CPC Definition - Subclass H02J
This place covers:
- ac and/or dc supplying systems;
- ac and/or dc distribution networks;
- circuit arrangements for battery supplies, including charging or control thereof, or coordinated supply from two or more sources of any kind;
- circuit arrangement providing remote indication and control of a network switch;
- systems for supplying or distributing electric power by electromagnetic waves.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Electrical networks for vessels | |
Electrical networks for aircrafts | |
Ground or aircraft-carrier-deck installations for supplying electrical power to stationary aircraft | |
Power supply circuits for apparatus for measuring X-radiation, gamma radiation, corpuscular radiation or cosmic radiation | |
Electric power supply circuits specially adapted for use in electronic time-pieces with no moving parts | |
For digital computers | |
For discharge tubes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steam turbines | |
Gas turbines | |
Wind power generation | |
Photovoltaic elements | |
Fuel cells | |
Boards, substations or switching arrangements | |
Electric protections | |
Circuits or apparatus for the conversion of electric power, arrangements for control or regulation of such circuits or apparatus | |
Control or regulation of electric motors, electric generators or dynamo-electric converters | |
Solar power generation | |
Control of high-frequency power | |
Additional use of power line or power network for transmission of information |
Claimed devices, systems, and methods always have to be classified. If there is additional information disclosed, then indexing codes for the additional information must be allocated.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Wireless energy transfer | non-conductive energy transfer, even if conductors can be used for implementing the separated sending and receiving units |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle | |
Electric circuits specially adapted for vehicles | |
Power supplies for memories | |
Power supply, e.g. DC power supply, for computers | |
Fuel cells | |
Power supplies for dc lamps |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Arrangements for reducing harmonics or ripples in converters |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements, systems and methods for the parallel connection of DC sources. Parallel operation must be interpreted as the operational characteristics allowing that the parallel-connected sources supply the load, for instance, how to share the load among the different sources, or how to sequentially switch different power sources on.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Parallel operation of dc sources involving batteries |
This place covers:
Parallel operation of DC sources, where the sources are switched mode power supplies (SMPS), i.e. power electronic converters with a DC output.
This place does not cover:
Parallel operation of dc sources using diodes blocking reverse current flow | |
Parallel operation of dc generators with converters, e.g. with mercury-arc rectifier |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Conversion of dc power input into dc power output without intermediate conversion into ac by static converters using semiconductor devices as final control devices for a single load | |
Single converters with a plurality of output stages connected in parallel |
This place does not cover:
Parallel operation of dc generators with converters, e.g. with mercury-arc rectifier |
This place covers:
Balancing the load in a DC distribution network, either by avoiding overloading one section of the network, or by load shedding
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Balancing the load in a network by batteries |
This place covers:
- Arrangements for selectively connecting the load to one among a plurality of power lines or power sources
- Arrangements for reducing harmonics or ripples
- Arrangements using a single network for simultaneous distribution of power at different frequencies; using a single network for simultaneous distribution of ac power and of dc power
- Arrangements for connecting networks of the same frequency but supplied from different sources
- Constant-current supply systems
- Arrangements for adjusting, eliminating, or compensating reactive power in networks
- Arrangements for preventing or reducing oscillations of power in networks
- Arrangements for eliminating or reducing asymmetry in polyphase networks
- Arrangements for balancing of the load in a network by storage of energy
- Arrangements for transfer of electric power between networks of substantially different frequency
- Arrangements for transfer of electric power between ac networks via a high-tension dc link
- Arrangements for parallely feeding a single network by two or more generators, converters or transformers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wind turbines | |
Computer systems for trading | |
Systems, methods for trading (electricity/gas/water) | |
Details of switches for load protection | |
Photovoltaic panel | |
Mechanical details of connectors | |
Electromechanical details | |
Load protection by tripping of the load for ac systems | |
Harmonic reduction application for converters | |
Details of converters for reactive power compensation and ac power generation from dc sources | |
Details of converters for HVDC | |
Preventing/reducing oscillation with a single generator |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for feeding a single network by two or more generators, converters or transformers in parallel |
In group H02H 9/08, the coil is not used for any reactive power compensation, but for limiting earth fault currents.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for adjusting voltage in ac networks by changing a characteristic of the network load by adjustment of reactive power |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Use of Petersen coils |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
if the bridge combines both series and shunt compensators |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements, devices and methods for preventing, avoiding or correcting oscillations of voltage, current or power in an AC power network
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for preventing or reducing oscillations of power in networks by control effected upon a single generator |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vehicle-to-grid [V2G] arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Vehicle-to-grid [V2G] arrangements | |
Parallel connections of DC/AC converters not for feeding a network, but a local load |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for mains of distribution networks containing both ac and dc (for instance, for planes) or for (rarely) networks whose nature (AC or DC) is not specified
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements, systems and methods for supplying a DC load from an AC power source. Only general purpose circuits (not application-oriented/driven) are classified here.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for transfer of electric power between ac networks via a high-tension dc link |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements for charging batteries. Rarely, general-purpose discharging, battery management, e.g. sequentially discharging batteries, or load-supplying, e.g. when they are not too concerned by the characteristics of the load.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Charging stations or on-board charging equipment for electrically-propelled vehicles | |
Details of telephone stands |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical circuits for vehicles | |
Vehicle starting circuits | |
Methods for charging or discharging secondary cells | |
Mechanical details of battery charger alternators | |
DC/DC power converters | |
AC/DC or DC/AC power converters | |
Perpetuum mobile | |
Control of alternators |
If the document deals with the controlled charging of a capacitor, e.g. a supercapacitor, it is mandatory to assign a combination of the symbol H02J 7/345 and CPC symbols, which would apply, if the capacitor was replaced with a battery.
This place covers:
Battery charging where power comes from one or more different DC power sources, e.g. charging from solar arrays. It may further involve the supply of a load and the resulting modes of operation (battery charging, battery supplying the load).
This place does not cover:
Arrangements for charging batteries from dynamo-electric generators driven at varying speed, e.g. on vehicle |
This place covers:
Power sources acting when the main source fails, i.e. uninterruptible (on-line and off-line) power supplies [UPS] and back-up power supplies
Power supplies able to operate in a "standby" mode (low power or sleep modes).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
With provision for charging standby battery | |
UPS for computers | |
UPS for communication stations | |
Details of lamp |
The following Indexing Codes are to be used for classifying additional information:
power saving operation when no load is present | |
common neutral | |
using a single transformer with multiple primaries (one for each ac energy source) and a secondary for the loads | |
electronic means for switching from one power supply to another, avoiding parallel connection |
This place covers:
Emergency light systems integrated typically by a back-up power source, a set of lamps and a dedicated auxiliary distribution system powering the lamps from the back-up power source
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
A lamp not being an emergency lamp, but a lamp which is normally fed by the mains and during contingency by a battery, even if no dc/ac converters are not involved |
This place covers:
Emergency, back-up or standby power supplies integrating power electronic converters for the different power conversions within the units: e.g. rectifiers, battery chargers, voltage regulators.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Emergency or standby power supply arrangements |
This place covers:
H02J 13/00 covers operation-related documents, i.e. there must be at least switching on/off or generator or load (or information of such an event) or any other similar action (i.e. sending settings of an inverter connecting a photovoltaic array to the power network.
It also covers specific monitoring of power networks (tailored to such application).
Concerning smart grids, documents where the relevant features concern electrical engineering and not ICT technologies, are classified here.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electricity meters involved (in particular smart meters) | |
Measuring of electric variables | |
Power strips with locally controlled on/off capability for computers | |
Data processing systems or methods adapted for electricity supply | |
Transmission systems for measured values or control signals | |
Details of switches | |
Circuits for indication of single switches | |
Power strips with locally controlled on/off capability | |
Power line carrier | |
Transmission of digital information | |
Telecontrol or telemetry systems | |
Wireless communication |
This place covers:
Energy storage systems having either relevant power management issues, or having (or be ready/able for) an interaction with the (AC or DC) power network (but with focus on the storage system). The subject-matter stays normally at system level (there are other CPC technical fields dealing with the specific storage technologies). Under this approach, the group has two subdivisions according to two different technologies:
- Systems for storing electric energy in the form of hydraulic energy
- Systems for storing electric energy in the form of pneumatic energy
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
This place covers:
Functional and operational aspects of systems for the wireless supply or distribution of electric power, regardless of the type of wireless power transmission used.
Circuit arrangements for the wireless supply or distribution of electric power.
In this main group, wireless supply or distribution of electric power involves both of the following steps:
- (1) conversion of electrical energy from a power source for transfer by wireless transmission;
- (2) reception of the wirelessly transmitted energy and re-conversion into electrical energy for distribution or delivery to an electrical load.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Inductive energy transfer between a charging station and an electric vehicle |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
WPT | Wireless Power Transfer |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "cordless power transfer" or "wireless power transmission" or "wireless energy transmission" or "wireless power transfer" or "contactless power transfer"
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using capacitive coupling between the plates of at least two capacitive elements, the plates being located in separate units involved in contactless power transmission.
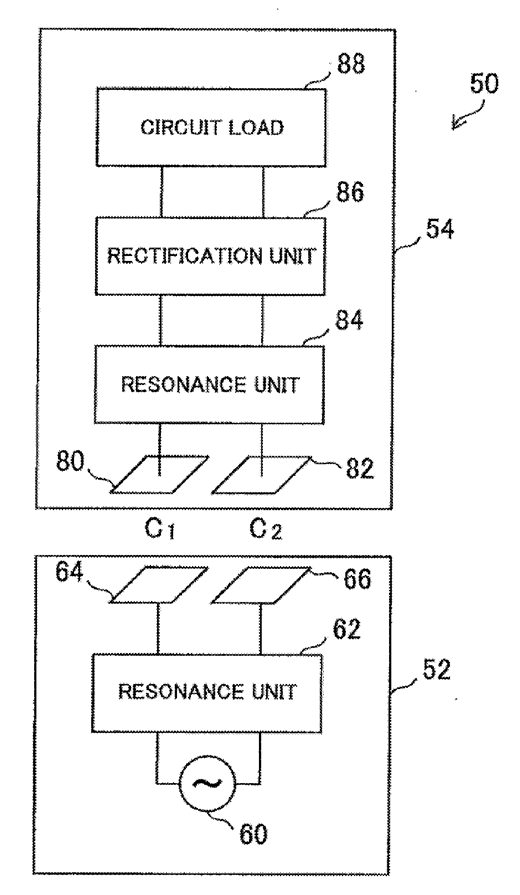
The figure below is an illustrative example which falls within the scope of this subgroup. In the figure, the pairs of plates 64 and 80, and 66 and 82 create two capacitive elements C1 and C2 through which power is transferred from a power transmitter 52 to a power receiver 54.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capacitors; Capacitors, rectifiers, detectors, switching devices, light-sensitive or temperature-sensitive devices of the electrolytic type |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using inductive coupling, i.e. electromagnetic interaction between two or more inductive coils, at least one coil being located in a unit separate from the others, the units being involved in contactless power transmission.
The figure below is an illustrative example which falls within the scope of this subgroup.
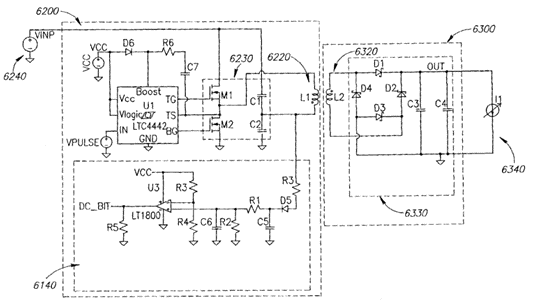
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnets; inductances; transformers | |
Adaptations of transformers or inductances for inductive coupling | |
Conversion of dc power input into dc power output | |
Conversion of ac power input into ac power output | |
Conversion of ac power input into dc power output; conversion of dc power input into ac power output | |
Induction heating |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using inductive coupling of the resonant type, i.e. in which at least one coil forms part of a resonant circuit.
In the illustrative example, resonant circuits Cr-Cp-Lp and Crs-Cs-Ls constitute a resonant circuit 40 which has a specific resonant frequency fr at which the total impedance of the resonant circuit 40 is minimized so that transmission efficiency of electric power between the power emitter circuit in PSU and power receiver circuit in PRU is increased.
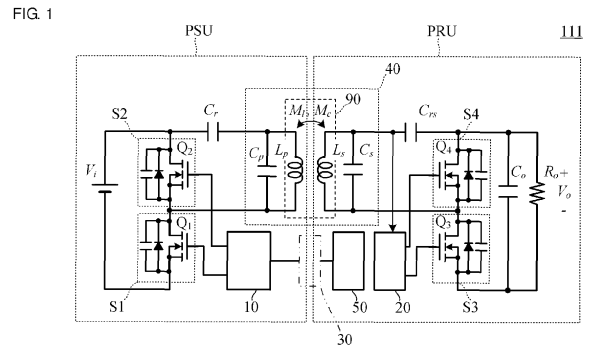
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-electric signal transmission systems using acoustic waves | |
Transmission systems employing ultrasonic waves |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using microwaves or radio frequency waves.
The figure below exemplifies the subject-matter to be classified in this subgroup. Power generated in power source 108 is converted into radiofrequency and transmitted by antenna 112 in transmitter 104 to antenna 124 in receiver 120, and used to power load 136.
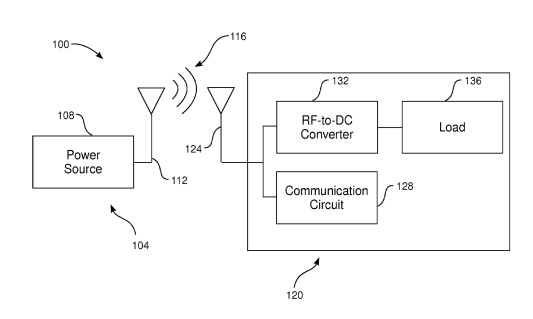
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using microwaves or radio frequency waves, characterised by the type of transmitting antennas, e.g. directional array antennas or Yagi antennas
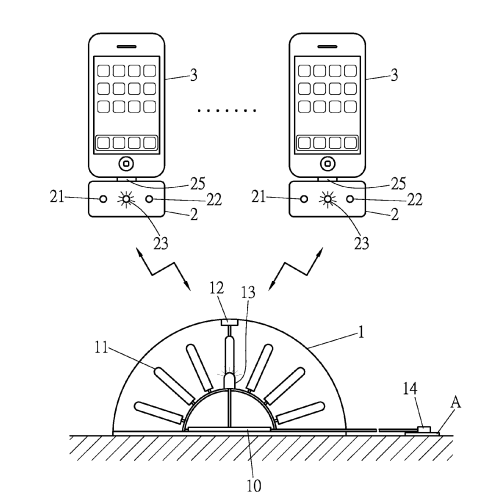
The figure below is an illustrative example relevant for this subgroup. The directional antenna 11 of the transmitting station 1 sends power to the receiver 21 of the charging device 2.
This place covers:
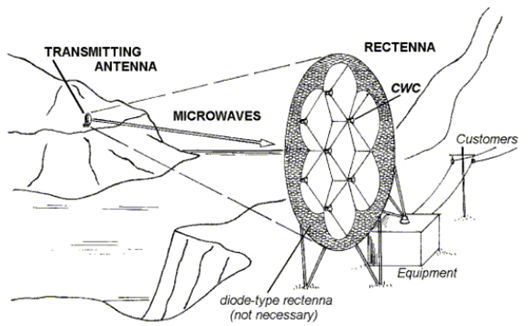
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using microwaves or radio frequency waves characterised by the type of receiving antennas, e.g. rectennas.
The figure below is an illustrative example relevant for this subgroup.
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using light, e.g. lasers
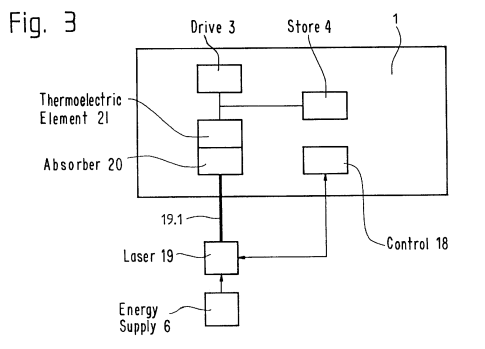
The figure below is an illustrative example for this subgroup. A laser 19.1 emitted by laser unit 19 heats absorber 20 and heat is converted into electrical energy by thermoelectric element 21.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-electric transmission systems using light waves | |
Lasers | |
Transmission systems employing infrared, visible or ultraviolet light |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power involving two or more transmitting or receiving devices.
The figure below is also an illustrative example for this subgroup. In the figure, the several transmitting devices transmit electric power to several receiving devices simultaneously.
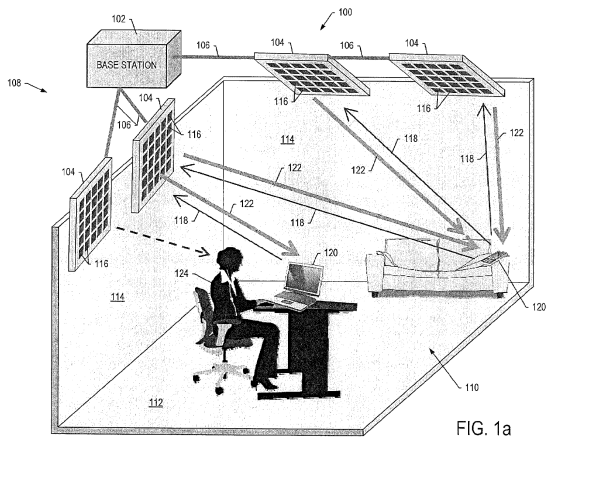
The figure below is also an illustrative example of this subgroup with two or more receiving devices involved. In the figure, the transmitting device transmits electric power to several receiving devices 1 simultaneously
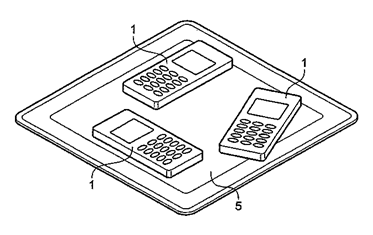
This place does not cover:
using additional energy repeaters between transmitting devices and receiving devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radio transmission diversity systems using a plurality of spaced independent aerials |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power using additional energy repeaters between transmitting devices and receiving devices. The repeater(s) must be physically located between the transmitting devices the receiving devices, and must be separate from them.
The figure below is an example falling within the scope of this subgroup. In the figure, the repeater C2 repeats electric power transmission between the transmitting device C1 and the receiving device C3.
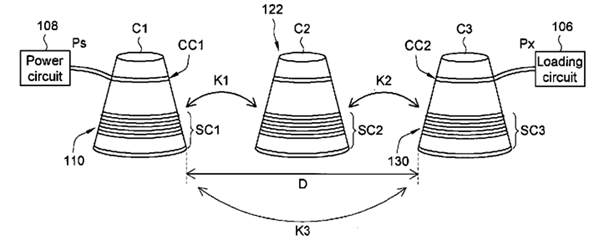
This place covers:
The figure below is an illustrative example for this subgroup. In the figure, the transmitting device 10 detects the presence of the foreign object 30.
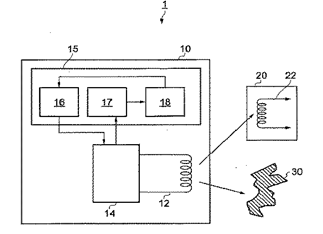
Mechanical aspects related to mechanical removing of foreign object are classified in the relevant field of technology.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detection of object presence using reflection of radio waves | |
Detection of object presence using reflection of acoustic waves | |
Electric or magnetic detection of objects | |
Optical detection of objects |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of transformers or inductances - special means for preventing or reducing unwanted electric or magnetic effects, e.g. leakage fields | |
Devices for absorbing waves radiated from an aerial | |
Suppression or limitation of noise or interference | |
Screening of apparatus or components against electric or magnetic fields |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
IC cards | |
Transmitting signals characterised by the use of a wireless electrical link | |
Non-electric signal transmission systems | |
Responders; (passive) Transponders | |
Near-field transmission systems, e.g. inductive loop type | |
Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves |
This place covers:
Circuit arrangements or systems for wireless supply or distribution of electric power electrically detecting and/or optimising the relative position between emitters, receivers and repeaters, aiming to increase the efficiency of the wireless power transmission, wherein active parts of these circuit arrangements or systems, e.g. coils or antennas, are involved in the detection and/or optimising of the position.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detection of object position using reflection of radio waves | |
Detection of object position using reflection or reradiation of electromagnetic waves other than radio waves | |
Control of position of vehicles, e.g. automatic pilot | |
Position control |