CPC Definition - Subclass B61F
This place covers:
- Parts of railway vehicles that are located under the body of the car, and that serves to support, guide and move the body on the rail;
- Parts of rail vehicles for cooperating with tracks of different widths;
- Devices or parts which prevent derailing;
- Means to protect vulnerable components on the lower side of the car body, e.g. wheel guards or obstruction removers
This place covers:
Details of bogies and their connections to the vehicle underframe to improve the running characteristic of the bogie, to reduce wear of the rail and prevent derailment of the vehicle.
Typical examples are:
- Method for optimizin guidance of railway vehicles.
- Railroad car truck suspension yaw stabilizer.
- Pneumatic spring between bogie and underframe.
- Self-steering bogies.
- Railway truck leveling device.
- Bogie for tilting-body type railcar.
- Lightweight truck bolster for railcar.
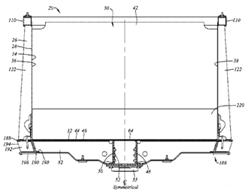
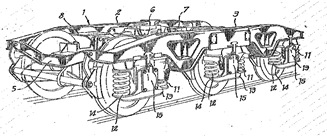
Following drawing show two examples:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Molding | |
Vehicle suspension arrangement in general | |
Stabilising vehicles bodies | |
Springs and shock absorbers in general |
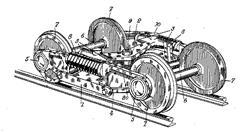
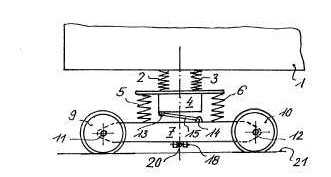
This place covers:
The title of this group is self-explanatory and do not need to be more specified.
Following drawing shows one example:
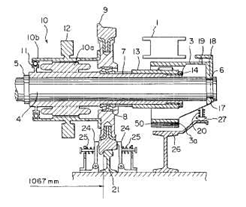
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable axle units for varying track |
This place covers:
Devices and methods to prevent derailment of the railway vehicle. It concerns additional components that are mounted on the vehicle.
Typical examples are:
- Derailment detector unit.
- Rail vehicle with guiding device.
- Inductive derailment sensor.
Following drawing shows one example (EP1422119):
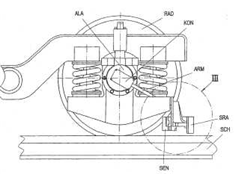
This place does not cover:
Preventing derailment by improving bogie components, e.g. improving the characteristics of the springs in |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Power and free systems with vehicles rolling trackless on the ground |
This place covers:
The title of this group is self-explanatory and do not need to be more specified.
Following drawing shows one example (DE29509473U):
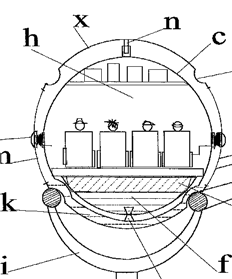
This place covers:
Railway vehicles having a wheel arrangement configuration that is not of the conventional type.
Following drawing shows one example:
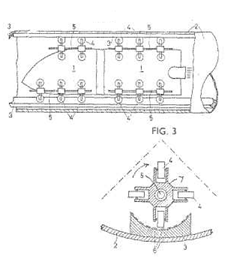
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wheel in general | |
Wheel characterised by rail-engaging elements | B60P17/00 |
This place covers:
The titles of this group are self-explanatory and do not need to be more specified.
Following drawing shows one example:
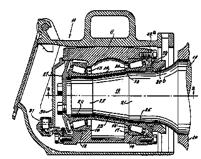
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speed measuring | |
Rotary current collectors with liquid contacts | |
Rotary current collectors with brush holders |
This place covers:
The titles of this group are self-explanatory and do not need to be more specified.
Following drawing shows one example:
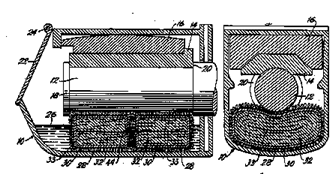
This place covers:
Devices and methods to protect the railway vehicle components from obstacle, e.g. ballast, or to minimize consequences of collisions with pedestrians.
Typical examples are:
- Method and device to detect impacts on specific zones on a railway vehicle.
- Collision protection system for rail vehicles.
- Track sweeper for rail vehicle.
Following drawings show two examples:
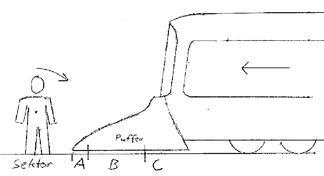
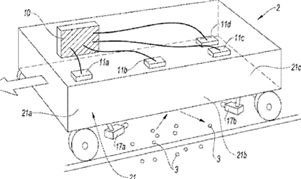
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Buffer cars |
This place covers:
Devices and methods that are not in B61F 1/00 - B61F 19/00.