CPC Definition - Subclass C10J
This place covers:
Processes or apparatus for production of fuel gases by carburetting air or other gases without pyrolysis, including controlling supply of air or liquid, temperature, humidity and other parameters.
Processes or apparatus for production of combustible gases containing carbon monoxide (including producer gas, wood gas, town gas, synthesis gas (syngas), manufactured gas and water gas) from solid carbonaceous materials. This includes fixed-bed gasification of lump fuel, gasification of granular or pulverulent fuels in suspension, gasification using molten salts or metals, carburetting by pyrolysis of carbonaceous material in the fuel bed and carburetting by pyrolysis of carbonaceous material in a carburettor.
Production of synthesis gas from liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons, and the synthesis gas per se, are covered by group C01B 3/00.
Destructive distillation processes, e.g. carbonisation or coking, and excluding gasification processes (see Glossary), are covered by subclass C10B. Combinations of gasification and destructive distillation are covered by group C10J 3/58.
Other gaseous fuels, including natural gas, substitute natural gas or synthetic natural gas (SNG) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), are covered by group C10L 3/00.
Purifying or modifying the chemical composition of combustible gases containing carbon monoxide is covered by subclass C10K.
This place does not cover:
Destructive distillation processes | |
Underground gasification of minerals |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Plants with an integrated combined cycle, having more than one engine delivering power externally to the plant | |
Plant characterised by the engines using gaseous fuel generated in the plant from solid fuel | |
Gas turbine plant with separate fuel gasifiers | |
Carburettors for supplying combustible mixtures to internal combustion engines | |
Incineration of waste with pyrolysis or gasification as pre-treatment | |
Combination of fuel cell with means for gasification of solid fuel |
Examples of places in relation to which this place is residual:
Separation of gases or vapour by diffusion | |
Multi-step process for production of hydrogen or of gaseous mixtures containing a substantial proportion of hydrogen | |
Multi-step process for preparation of ammonia | |
Multi-step process for preparation of hydrocarbons from carbon monoxide with hydrogen | |
Multi-step process for preparation of compounds having hydroxy or O-metal groups bound to a carbon atom not belonging to a six-membered aromatic ring by reduction of oxides of carbon exclusively with hydrogen or hydrogen-containing gases, one step being the formation of initial mixture of carbon oxides and hydrogen for synthesis | |
Preparation of urea | |
Multi-step process for production of liquid hydrocarbon mixtures of undefined composition from oxides of carbon | |
Production of synthetic natural gas | |
Plants with an integrated combined cycle, having more than one engine delivering power externally to the plant | |
Plant characterised by the engines using gaseous fuel generated in the plant from solid fuel | |
Gas turbine plant with separate fuel gasifiers | |
Incineration of waste with pyrolysis or gasification as pre-treatment | |
Combination of fuel cell with means for gasification of solid fuel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for generating gases | |
Apparatus for chemical or physical process conducted in the presence of fluids and solid particles | |
Coupling of an air fractionation unit (ASU) to an oxygen-consuming unit | |
Processes or apparatus for separating of H2/CO mixtures, i.e. synthesis gas, involving the use of liquefaction or solidification |
In the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place ("last place rule").
Multiple classification symbols may be allocated to cover the disclosed subject-matter.
Details of gasification apparatus are mandatory classified with Indexing codes of C10J 2200/00 subgroups.
Details of gasification processes are mandatory classified with Indexing codes of C10J 2300/00 subgroups.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Carburetting | Carburetting air or gas generally comprises passing it in contact with liquid fuel and thereby mixing the air/gas and fuel. This often involves lowering the air pressure e.g. in a venturi. |
Destructive distillation | The process of pyrolysis conducted in a distillation apparatus to allow the volatile products to be collected. An example is tar making from pinewood slices (which are rich in terpenes), which are heated in an airless container causing the material to decompose, leaving charcoal and turpentine as by-products. |
Gasification | Gasification is somewhat similar to pyrolysis and confusion between these terms is common. Gasification is a partial oxidation process that converts materials such as coal, biomass or plastic waste into a gaseous mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen (also known as synthesis gas) by reacting the raw material at high temperatures with controlled amounts of oxygen and/or steam. See also the entry for pyrolysis. |
Producer gas | A gas mixture containing carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen (N2). In the USA, producer gas is a generic term referring to wood gas, town gas, synthesis gas, syngas or raw gas. In the UK, producer gas, also known as suction gas, means a fuel gas made from coke or other carbonaceous material. Air is passed over the red-hot fuel and carbon monoxide is produced in an exothermic reaction which reads 2C + O2 → 2CO. The nitrogen in the air remains unchanged and dilutes the gas, so it has a low calorific value. The gas may be used to power gas turbines which are suited to fuels of low calorific value. |
Pyrolysis | The chemical decomposition of organic materials by heating in the absence of oxygen or any other reagents, except possibly steam. Pyrolysis is somewhat endothermic and the products can be gases, liquids (e.g. light crude oil from depolymerisation of organic waste) and/or solids (e.g. coke and volatiles produced by coking coal). See also the entry for gasification. |
Synthesis gas (syngas) | A gas mixture that contains varying amounts of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) generated by the gasification of a carbon-containing material to a gaseous product with a heating value (but less than half the energy density of natural gas). When used as a fuel, it is produced by gasification of coal or municipal waste by the following reactions: C + O2 → CO2; CO2 + C → 2CO; C + H2O → CO + H2. The name comes from the gas's use as an intermediate in creating synthetic natural gas (SNG) and in producing ammonia or methanol. |
Town gas | Also known as coal gas, and contains hydrogen (H2), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrogen (N2) and volatile hydrocarbons. It is made by blowing air and steam over an incandescent fuel bed, usually of coke or coal. The words "coal gas" could also be used to mean gas made by the destructive distillation of coal. The gas was used inter alia for lighting before the advent of electric lighting, and for heating and cooking before natural gas became widely available. |
Water-gas | A mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) produced by passing steam over red-hot coke using the endothermic reaction C + H2O → CO + H2. This product had a lower calorific value than coal gas so the gas was often passed through a heated retort into which oil was sprayed; the resulting mixed gas was called carburetted water gas. |
Wood gas | The product of thermal gasification of biomass (e.g. coal, wood chips, sawdust, charcoal) in a gasifier or wood gas generator. It is the result of a high temperature reaction (> 700 degrees C) where carbon reacts with steam or a limited amount of air producing carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2) and methane (CH4). It can be filtered, purified or scrubbed and used to power internal combustion engines, gas turbines, Stirling engines or fuel cells. |
In patent documents the following synonyms are often used:
Producer gas | Wood gas, town gas, syngas, synthesis gas, raw gas (in USA) |
Producer gas | Suction gas (in UK) |
Wood gas | Holzgas, air gas, blue gas |
Coal gas | Town gas |
This place covers:
Fuel gases produced by carburetting air or other gases without pyrolysis
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Carburettors for supplying combustible mixtures to internal combustion engines |
This place covers:
Production of combustible gases containing carbon monoxide from solid carbonaceous fuels as well as a slurry of solid carbonaceous, such as a coal water slurry.
This place covers:
All beds undergoing reaction of gasification of solid fuel, e.g. fixed-bed, moving bed gasification, such as a Lurgi gasifier, rotary drum gasification.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Feeding of the particles in the reactor | |
Feeding or discharging devices | |
Feeding or distributing of lump or pulverulent fuel to combustion apparatus | |
Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Feeding or discharging devices | |
Grates; Cleaning or raking grates | |
Removing ash, clinker, or slag from combustion chamber | |
Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge |
This place covers:
Apparatus for fixed bed gasification of lump fuel adapted for use on vehicles, e.g. portable gasification apparatus, gasification occurring on a vehicle burning the produced gas in the engine
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangement concerning gas-producing plants in connection with fuel supply of combustion engines |
This place covers:
Gasification in stationary fluidised bed
This place does not cover:
Gasification in circulating fluidised bed |
This place covers:
Gasification of granular or pulverulent flues in entrained bed, such as GE-Texaco gasifier, E-gas gasifier, Shell gasifier, Prenflo gasifier or TPRI gasifier, such as shown in following figures:
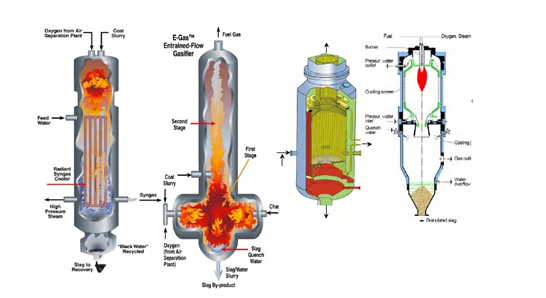
Fluidised bed processes are classified in C10J 3/466
Reactors for fluidised bed processes are classified in C10J 3/485
Fluidized bed processes and reactors by the Winkler technique are classified in C10J 3/54 and C10J 3/56
Dense cloud gasification, e.g. dense fluidized bed, is classified in C10J 3/463
This place covers:
Gasifiers with stationary fluidised bed
This place does not cover:
Gasifiers with circulating fluidised bed |
This place covers:
Gasifiers with nozzles, gasifiers with screw feeders, feed pressurisation using lock hoppers, or preparation, such as milling and drying, of fuel for gasification process
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Feed or outlet devices; Feed or outletcontrolling devices | |
Feeding or discharging devices | |
Fuel feeders specially adapted for fluidised bed combustion apparatus | |
Burners for combustion of pulverulent fuel | |
Preparation of lump or pulverulent fuel in readiness for delivery to combustion apparatus | |
Feeding or distributing of lump or pulverulent fuel to combustion apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Feeding or discharging devices | |
Removing ash, clinker, or slag from combustion chamber |
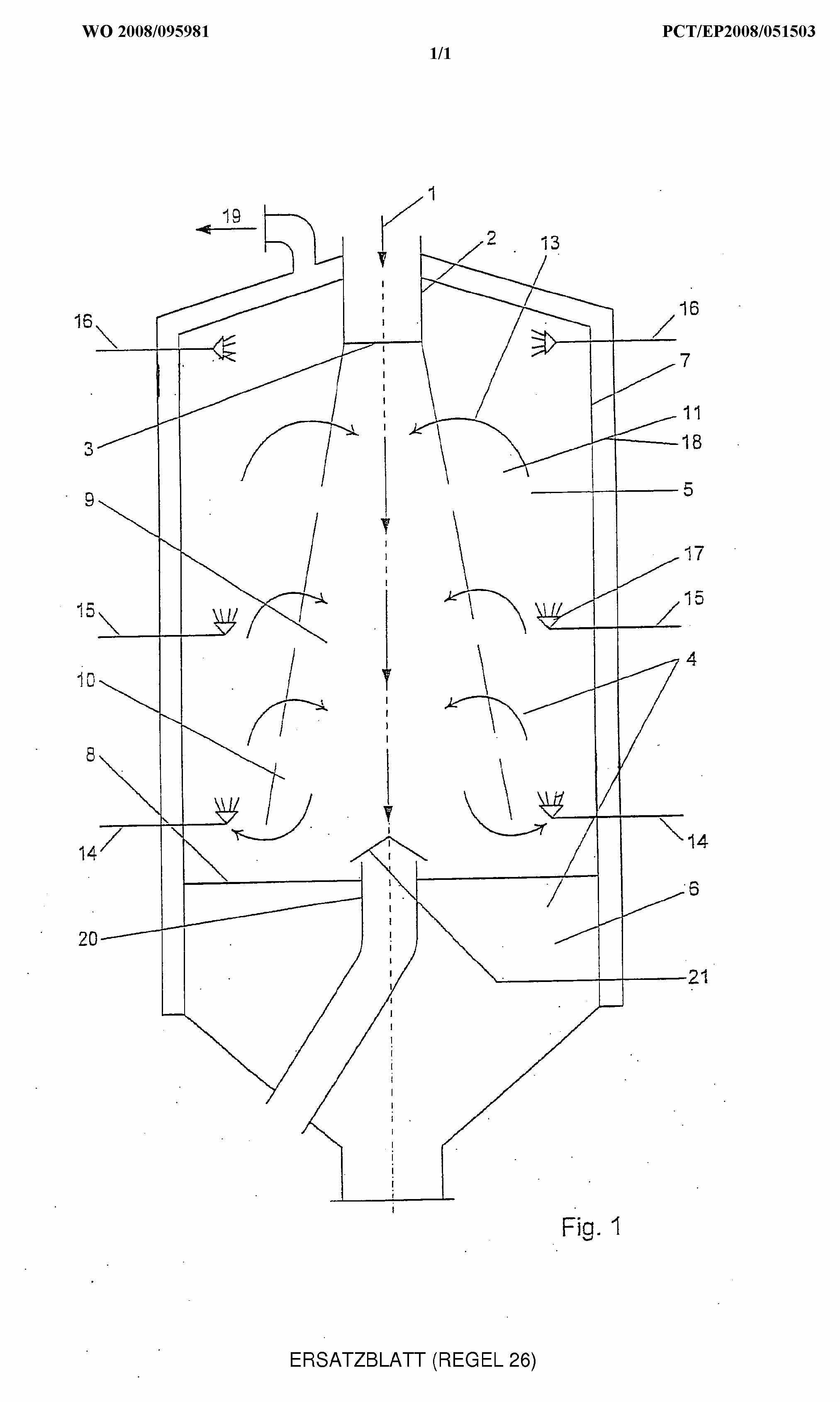
This place covers:
Gasification in a circulating fluidised bed or expanded bed, such as shown in following figure:
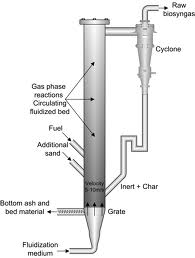
This place covers:
Gasification including a pre-distillation before gasification, such as a pyrolysis step prior to gasification step.
This place covers:
Gasification including a pre-distillation before gasification whereby the distillation products such as pyrolysis gas (pyrogas) are withdrawn separately from the syngas. Examples are shown in the following figures:
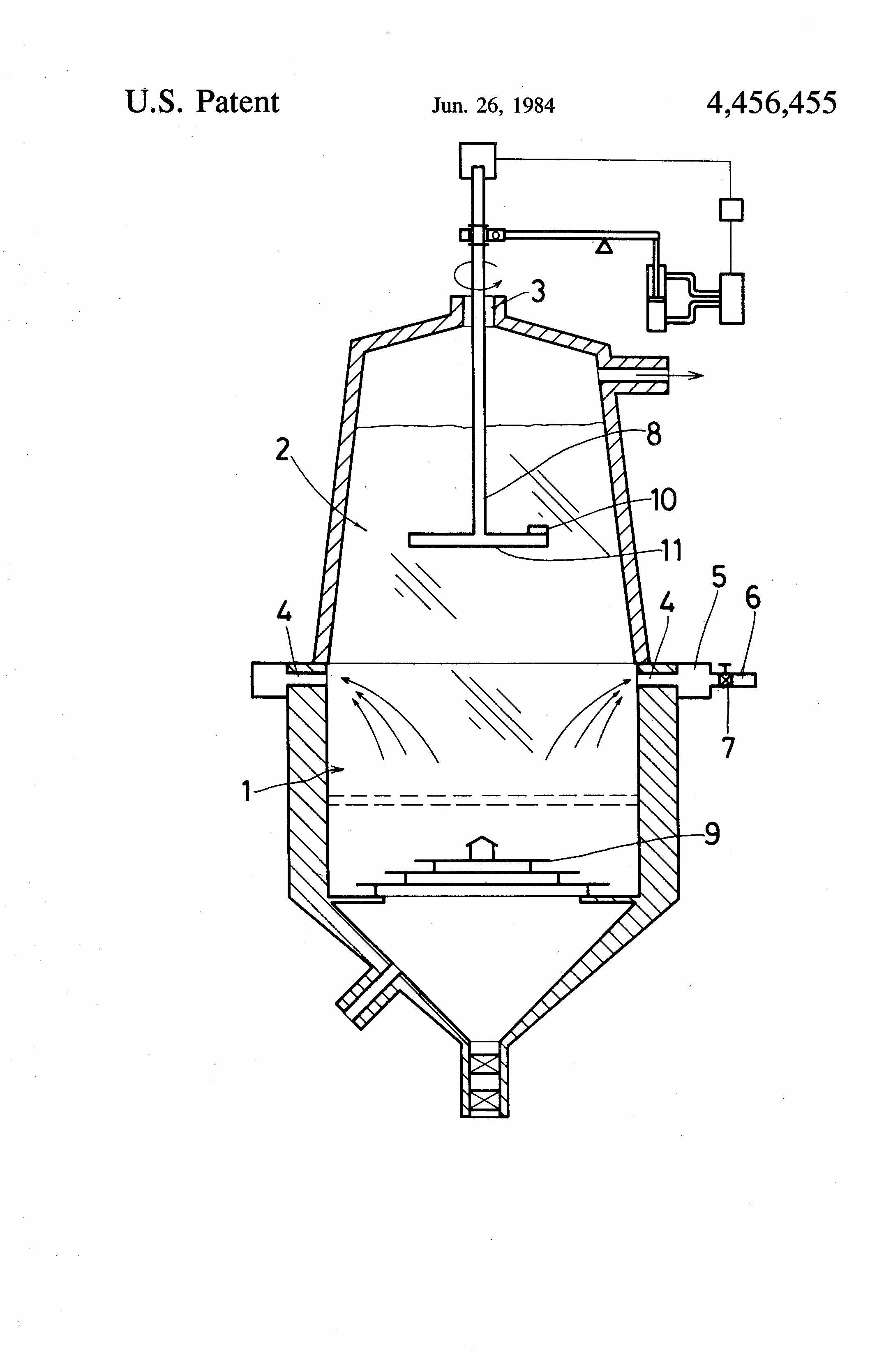
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Distillation products | Volatile products released from solid charge during pre-distillation or pyrolysis pre-step. |
This place covers:
Gasification including the decomposition of the distillation products, such as pyrolysis gas (pyrogas) and/or pyrolysis liquids (pyroliquids). The decomposition may occur in a reforming zone separate from the gasification zone, such as partial combustion of pyrolysis gas or cracking of pyrolysis tar. Examples are shown in the following figures:
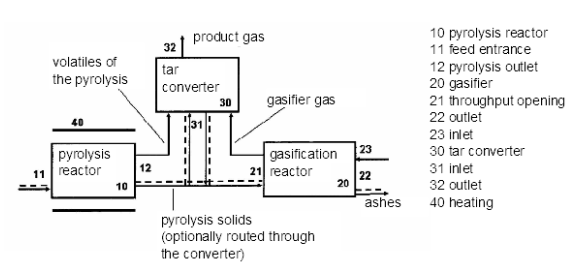
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Distillation products | Volatile products released from solid charge during pre-distillation or pyrolysis pre-step. |
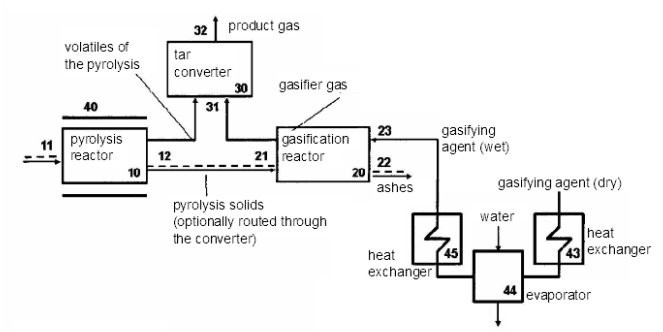
This place covers:
Gasification including the decomposition of the distillation products, such as pyrolysis gas (pyrogas) and/or pyrolysis liquids (pyroliquids).
Examples are shown in the following figures:
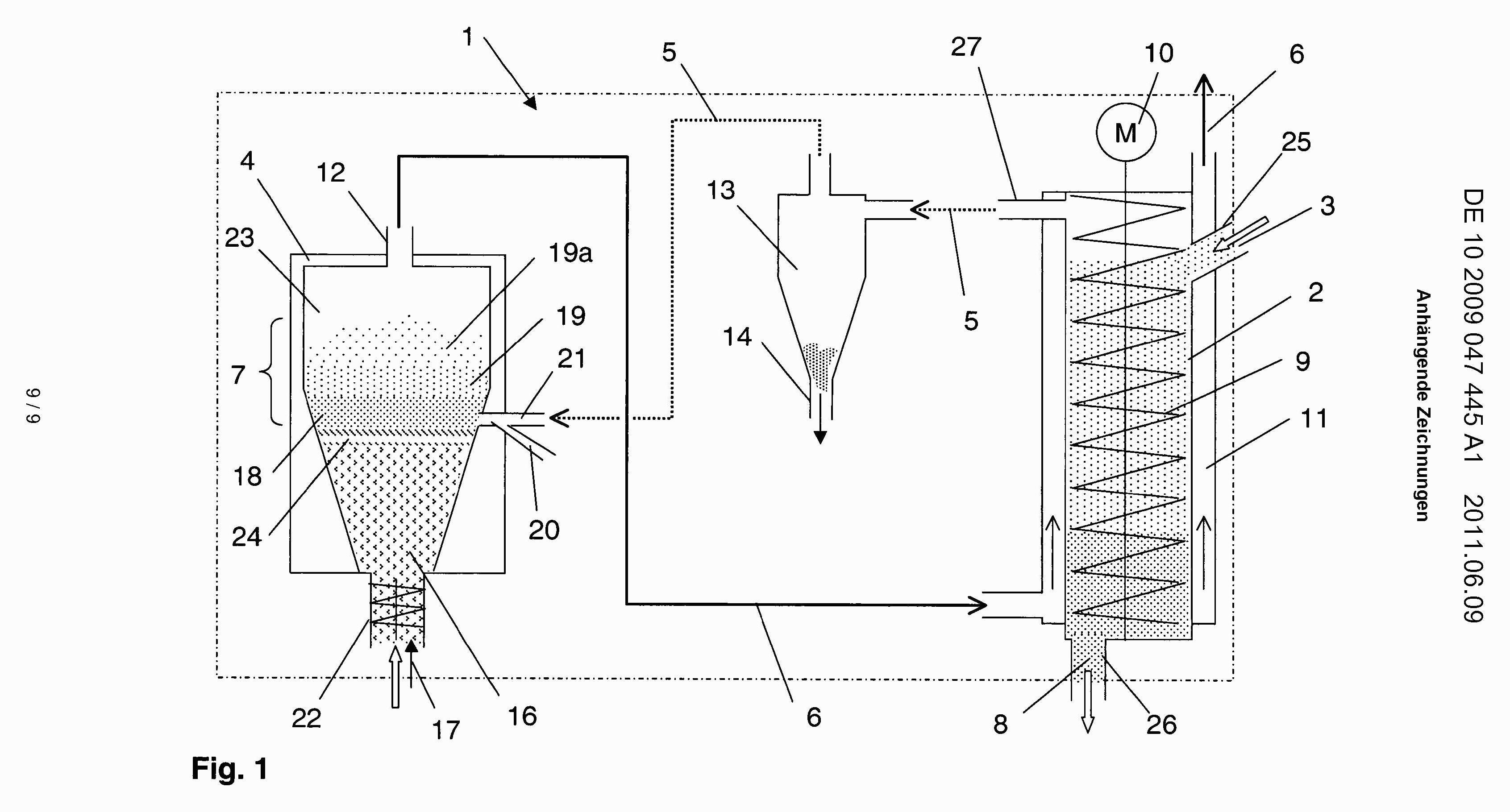
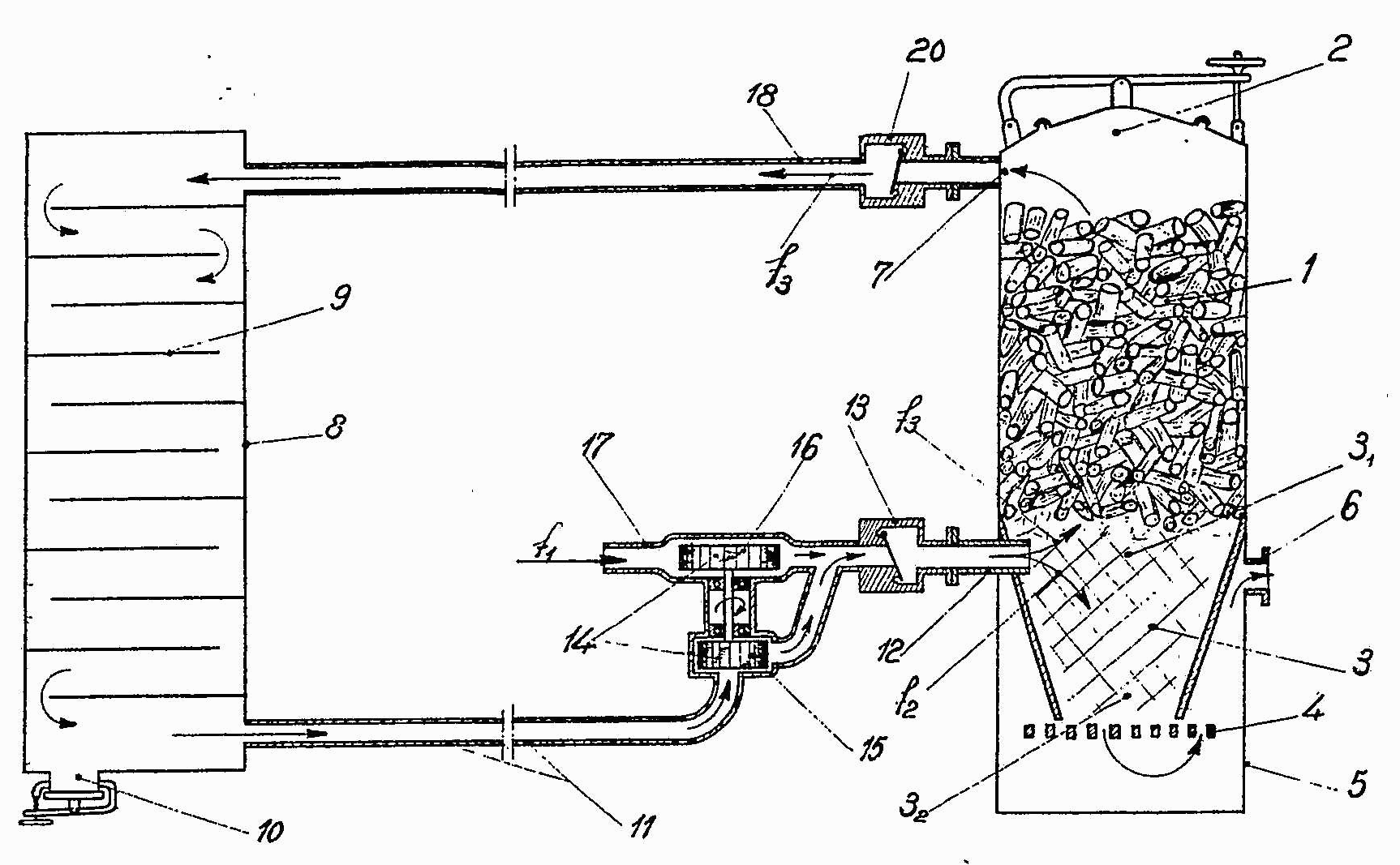
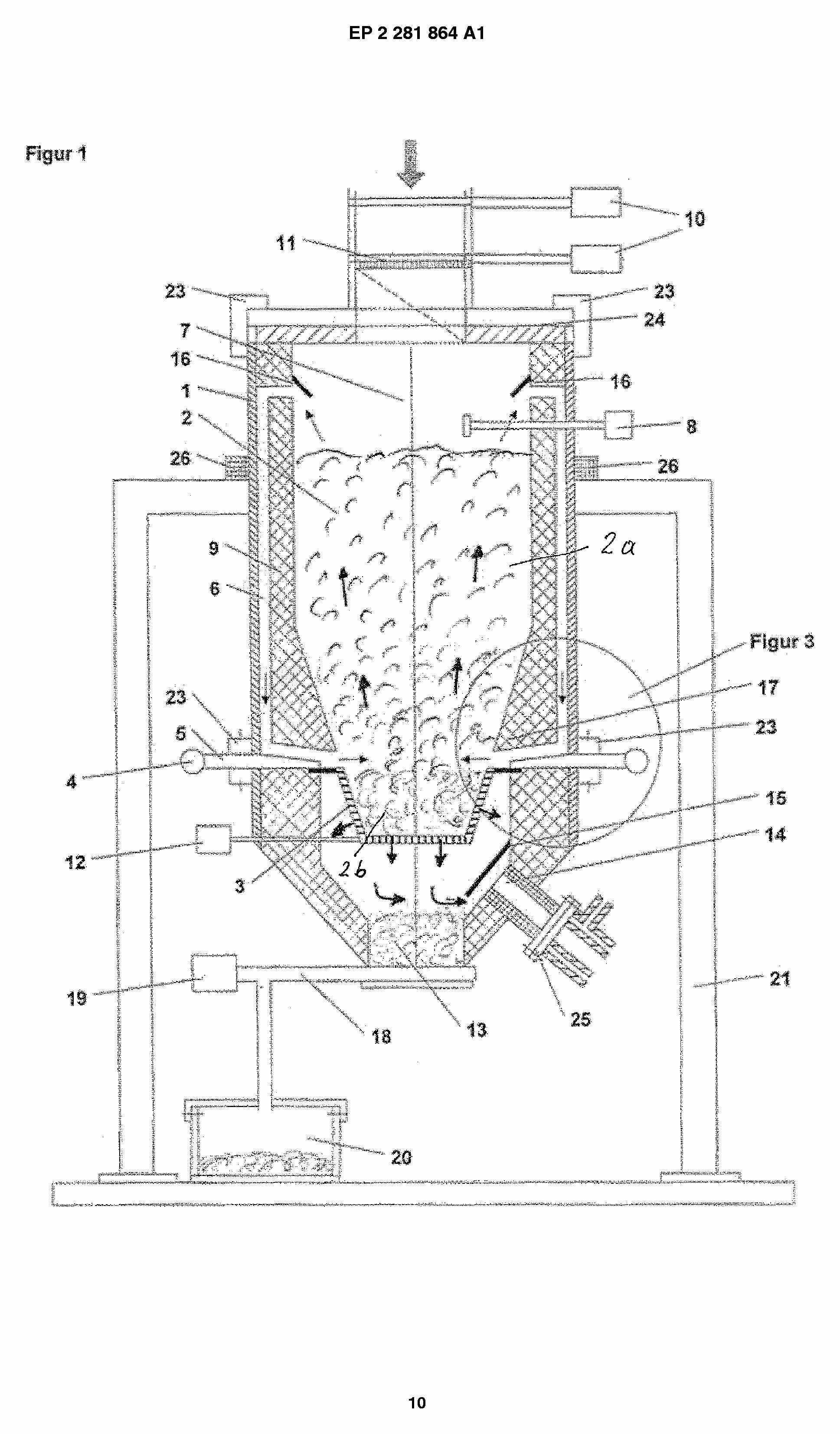
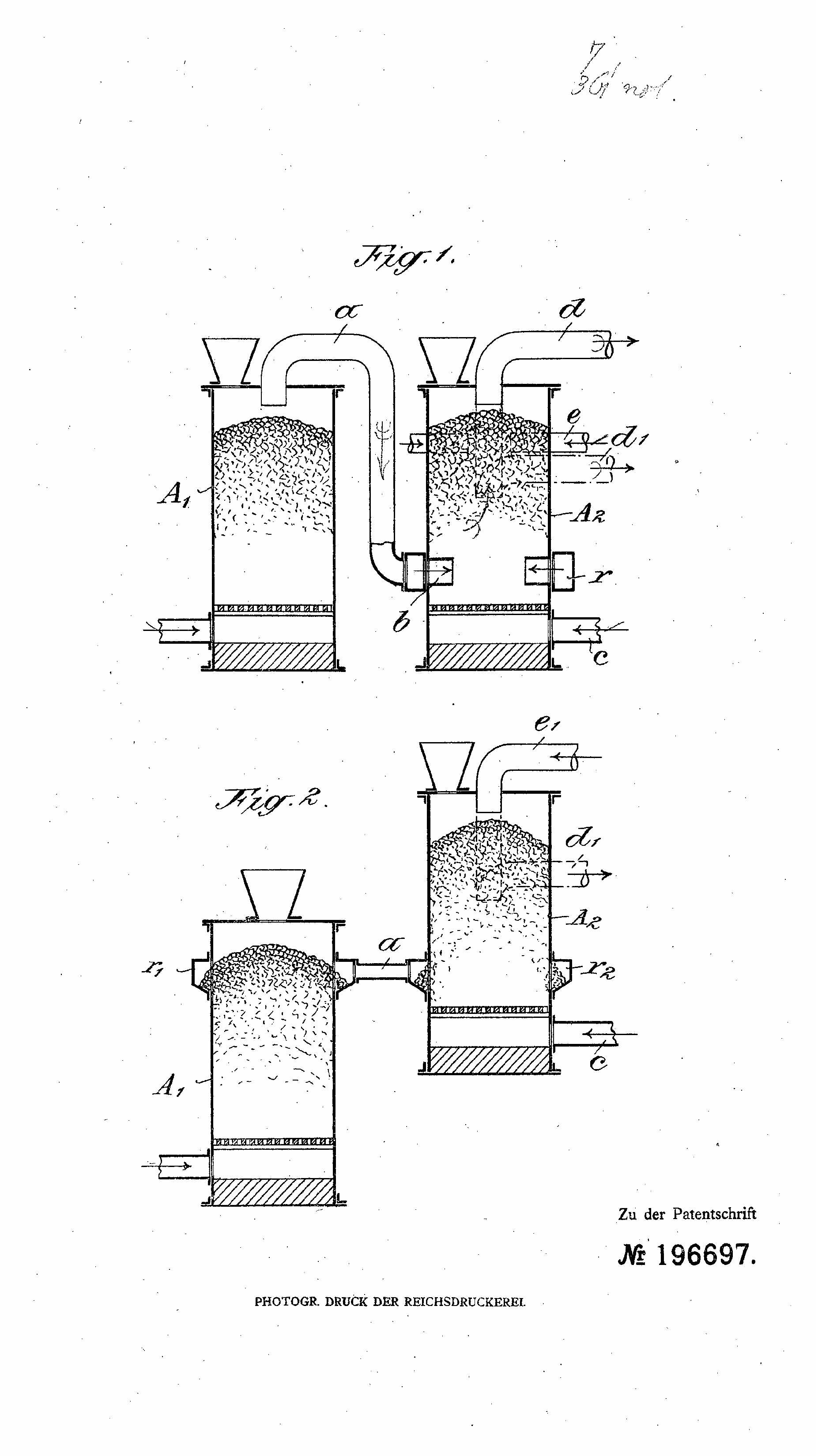
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Gasification zone | Zone where solids are converted by gasification, such as by partial combustion or steam reforming |
This place covers:
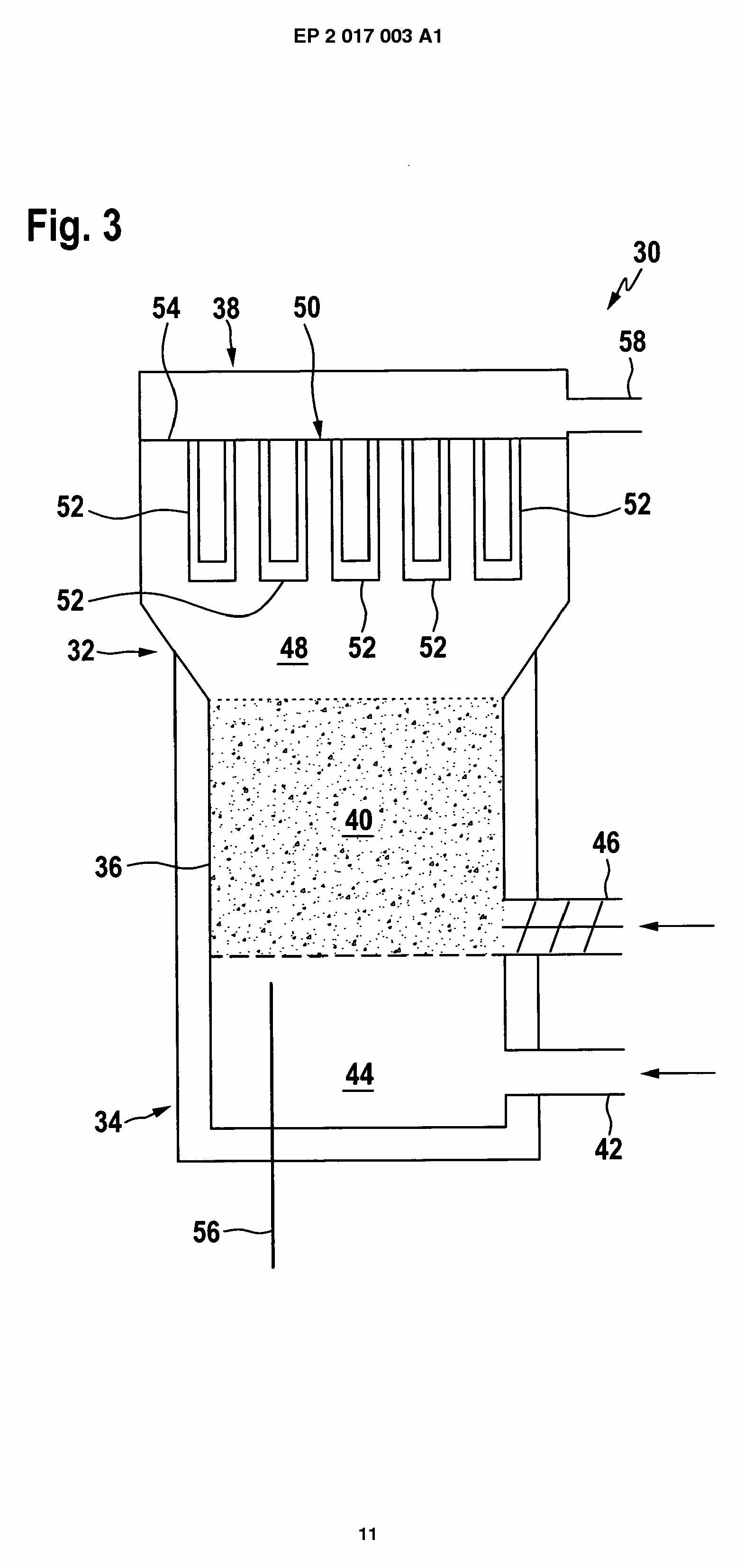
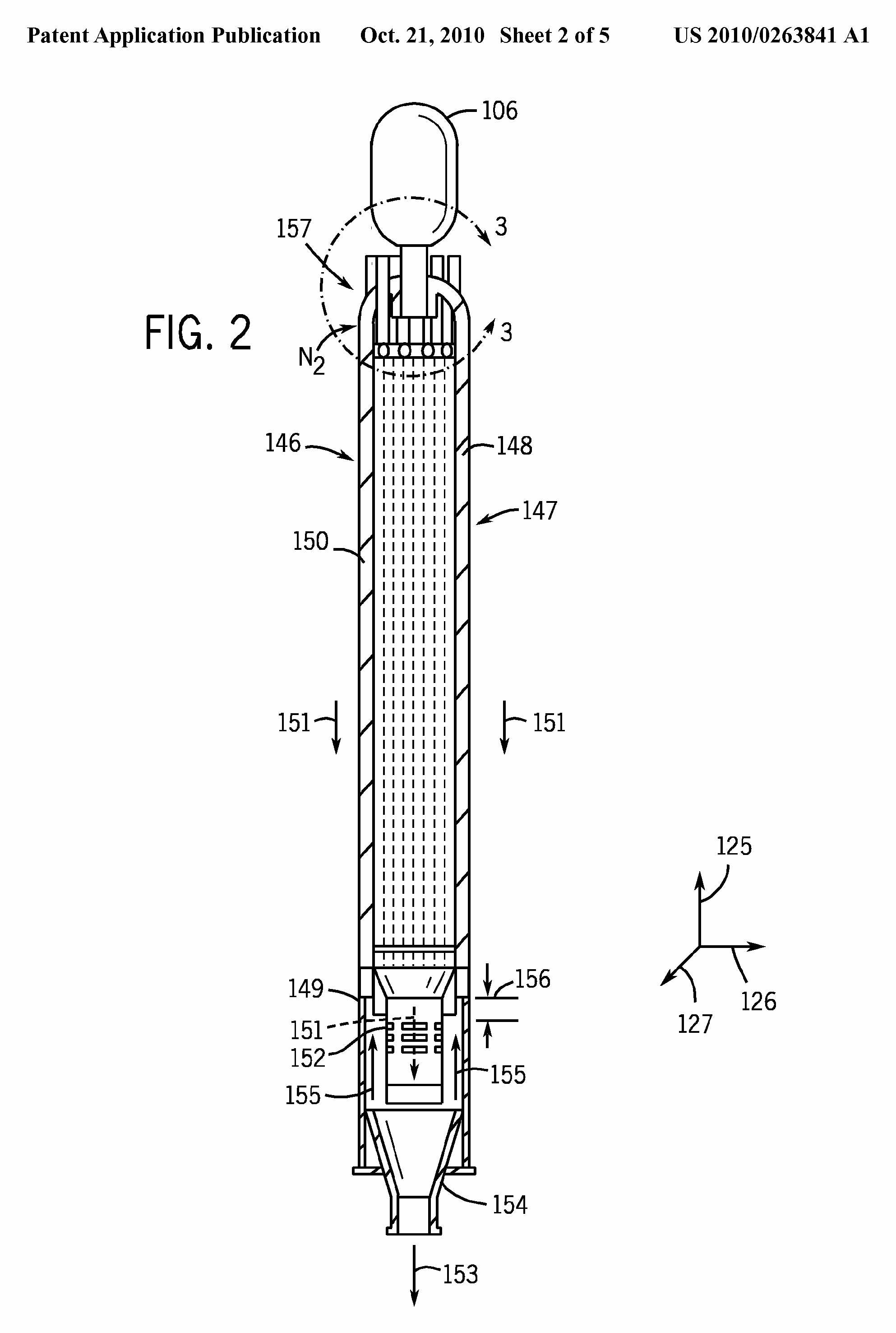
Gasifiers having cooling means inside or on the outside of the gasification chamber itself, i.e. same vessel, such as shown in the following figures:
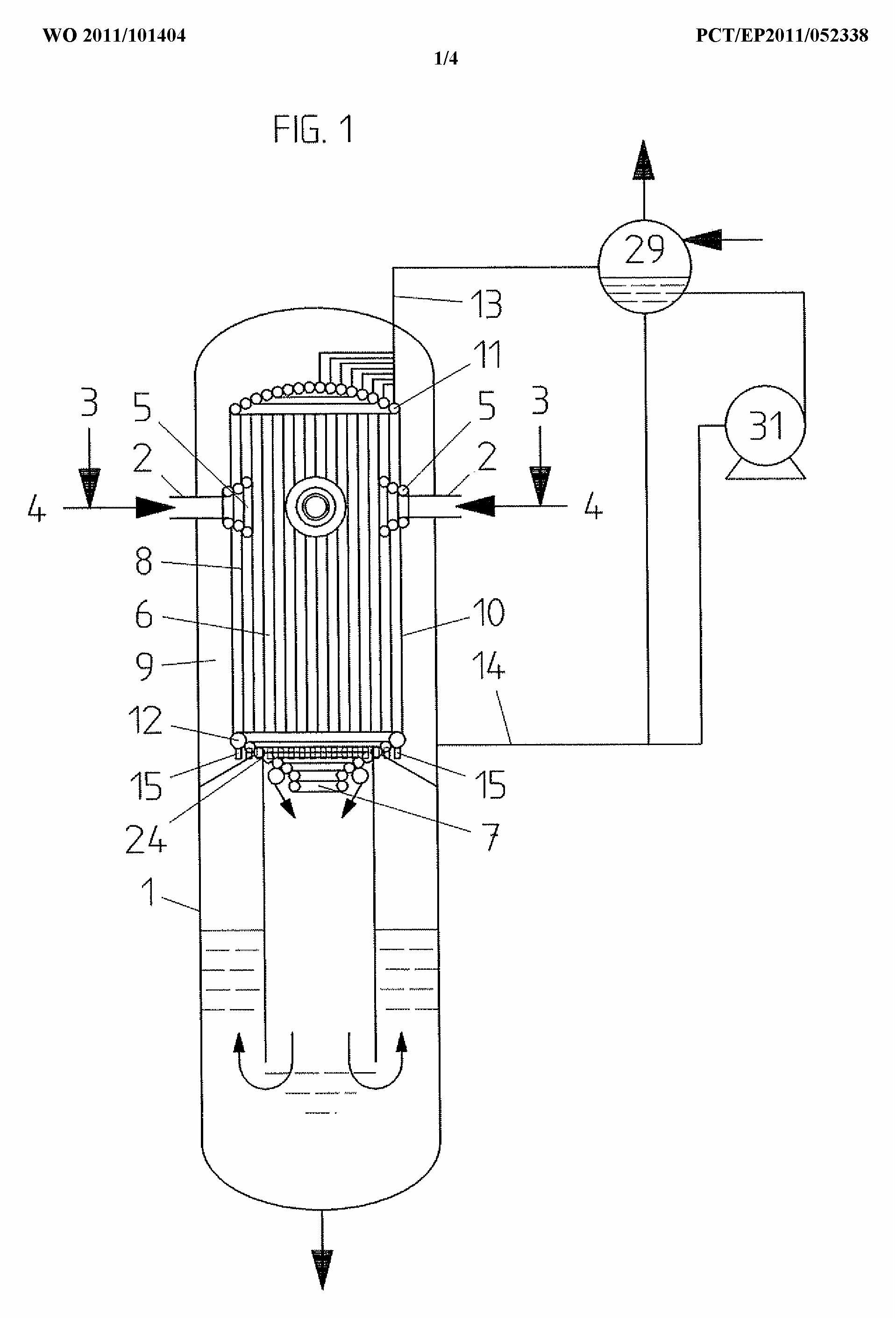
This place does not cover:
Gasification with separate waste heat boilers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heat-exchange apparatus, not provided for in another subclass, in which the heat-exchange media do not come into direct contact |
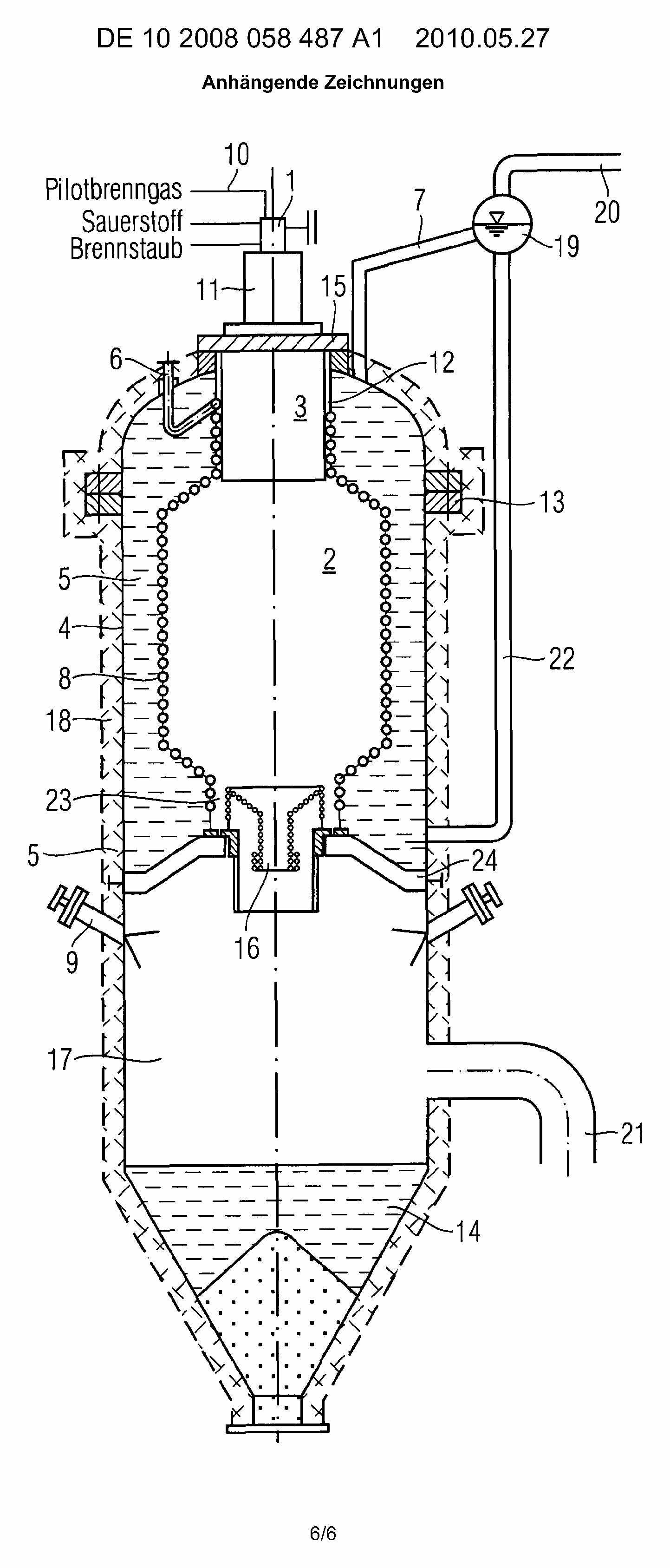
This place covers:
Gasifiers having a gas filter, cyclone, water spray or a quench, e.g. such as shown in the following figures:
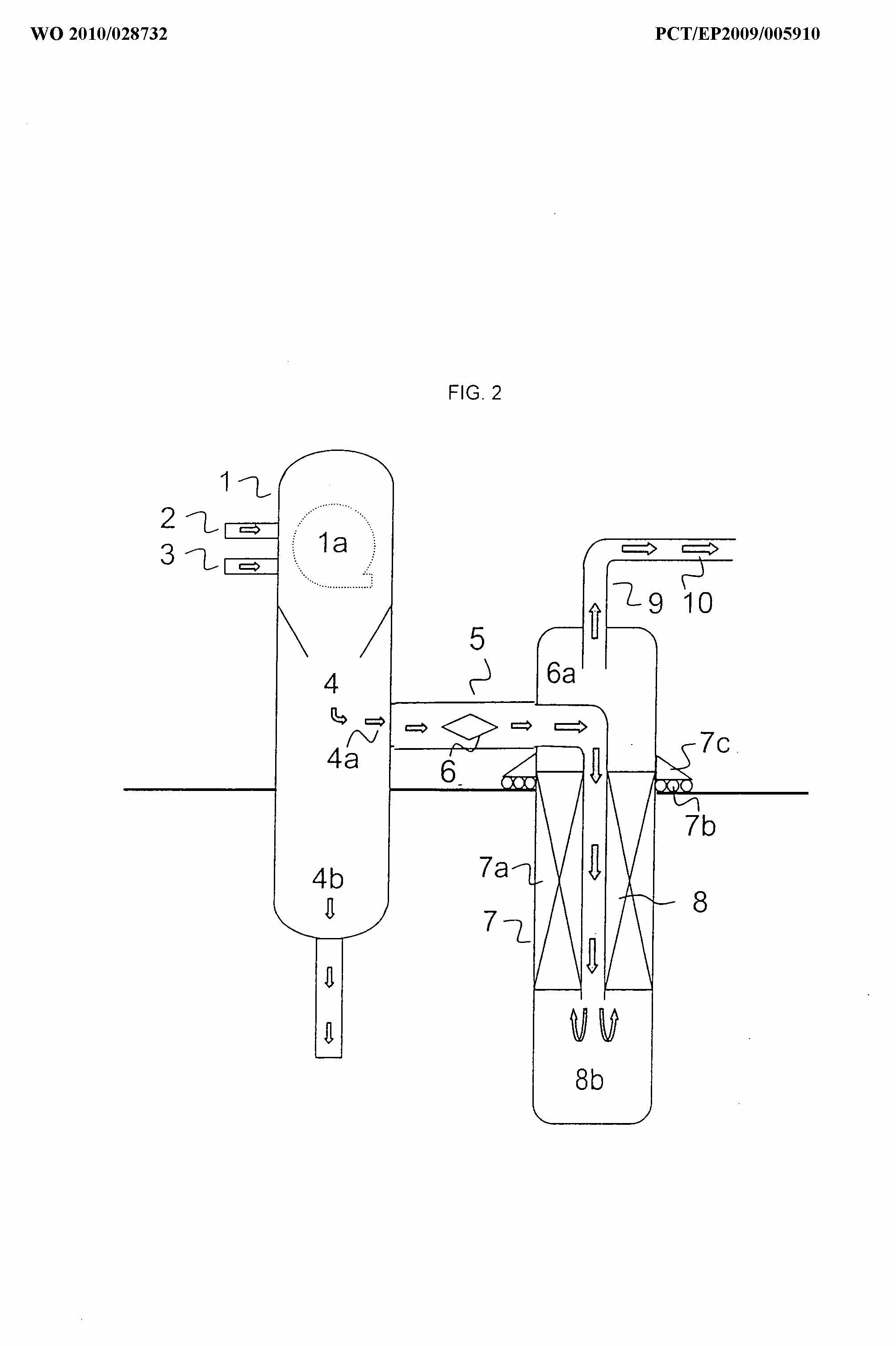
Tar cracking, e.g. reforming, partial oxidation
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters, i.e. particle separators, or filtering processes specially modified for separating dispersed particles from gases or vapours | |
Separating dispersed particles from gases, air or vapours by liquid as separating agent | |
Apparatus using free vortex flow, e.g. cyclones | |
Purifying combustible gases containing carbon monoxide |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "nozzle scrubber", "orifice scrubber" and "venturi scrubber"
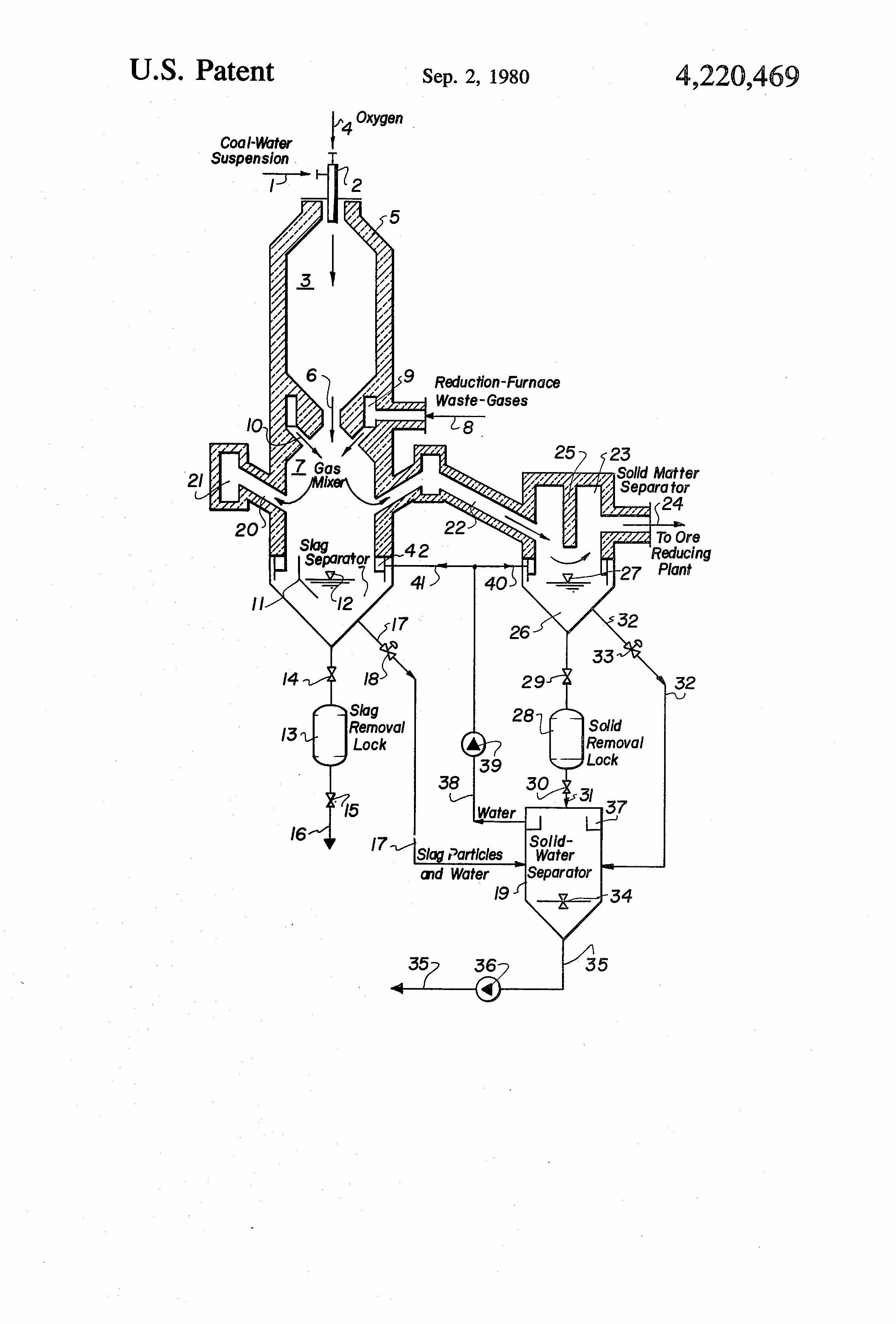
This place covers:
Gasifiers connected with a separate heat exchanger, such as shown in following figures:
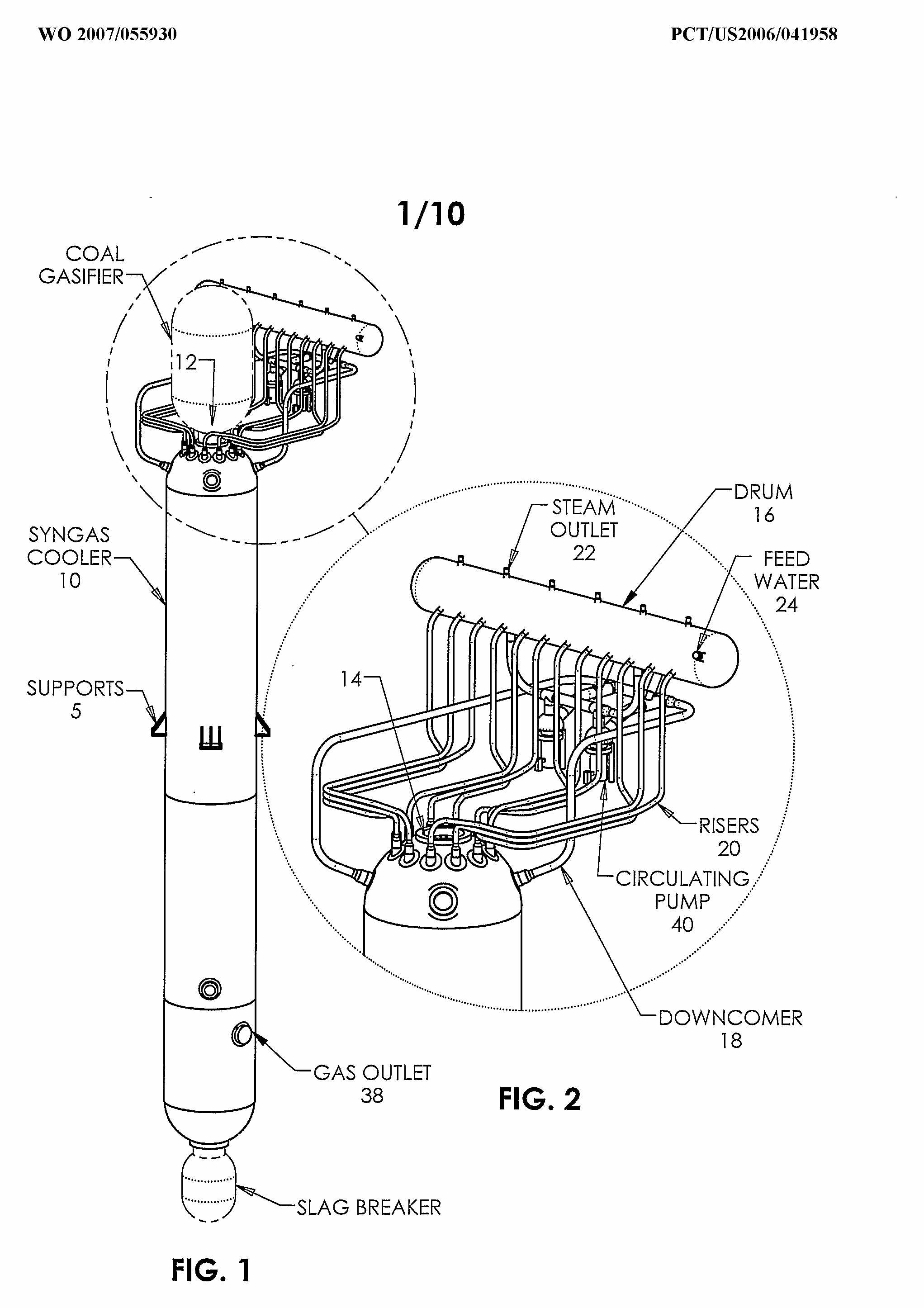
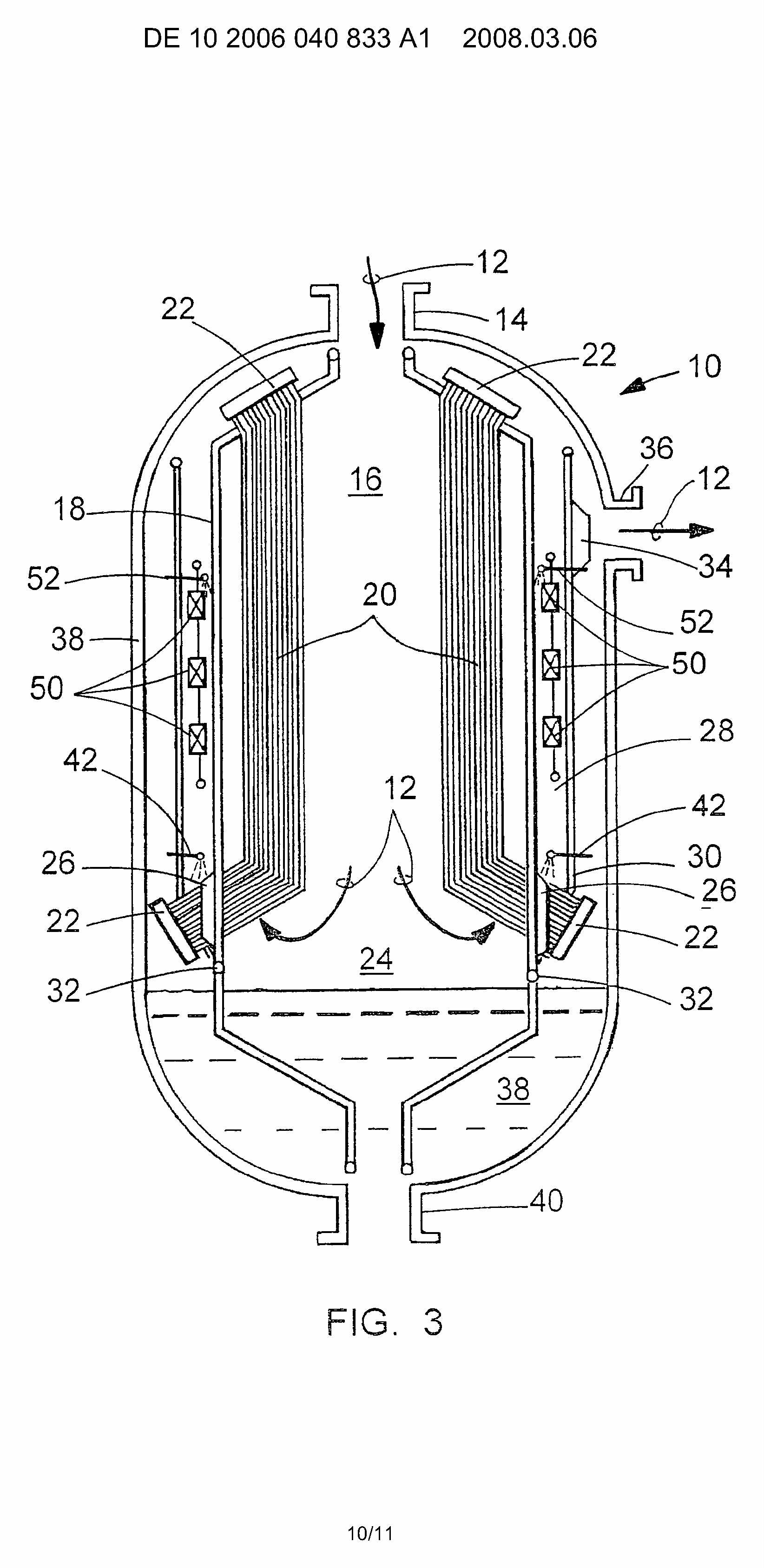
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods of steam generation characterised by form of heating method by exploitation of the heat content of hot gas being loaded with particles, e.g. waste heat boilers after a coal gasification plant | |
Heat-exchange apparatus, not provided for in another subclass, in which the heat-exchange media do not come into direct contact |