propulsive thrust | |
Manipulation of neutral molecules by optical means | |
Handling charged particles |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for generating neutron beams, e.g. by impacting a target in a sealed envelope, by collision of particle beams, for logging tools, for material detection).
This place does not cover:
Vessels or containers of electric discharge tubes with improved potential distribution over surface of vessel | |
Shields of X-ray tubes associated with vessels or containers |
This place covers:
Electrostatic generators provided with high-voltage cascades, e.g. Greinacher cascade.
This place covers:
Materials and devices used as a target for producing secondary particles upon impact of an impinging beam.
This subclass includes also auxiliary components of the targets, such as windows, radiation protective screens, cooling arrangements.
This place covers:
Polarised targets used in quantum physics (e.g., targets for polarising neutron beams, spin-polarised thermonuclear fuels) and arrangements for their production.
This place does not cover:
Manipulation of particles by means of polarising devices |
This place covers:
Constructive arrangements and components of linear accelerators, magnetic induction accelerators and magnetic resonance accelerators (e.g. magnet systems, power supply systems), their auxiliary systems (e.g. beam injection systems, undulators) and irradiation systems using such accelerators.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "LINAC" and "Linear accelerator"
- "CW" and "Continuous wave"
This place covers:
Systems for delivering the accelerated beam of particles to the target.
This place covers:
Systems for supplying microwave or radio-frequency energy to the different components and auxiliaries of the accelerator, e.g. accelerating cavities, electromagnets, particle sources.
This place covers:
All kind of magnets and superconducting magnets used in particle accelerators, e.g. for beam bunching (undulators, wigglers), focusing, bending or deflecting.
This place does not cover:
Free-electron lasers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnets in general |
This place covers:
Arrangements for storing and accelerating plural particle beams at the same time (e.g. for beam collision purposes) and for beam merging (e.g. funneling).
This place does not cover:
Beam collisioners for nuclear fusion |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for forming and injecting particle beams into an accelerator by mechanical, electrostatic or magnetic means (e.g. ion and electron sources, pre-accelerators).
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
ECR | Electron Cyclotron Resonance |
PIG | Cathodic source of light ions |
EBIS | Electron-Beam Ion Source |
CSD | Charge State Distribution |
This place covers:
Arrangements for extracting the charged particles from the accelerators, e.g. septa, stripping foils.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for modifying the trajectory of the extracted beam (gantries) |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for varying the energy of the extracted beam, by electromagnetic or mechanical means or by emittance variation (e.g. RF cavities, stripping foils, stochastic cooling).
This place covers:
The vacuum chambers, cavities and resonators used in a charged particle accelerator and their auxiliary systems (e.g. vacuum pumps, cryostats).
This place does not cover:
Accelerating tubes for direct-voltage accelerators |
This place does not cover:
Travelling-wave tubes |
This place covers:
Specific components and systems of linear accelerators (e.g. drift tubes, arrangements for coupling cavities, arrangements for coupling power to cavities) and of the accelerators covered by H05H 15/00.
This place does not cover:
Details of the accelerators covered by H05H 9/00 - H05H 13/10 | |
Other details |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
RF supplying systems |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for accelerating electron beams by means of an electromagnetic wave (microwave) travelling in a tube serving as waveguide.
This place does not cover:
Travelling-wave tubes |
This place covers:
Linear accelerators wherein electric fields are set up as standing waves within a resonant cavity, with drift tubes suspended along the central axis.
Linear accelerators for hadron particles, e.g. protons, neutrons and ions.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
HADRON | composite particle subject to strong interaction |
LINAC | Linear Accelerator |
This place covers:
Linear accelerators with drift tubes suspended along the central axis.
This place covers:
Linear accelerators combining the features of H05H 9/042 - H05H 9/045.
This place covers:
Linear accelerators for lepton particles, e.g. electrons.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
LEPTON | Elementary particle not subject to strong interaction |
This place covers:
Betatrons.
This place covers:
Cyclotrons, synchrotrons, synchrocyclotrons, fixed-field alternating-gradient accelerators and microtrons.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Strophotrons, turbine tubes |
This place covers:
Systems and methods for accelerating or decelerating charged particles by means other than linear or magnetic resonance accelerators, e.g. laser pulses, resonance converters, magnetic monopole accelerators, dielectric-wall accelerators, inductive amplification of particle energy.