CPC Definition - Subclass B32B
This place covers:
- Layered products characterised by the structure or materials of the layers, including products formed from separate layers, wherein the layers lose their individuality in the final product, e.g. products formed from a plurality of fabrics that are compressed into a unitary mat, or consolidated into a single layer after impregnation with a resin.
- Methods or apparatus for making layered products; methods or apparatus for treating layers or layered products either preliminary to or subsequent to their manufacture, when the treatment is in connection with said manufacture.
Classification of layered products is provided for in many technical areas, most of which are confined to a particular kind of material. However, in order that this subclass may provide a basis for making a complete search with respect to layered products, any layered product that specifies relevant useful information is classified in this subclass even though it may also be classified in other classes.
Classification in other areas should be made in the following situations:
- If the process or apparatus used in, or used in connection with, the production or treatment of any product is fully classifiable in a single other class or subclass for processes or apparatuses, e.g. B05, B29C, B44D, C08J, or C23, then classification should be made in the appropriate process or apparatus area.
- If a composition or preparation or treatment thereof is not essentially restricted to a layered product, then classification should be made in the appropriate composition, preparation, or treatment area.
- Adhesive tape, film or sheet comprising a single layer substrate, an adhesive coating not constituting a layer (see glossary of terms below), and a single layer liner or sheet should be classified only in the appropriate areas, e.g. C09J.
- If a product is fully classifiable in another area such as A61F 13/00 (e.g. absorbents), C09J 7/00 (e.g. adhesive tapes), C22C 26/00, C22C 29/00, and C22C 32/00 (e.g. Alloys), H05K (e.g. Printed circuits) or G02B [excluding G02B 6/00] (e.g. Optical elements), then classification should be made in the appropriate other area.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wearing apparel | |
Outerwear, protective garments | |
Headwear | |
Footwear | |
Furniture; Domestic articles or appliances | |
Household or table equipment | |
Floor fabrics | |
Implements for cleaning, e.g. cloths, pads, sponges, mops | |
Surgery, e.g. instruments or drapes | |
Diapers and absorbent articles | |
Containers for medical purposes | |
Chemical aspects of bandages, dressings, absorbent pads or surgical articles | |
Sport articles | |
Separation filters | |
Processes for applying liquids or other fluent materials to surfaces | |
Working or preserving wood | |
Manufacturing articles made of fibres or particles of wood | |
Working cement, clay or stone | |
Shaping or joining of plastics | |
Producing particular articles from plastic | |
Mechanical working or deformation of paper or cardboard | |
Printing, marking or copying | |
Printed matter of special format, e.g. cards, banknotes or identity cards | |
Decorative products | |
Fuel tanks | |
Vehicle fittings, vehicle parts | |
Ships or other waterborne vessels | |
Airplane fuselage or wings | |
Containers; Packages | |
Surface treatment of glass, e.g. coating | |
Cement compositions; Ceramics | |
Joining ceramic layers with other ceramic layers or layers of other materials by heating | |
Manufacture of polymeric films or sheets | |
Coating of polymeric articles | |
Production of macromolecular porous or cellular articles | |
Compositions of macromolecular compounds | |
Coating compositions | |
Adhesive processes | |
Adhesive tapes, films or sheets | |
Fireproofing materials | |
Coatings on or with metals | |
Electrolytic deposition of metals | |
Woven materials | |
Non-woven materials | |
Treatment of fabrics | |
Polymeric coatings on fibrous web | |
Impregnation or coating of paper; special paper | |
General building structures; insulation or protection | |
Structural elements; building materials | |
Roof coverings | |
Wall coverings | |
Floor coverings | |
Vibration damping, springs | |
Rigid pipes | |
Hoses or flexible pipes | |
Thermal insulation | |
Optical elements | |
Digital marking record carriers, e.g. credit cards | |
Labels or advertisements | |
Sound insulation | |
Magnetic recording | |
Optical recording | |
Batteries, e.g. separators | |
Printed circuits | |
Etched metallic pattern on the surface of a printed circuit board |
Classification guidance:
- If the invention is characterised by several aspects, e.g. surface structure and/or material of the layer(s) or production method, several classification symbols are given.
- Layers with mixtures of essential materials covered by two or more subgroups are classified in each appropriate subgroup.
- When layer materials are generally too defined or too many possibilities are disclosed, then subgroups corresponding to the materials indicated in the examples are allocated. In the absence of examples, the pertinent more general main groups or subgroups are allocated.
- If a layered product is characterised by the way it is produced and not by its structure or composition, the production method should be classified in groups B32B 37/00 or B32B 38/00, or in other subclasses, e.g. B29C, for example in groups B29C 45/16 or B29C 48/18.
- Coating operations are classified in B32B 2037/243 as long as a lamination process as defined in B32B 37/00 is present.
Allocation of Indexing symbols:
The following Orthogonal Indexing Symbols are mandatory in this subclass:
- B32B 2250/00 - B32B 2274/00, which are used in connection with B32B 1/00 - B32B 15/00 (with the exception of B32B 15/01), B32B 17/00 and B32B 19/00 – B32B 29/00;
- B32B 2305/00 and B32B 2309/00 - B32B 2398/00, which are used in connection with B32B 17/10005 - B32B 17/1099 and B32B 33/00 - B32B 43/00;
- B32B 2307/00 (properties) and B32B 2405/00 - B32B 2607/00 (particular articles), which are used in connection with the whole subclass B32B with the exception of B32B 15/01 and B32B 18/00.
Breakdown Indexing symbols, e.g. B32B 2037/0061 or B32B 2038/0016, are used for additional classification in B32B 37/00 – B32B 43/00.
Combination Sets (C-Sets):
In this subclass, C-Sets classification is applied to the following groups, listed in the table below, if the document discloses a pertinent combination of technical features that cannot be covered by the allocation of a single symbol. The fourth column of the table indicates the place where the detailed information about the C-Sets construction and the associated syntax rules can be found, in the definition section "Special rules of classification".
C-Sets ID | Base Symbols | Subsequent Symbols | C-Sets Formula; Location of C-Sets Rules |
#B32Ba | (B32B 17/10005, B32B 2319/00 – B32B 2386/00), laminated safety glass structure comprising a polymeric intermediate layer sandwiched between interlayers, and the polymeric material of the polymeric intermediate layer; see B32B 17/10005. |
The specific C-Sets rule is located at only one place of the base symbol in the section "Special rules of classification" in the definition. If the C-Sets rule is applicable to all groups of a subclass, it is located at the subclass level only. If the same C-Sets rule is applicable to multiple groups or subgroups within the same subclass, the C-Sets rule is placed at the highest group or subgroup of the multiple groups.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Adhesive | Substance applied in any state or in any manner that has bonding properties. |
Coating | A coating in the sense of B32B is obtained by processes such as: (A) Brushing, flowing, spraying, dipping or doctor blading a solution or dispersion; (B) Sputtering, vapour/plasma/vacuum depositing; (C) Deposition of loose particles or fibres, e.g. by sprinkling, flocking, air laying; and (D) Deposition of fibres/pulp/particles in a wet slurry as in paper making (wet laying). Coatings are not considered defined B32B layers (see definition of Layer below). |
Discontinuous layer | A layer formed of separate pieces of material having both a physical discontinuity and a continuous path through each of its major directions (e.g. x and y, or length and width). Examples include a grating, a honeycomb, a frame, or separate pieces of material that are juxtaposed side-by-side. Examples of discontinuous layers are as follows: |
Embedded layer | A layer that is set, surrounded, enveloped, or enclosed in an impregnating material, mass of plastic or similar substance that penetrates and/or lies on side edges of the layer. |
Fibrous layer | Random assembly of fibres or filaments, usually of limited length, e.g. felt or fleece, the fibres being interengaged or connected, e.g. by adhesive. |
Filamentary layer | Layer of threads, filaments, tapes or ribbons of any substance (including wires) of more or less unlimited length secured together; it may be, e.g. woven, knitted, braided, netted, spunbonded, or formed of threads or filaments crossed or laid side by side and bonded together. |
Film | Within B32B, a film that is formed by extrusion or moulding or that is formed as a self-supporting transfer coating is a layer. A film that is formed in-situ by coating is not considered to be a layer within the scope of B32B. |
Impregnated layer | A layer that is at least partially filled by a material and has been obtained by permeating or saturating at least a part of the layer with a liquid substance, e.g. dispersions, uncured polymer, melted or molten polymer, glass, metals, settable compositions. |
Juxtaposed side-by-side | In direct contact or with a bonding material, e.g. adhesive or mortar, in between. |
Laminating | Laminating is the action of combining previously unconnected, but possibly laid up, layers to become one product whose layers will remain together. |
Lay-up | Lay-up is the action of combining separate layers, one on top of the other, in order to form a half-product for entering the laminating process. |
Layer | Sheet, strip or stratum having a small thickness relative to its other dimensions. It may be deformed out of the flat plane to form a three-dimensional shape; it may or may not be homogeneous or cohesive; it may be an assembly of fibres or pieces of material. It may be discontinuous, e.g. in the form of a grating or a honeycomb. It may or may not be in complete contact with the next layer, e.g. a corrugated layer against a flat layer. The layer has to have one of the following forms: (1) Preformed layer, i.e. taking the form of a layer at some stage before being brought into combination with another layer; (2) Layer formed in-situ, i.e. taking the form of a layer while or after being brought into combination with another layer. Additional explanations of (1) Preformed layer and (2) Layer formed in-situ are located following the Glossary of Terms. In B32B, with the exception of B32B 15/01 - B32B 15/018 and interlayers/composite interlayers proper for B32B 17/10005 - B32B 17/1099, the following is excluded from the definition of a layer: A coating formed directly onto a substrate layer, which at the moment of its contact with the substrate does not have the form of a layer (unless the coating falls within the definition of (2) Layer formed in-situ as further explained below after the Glossary of Terms). |
Layered product | Product comprising at least two superposed layers secured together; the term "secured" is to be interpreted broadly to include any method of uniting or securing the layers, e.g. needling, stitching, gluing, nailing, dovetailing, welding or the interposition of an adhesive or adhesive-impregnated support. Products wherein layers are obtained by co-extrusion or by simultaneous injection moulding of materials are included in this definition. It also encompasses two layers of ceramic powders that are pressed together in a press. It may also be an intermediate stage in the production of an article which is not layered in its final form, e.g. a panel with a protective layer that is stripped off when the panel is placed in its position of use. It is normally of substantially uniform thickness overall, i.e. ignoring local variations such as are produced by a corrugated face layer. The layered product may be in the form of an article, e.g. a container. |
Next to | With no other layer being interposed. |
Partial laminating | Partial laminating occurs (1) when one layer does not fully cover a surface of another layer, whereby the layer with the greater surface area is laminated on only part of its surface, or (2) when two coextensive layers are bonded on only part of their facing surfaces. |
Particulate layer | Preformed layer of particles, e.g. chips, powder, granules, flakes, in which the particles are bonded together, e.g. sintered or by a binder. |
Spaced fabric | A fabric that includes at least two outer fabrics joined together by connecting yarns that create an intermediate gap between the outer fabrics, to form a three-dimensional fabric. The spaced fabric can be a single layer or multiple layers. (1) A spaced fabric is considered a single layer for B32B when woven or knit fabrics are produced in a single step wherein the yarns simultaneously form a fabric that comprises outer plies with middle connecting (spacer) yarns. (2) A spaced fabric is considered to include multiple layers for B32B when the fabric is made from at least two preformed fabrics that are joined together with connecting yarns to create a laminate structure with a space between the outer fabrics. |
The layer has to have one of the forms defined hereunder:
Preformed layers
Preformed layer, i.e. taking the form of a layer at some stage before being brought into combination with another layer. Preformed layers include:
- coherent solid layers including honeycombs or similar layer of regularly arranged cells;
- non-coherent solid layers consisting of assemblies of strands, strips, tiles or like elements, which are juxtaposed side-by-side;
- fleeces or fabrics (including spaced fabrics);
- preformed paper webs;
- doughs which are cast onto a plate to form a solid sheet when set (including set mortars, cements and concretes);
- self-supporting pre-moulded layers, e.g. pre-extruded, pre-cast;
- self-supporting transfer coatings.
Layers formed in-situ
Layers formed in-situ, i.e. taking the form of a layer while or after being brought into combination with another layer. Layers formed in-situ include:
- layer formed by casting, extrusion or moulding (e.g. injection, rotational process) of a melt material;
- by assembling strands, strips, tiles or like elements juxtaposed side-by-side onto a preformed layer;
- fleeces and fabrics formed onto a preformed layer and bonded or impregnated into a cohesive sheet, e.g. spunbonded fabric;
- mortars, cements and concrete layers formed onto a preformed layer.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "Synthetic rubber" and "thermosetting synthetic rubber"
- "Layer of particles", "layer formed of particles" and "layer made of particles"
- "Layer of fibres", "layer formed of fibres" and "layer made of fibres"
- "Spaced fabric", "three-dimensional fabric", "3-D fabric" and "spacer fabric"
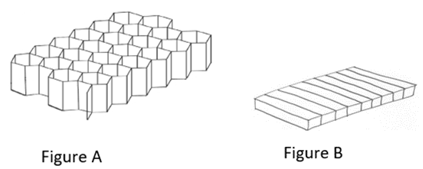
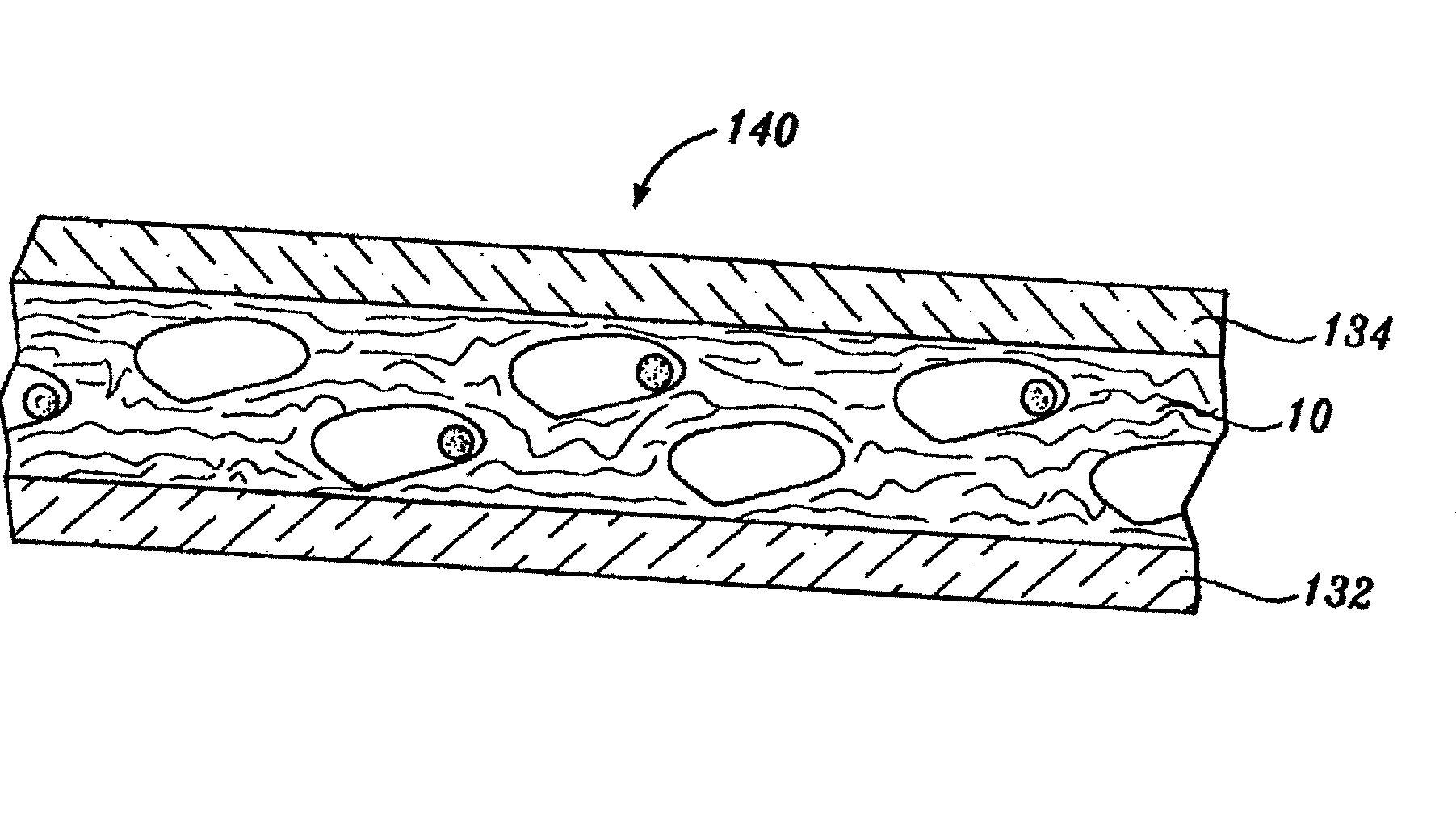
This place covers:
Layered products having a non-planar shape, such as an article having a shape that defines an internal cavity, e.g. a container, or in the form of a tubular product.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Containers for medical or pharmaceutical purposes | |
Fuel tanks | |
Containers; Packages | |
Vessels for containing or storing compressed, liquefied or solidified gases; Fixed capacity gas holders |
For classification of a product in this group, surface unevenness, surface non-uniformity and the shape of individual layers are ignored.
Layered products in the shape of a container or receptacle are also classified in B32B 2439/00 – B32B 2439/80.
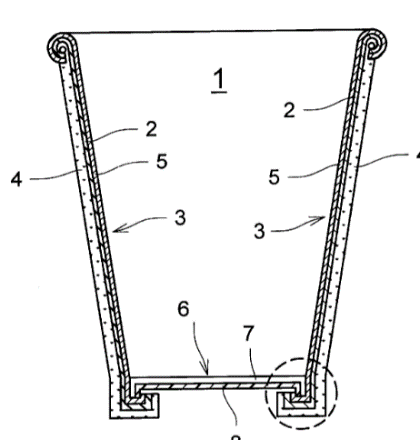
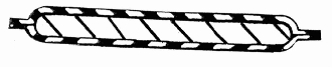
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by a hollow structure with an elongated length, e.g. a hose, pipe or sleeve, wherein the hollow structure may, or may not, be closed at one end.
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
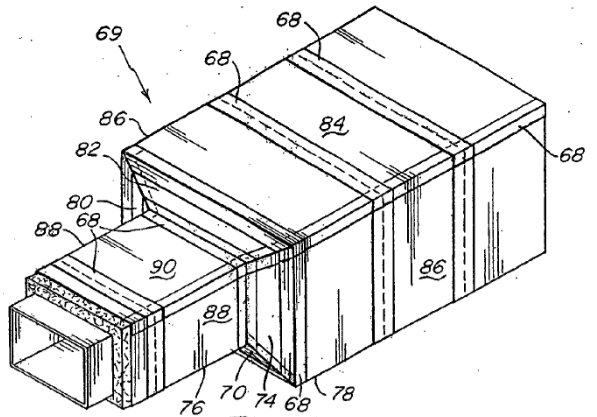
2.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Sausage casings | |
Catheters | |
Tubes for medical use | |
Rigid pipes | |
Hoses, i.e. flexible pipes | |
Thermal insulation sleeves |
Layered products in the shape of a tube, hose, pipe or sleeve are also classified in B32B 2597/00.
In patent documents, the word/expression in the first column is often used instead of the word/expression in the second column, which is used in the classification scheme of this place:
Tubular product | Tube, pipe or hose |
This place covers:
Features of form of any of the individual layers of a layered product. Examples include:
- a layer with an edge feature, e.g. chamfered or beveled edge;
- a discontinuous layer, e.g. a honeycomb or tiled floor layer;
- a layer having an internal cavity within the layer;
- a corrugated layer
- an apertured layer; and
- a layer having a variation in thickness, e.g. roughened or grooved.
B32B 1/00 – B32B 1/08 cover layered products where all the layers cooperate to define a non-planar shape, whereas B32B 3/00 – B32B 3/30 cover features related to the shape of individual layers in planar or non-planar layered products.
The following physical structure of an individual layer does not constitute a feature of form that is proper for this main group:
- A fibrous or filamentary layer, which is provided for in B32B 5/02 – B32B 5/12 and/or B32B 5/22 – B32B 5/2795;
However, if a layered product has a fibrous, filamentary, foamed or particulate layer having a feature of form proper for this main group, it should also be classified in this main group. For example, a layered product having a non-woven fibrous layer with apertures in the layer would be proper for B32B 3/266 and B32B 5/022.
Layered products having a layer of regularly-arranged cells shall be placed in B32B 3/12 regardless of whether the layer was formed from one piece or separate pieces of material juxtaposed side-by-side.
Layered products having a layer with a feature of form that differs physically in different parts of the layer are provided for in both B32B 3/00 – B32B 3/30 and B32B 5/14 – B32B 5/147. For example, a layer having a density variation in apertures across its surface area would be provided for in B32B 3/266 and B32B 5/142.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
added member | any discrete element(s) secured to the layered product that does not constitute a layer or adhesive as per the B32B definitions, e.g. an insert or a spacer element. |
juxtaposed side-by-side | in direct contact or with a bonding material, e.g. adhesive or mortar, in between. |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
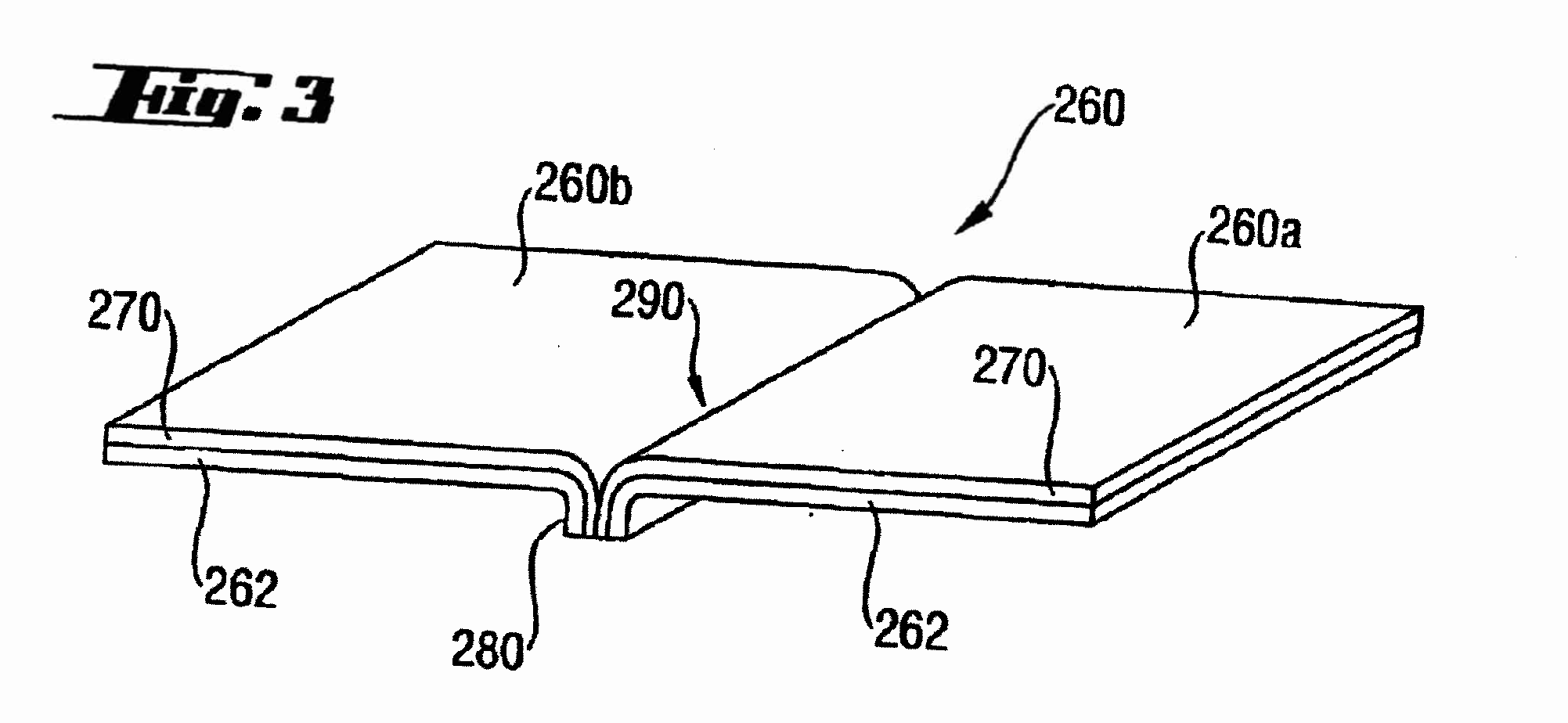
This place covers:
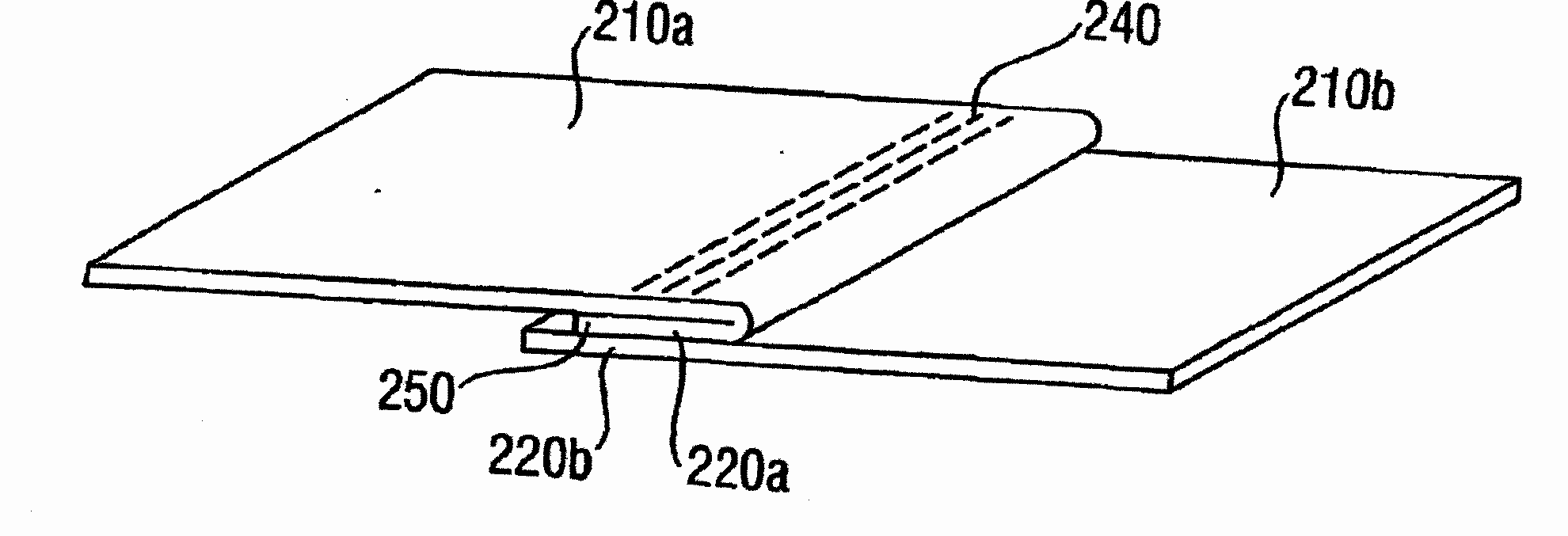
This place covers:
![]()
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Use or provision of nails, stitches, or similar separate fastening elements for these purposes |
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Products characterised by a layer formed by regularly laid parallel cords or filaments, which may be bunched, flat or slightly separated |
This place covers:
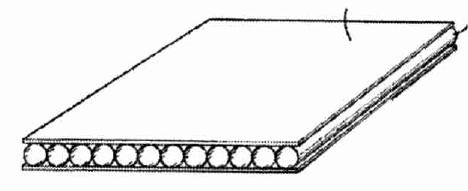
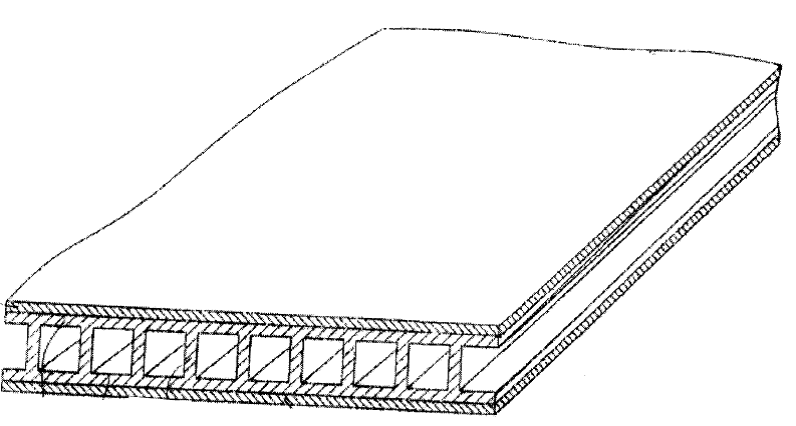
Layered products comprising honeycombs and similar layers of cells having a regular, repeating, geometric structure.
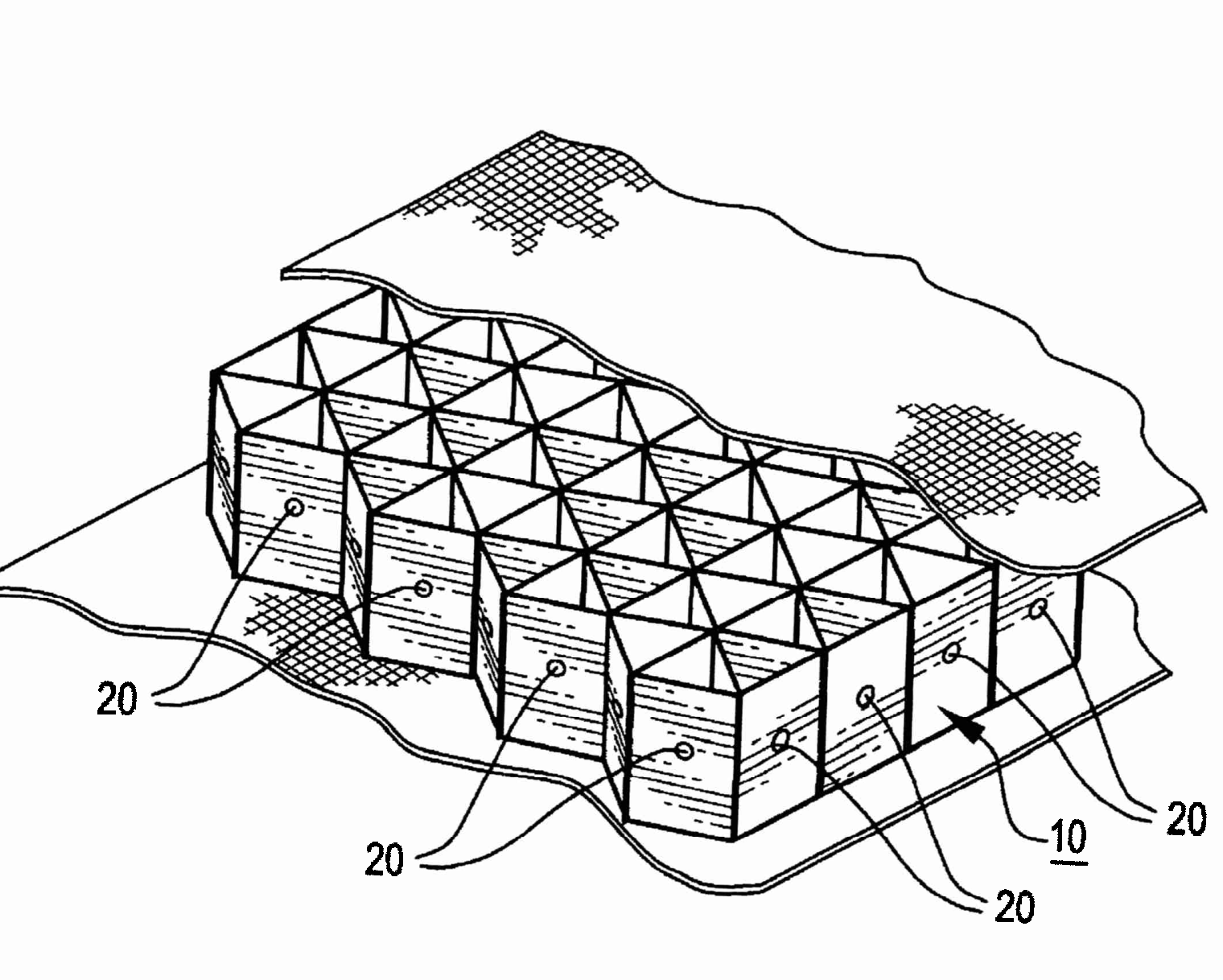
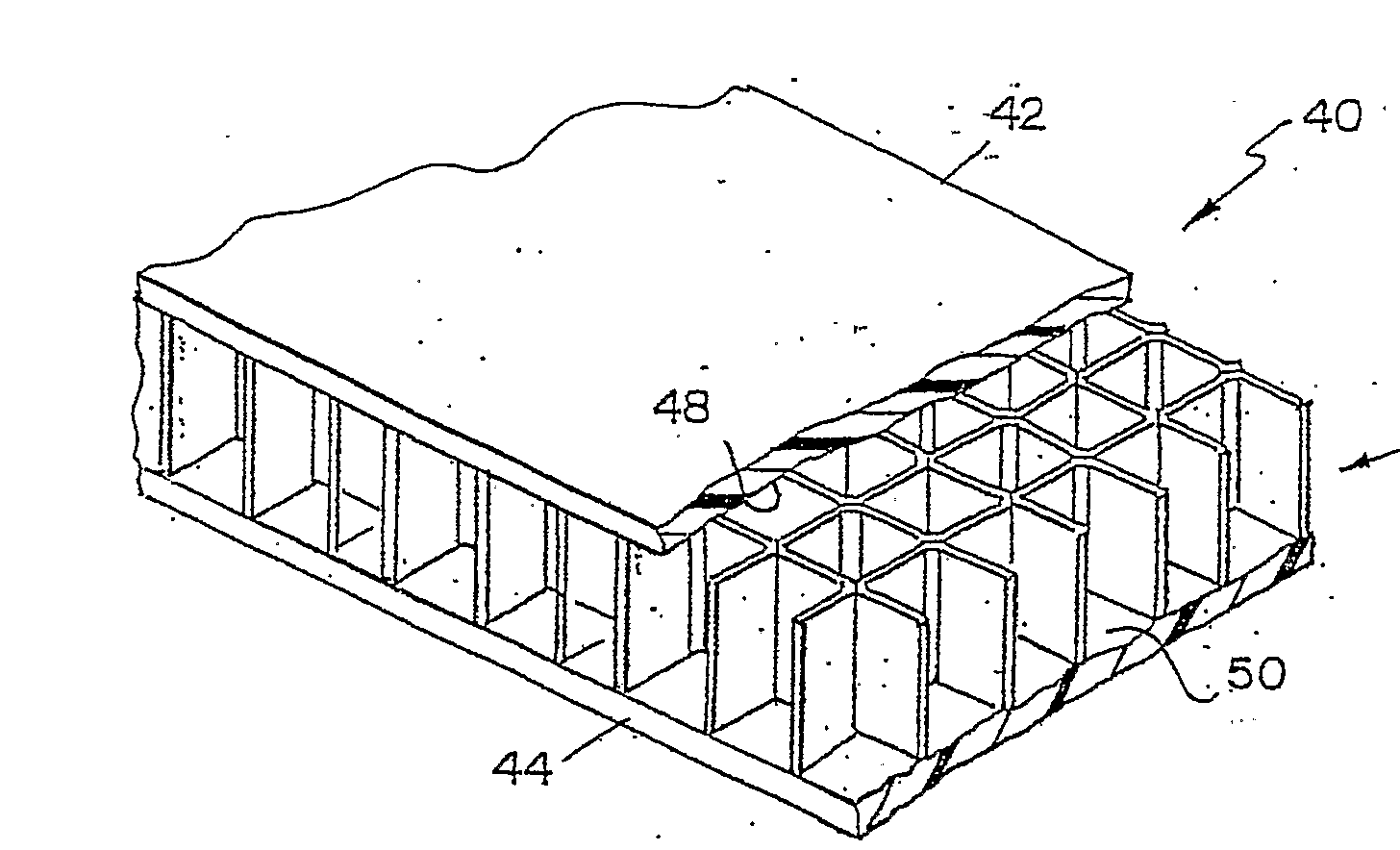
This place covers:
Layered products comprising a face layer formed by elements, e.g. tiles, strips, rods, bricks and other elements, which are juxtaposed side-by-side, e.g. mosaics. The elements are laid out in a specific manner rather than merely agglomerated or scattered and are larger than mere particles.
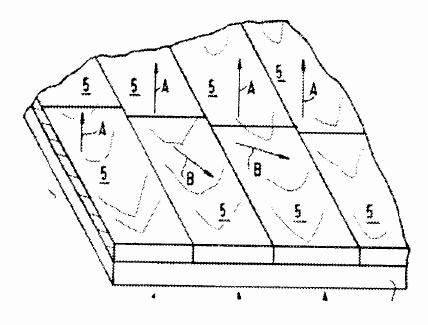
This place covers:
Layered products comprising an internal layer formed by elements, e.g. tiles, strips, rods, bricks and other elements, which are juxtaposed side-by-side, e.g. mosaics. The elements are laid out in a specific manner rather than merely agglomerated or scattered and are larger than mere particles.
This place covers:
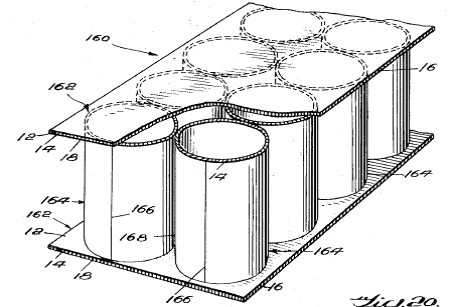
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Products characterised by a foamed layer | |
Products characterised by a synthetic resin layer comprising fillers which create voids or cavities, e.g. by stretching |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Cavities | Hollow spaces within a layer |
This place covers:
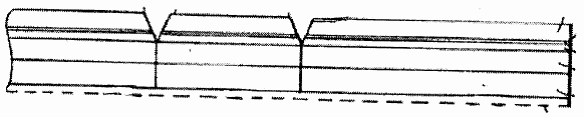
Layered products comprising a layer having changes of thickness which are not of a minor and accidental nature, or a mere, non intended result of a surface structure, e.g. grooves, ribs or protuberances.
This place covers:
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Corrugated paper or corrugated cardboard |
This place covers:
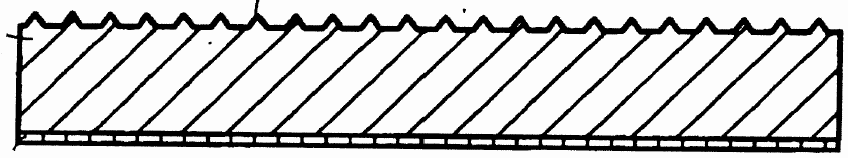
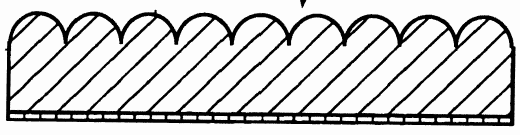
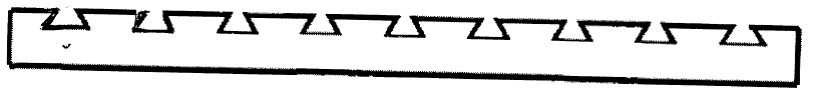
This place covers:
Layered products comprising at least one layer that is a fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foamed layer (see definitions in B32B subclass glossary). A layered product can include:
- Multiple fibrous or filamentary layers, e.g. multi-layered fabrics
- Multiple particulate layers
- Multiple foamed layers
- Combinations of fibrous, filamentary, foamed and/or particulate layers
- Fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foamed layers that are impregnated or embedded
- A fibrous, filamentary, particulate or foamed layer that is combined with another layer
Layered products characterised by a layer differing constitutionally or physically in different parts, e.g. a synthetic resin layer that has greater crosslinking near its faces; a cementitious layer with different density from core to outer faces.
In classifying a layered product comprising a fibrous, filamentary, foamed or particulate layer, each layer in the layered product is classified in the appropriate subgroup for that specific layer based on material, adjacency and/or structure. The fibrous, filamentary, foamed or particulate layer(s) is classified in B32B 5/00 and the layer(s) of other materials are classified in other B32B subgroups as appropriate for the specific layer. Several classification symbols can be given.
- Layered products that comprise a fibrous, filamentary, foamed or particulate layer and that have at least one additional layer covered by material subgroups B32B 9/00 - B32B 29/00, e.g. synthetic resin, paper, leather, metal, etc., are also classified in the appropriate material subgroups B32B 9/00 - B32B 29/00 for the additional layer.
Example:
- A fibrous or filamentary layer made from synthetic resin fibres, e.g. polypropylene, would be classified in B32B 5/00 for the fibrous layer structure and B32B 2262/0253 for the polypropylene fibres. Classification in B32B 27/00 is not given.
- If the fibrous layer is next to a synthetic resin layer, e.g. a polypropylene resin film, classification is given in B32B 27/12 for the adjacency of the fibrous layer to the synthetic resin and B32B 27/32 for the polypropylene synthetic resin layer.
- If the fibrous layer has apertures formed in the layer, classification in B32B 3/266 also is provided. If adhesive is used to bond the layers classification in B32B 7/12 is also provided.
Layers in which the fibres, filaments or particles are present as additives or filler material are classified in the appropriate material subgroup of the matrix material, e.g. B32B 25/02.
Classification in other areas of B32B should be made in the following situations:
- Layers formed of metallic wires are classified in B32B 15/02.
- Layers formed of natural mineral fibres or particles are classified in B32B 19/00.
- Layers formed of wood fibres or particles are classified in B32B 21/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products comprising a layer of bituminous or tarry substances in which fibres, filaments or particles are present as additives, e.g. as fillers | |
Layered products comprising a layer of a water-setting substance in which fibres, filaments or particles are present as additives, e.g. as fillers | |
Layered products comprising a layer of a natural or synthetic rubber in which fibres, filaments or particles are present as additives, e.g. as fillers | |
Layered products comprising a layer of a synthetic material in which fibres, filaments or particles are present as additives, e.g. as fillers | |
Shaping composites, i.e. plastics material comprising reinforcements, fibrous reinforcements only | |
Production of macromolecular porous or cellular articles | |
Woven materials | |
Knitted materials | |
Non-woven materials | |
Tufted materials | |
Producing multi-layer textile fabrics | |
Artificial leather, oilcloth or other material obtained by covering fibrous webs with macromolecular material; characteristics of foam layer; obtained by applying a ready-made foam layer |
- B32B 5/28 contains documents published before 2006 and is no longer used for the classification of documents after this date.
- Coating on a fibrous, filamentary or particulate layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00.
- The fibres, filaments or particles of a fibrous, filamentary or particulate layer may be impregnated, embedded or bonded with a substance such as a synthetic resin. The impregnating or embedding substance is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2260/00.
- The structure or nature of the fibres or filaments forming the fibrous or filamentary layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2262/00.
- The nature of the particles forming the particulate layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2264/00.
- The nature of the foam forming the foamed layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2266/00.
This place covers:
Layered products comprising a fibrous or filamentary layer, e.g. woven; non-woven; knit; nets produced from fibres, filaments, yarns, threads; ribbons or tapes; or a layer formed by regularly laid parallel cords or filaments, which may be bunched, flat or slightly separated, e.g. juxtaposed-side-by-side.
Classification of fibrous and filamentary layered products is provided for in many technical areas of CPC depending on the structure of the fabric or textile layers, yarns, fibres or filaments. However, in order that this subgroup may provide a basis for making a complete search with respect to fibrous or filamentary layered products, any layered product that specifies relevant useful information is classified in this subgroup even though it may also be classified in other Subclasses. Several classifications symbols can be given.
Classification in other areas should be made in the following situations:
This place does not cover:
Layer formed of metallic wires | |
Layer formed of natural mineral fibres | |
Layer formed of wood fibres |
- Layered products wherein all layers are fibrous or filamentary layers are also classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2250/20.
- Layered products where the fibrous or filamentary layer is coated or impregnated are classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00 or B32B 2260/00.
- The structure or nature of the fibres or filaments forming the fibrous or filamentary layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2262/00.
- The structure or nature of the fibres or filaments forming the fibrous or filamentary layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2262/00.
- For conjugate and/or mixed fibres or filaments associated with a specific layer, e.g. the woven layer, knit, non-woven or netting layer, classification is required with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2262/12 - B32B 2262/156.
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by a particular arrangement of the fibres or filaments of the layers, e.g. fibres or filaments of the different layers being parallel or perpendicular to each other. The layers may be next to each other or separated by other layers.
This place does not cover:
Layer formed of natural mineral particles | |
Layer formed of wood fibres, chips or particles |
- The structure or nature of the particles forming the particulate layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2264/00.
- Coated or impregnated particulate layers are classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00 or B32B 2260/00.
- Layered products wherein all layers are foamed layers are also classified in B32B 2250/22.
- The structure or nature of the foam forming the foamed layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2266/00.
This place covers:
In-situ foams include a foamable layer that is assembled or installed and then foamed in or within the laminate or installation, e.g. a foamable polymer layer between two exterior layers, wherein the polymer layer is converted to foam after assembly between the exterior layers. The foamable layer can be preformed or can take the form of a layer while or after being brought into combination with another layer, e.g. casting, extrusion or molding of a melt material.
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by the adjacency of more than one fibrous or filamentary layers, i.e. woven, non-woven, knit or net layers, which are adjacent at least one or more woven, non-woven, knit or net layers. For example, a woven layer adjacent a non-woven layer; a knit layer adjacent a non-woven layer; a woven layer adjacent one or more non-woven layers.
Classification in subgroups B32B 5/26-B32B 5/2795 is determined by the subgroup with the most specific subject matter. Classification in B32B 5/26-B32B 5/2795 is only required in the subgroup with the lowest level of indentation.
- Example 1: A layered product comprising a woven layer next to a non-woven layer. Classification in B32B 5/275 is provided because this subgroup has the lowest level of indentation directed to the specific combination of layers.
- Example 2: A layered product comprising a melt-blown non-woven layer next to a spunbond non-woven layer. Classification in B32B 5/269 is provided because this subgroup has the lowest level of indentation directed to the specific combination of layers.
Layered products wherein all layers are fibrous or filamentary layers are also classified in B32B 2250/20.
Layered products wherein two or more fibrous or filamentary layers are impregnated are classified in B32B 2260/023.
Layered products with conjugate and/or mixed fibres or filaments associated with a fibrous or filamentary layer, i.e. woven, non-woven, knit or netting, are classified in B32B 2262/12-B32B 2262/156.
Layered products wherein all layers are foamed layers are also classified in B32B 2250/22.
This place covers:
This group covers layered products in which the relationship between the layers is important. The relationship could be, for example, the differences between physical or chemical properties, patterns of connection, and the orientations of features.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
In respect of orientation of features, see the relevant groups for the features concerned, e.g. for direction of fibres | |
In respect of substances |
This place covers:
This group covers layered products characterised by having two or more layers, one of which differs from another with respect to a physical property, e.g. density, melting point, refractive index. Examples of this type of product are those comprising layers of:
- Hard and soft wood,
- High and low density PE,
- Harder and softer nylon,
- Oriented and non-oriented PP,
- Plasticized and non-plasticized PVC.
This place covers:
This group covers layered products characterised by having two or more layers, one of which differs from another with respect to the orientation of features, e.g. the direction of one layer's corrugation or joints differs from that of another layer. The layers may be next to each other or separated by other layers.
If there is only one corrugated layer in a layered product, it is classified in B32B 3/28 or B32B 29/08.
This place does not cover:
Direction of fibres or filaments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products characterised by a layer comprising a deformed thin sheet, e.g. corrugated, crumpled | |
Corrugated paper or cardboard |
This place does not cover:
Fibrous or filamentary layer mechanically connected, e.g. by needling, sewing, stitching, hydroentangling, hook-and-loop fastening to another layer, e.g. of fibres, of paper |
This place covers:
This group covers layered products in which a pair of interconnected layers is bonded by one or both layers having inter-reactive properties, wherein neither layer of the interconnected pair comprises an adhesive – whether a coated adhesive, a tie layer, or a layer described as acting as an adhesive.
This place covers:
This group covers layered products comprising an adhesive – whether a coated adhesive, a tie layer or a layer described as acting as an adhesive – inserted between two layers to bond them.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesive processes in general or use of a material as adhesive |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products characterised by having a fibrous or filamentary layer made of a substance not covered by groups B32B 11/00 - B32B 17/00 or B32B 19/00 - B32B 29/00 | |
Layered products characterized by having a particulate layer made of a substance not covered by groups B32B 11/00 - B32B 17/00 or B32B 19/00 - B32B 29/00 | |
Layered products characterised by having a foamed layer made of a substance not covered by groups B32B 11/00 - B32B 17/00 or B32B 19/00 – B32B 29/00 | |
Products comprising at least two ceramic layers | |
Joining ceramic layers with other ceramic layers or layers of other materials by heating |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Artificial stone | Material made by crushing and grinding natural stone and then re-constituting it, e.g. with cement mortar or with a resin binder |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Product characterised by a fibrous or filamentary layer embedded or impregnated in a bituminous substance | |
Product characterised by a particulate layer embedded or impregnated in a bituminous substance |
- The nature of the fibres or filaments is classified in B32B 2262/00.
- The nature of the particles is classified in B32B 2264/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cements; Compositions thereof, e.g. mortars, concrete or like building materials |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Product characterised by a fibrous or filamentary layer embedded or impregnated in a water-setting substance | |
Product characterised by a particulate layer embedded or impregnated in a water-setting substance |
- The nature of the fibres or filaments is classified in B32B 2262/00.
- The nature of the particles is classified in B32B 2264/00.
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by having a continuous or discontinuous metal layer.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products characterised by having a metallic fibrous or filamentary layer | |
Layered products characterised by having a metallic particulate layer | |
Layered products characterised by having a metallic foamed layer | |
Coatings on or with metals | |
Electrolytic deposition of metals |
Coating on a metallic layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00
This place covers:
Layered products with all layers being metallic in the form of sheets/plates, distinct layers. They can be made by any possible method such as roll bonding, cladding, brazing, coating etc.
If the layered product comprises a layer that is not metallic such as polymer, ceramic, glass etc. then it is not classified in B32B 15/01- B32B 15/018, but in other parts of B32B.
This place does not cover:
Making layered metal workpieces by pressure cladding | |
Making coatings with a metallic material characterised by its composition |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Biomedical applications, stents | |
Rolling of metals | |
Powder metallurgy | |
Changing the physical structure of ferrous metals/alloys | |
Changing the physical structure of non ferrous metals/alloys | |
Heat exchangers | |
Armour constructions/plates | |
Electrical wires | |
Magnets | |
Batteries/fuel cells | |
Electrical connectors | |
Electronic components |
- In metallic layered products having layer(s) of a specific composition, in addition to classification in B32B 15/01, the composition of each layer is classified in C22C (C22C 5/00 - C22C 45/00).
- When the layered product is intended for a particular use then the use is classified as well (see informative references for illustrative uses).
- Galvanized steels having a specific composition of a substrate and/or of the Zn layer are classified in B32B 15/013.
- Brazing sheets/composite materials (e.g. for heat exchangers) with all layers formed of aluminium or aluminium alloys are classified in B32B 15/016.
- A layered product consisting of a layer of steel, a layer of aluminium alloy and a layer of Ni alloy will be classified in both other B32B 15/012 and B32B 15/015.
This place covers:
Layered products comprising:
- inorganic glass in sheet or film form, fibres of glass or slag secured to another layer of inorganic glass;
- glass in the form of a sheet or film bonded with a transparent synthetic resin to another transparent layer; and
- laminated glazings.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Automotive windows | |
Railway windows | |
Canopies; windscreens or similar transparent elements for aircraft | |
Antiballistic glazings | |
Liquid crystal displays | |
Photovoltaic modules | |
Heating windshields |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products comprising a fibrous layer | |
Furniture panels or shelves | |
Show cases or cabinets | |
Fibre-reinforced material | |
Producing optical elements from plastics | |
Designs with unusual light effects | |
Glass compositions | |
Coatings on glass | |
Surface treatment of glass fibres | |
Joining pieces of glass to pieces of other inorganic material | |
Manufacture of prepregs | |
Compositions of polymers | |
Coverings or linings of glass, e.g. for walls or ceilings | |
Layout of fixed or moving closures, e.g. windows | |
Insulating glass windows | |
Constructional features of refrigerators | |
Optical devices made from glass | |
Alarm windows | |
Billboards | |
Window antennas | |
Printed circuit boards comprising glass substrates | |
Transparent shielding materials against electric or magnetic fields |
- B32B 17/00 requires that the layered product comprises at least one glass layer and at least one layer of another material; a layered product comprising both a glass layer and a glass fibre layer is classified in both B32B 17/02 (or B32B 17/04) and B32B 17/06.
- The layer adjacent to the glass layer is specified by classifying in one of the appropriate groups selected in the range B32B 17/06 - B32B 17/10005.
- Layered products comprising a layer of glass next to a layer of synthetic resin are classified in B32B 17/10.
- Layered products comprising a layer of glass next to a layer of synthetic resin that are considered to be laminated safety glass or glazing are classified in B32B 17/10005 and its subgroups.
- The layer of synthetic resin is further specified in B32B 17/1055 and its subgroups when it is used as an interlayer to create the laminated safety glass or glazing. The resin interlayer or all components of a composite interlayer are to be considered a layer proper for B32B and can be made by any process, including a coating process.
- B32B 17/10005 - B32B 17/1099, a layer of organic glass is not considered as a glass layer but as a synthetic resin layer which is classified using orthogonal Indexing symbols selected from the groups B32B 2319/00 - B32B 2386/00 allocated as single symbols or in C-Sets as explained in B32B 17/10005.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Laminated safety glass or glazing, safety glazing, laminated glazing | Inorganic glass layer in sheet form bonded to another inorganic glass layer in sheet form or to a durable polymeric sheet or film via a resin interlayer, and wherein the interlayer keeps the laminated safety glass or glazing bonded even when struck or broken, preventing the glass from shattering. |
Interlayer | An internal layer of thermoplastic polymer bonding the components of a laminated safety glass or glazing to one another. |
Intermediate layer, intermediate film | An internal layer or film used as a barrier or as a carrier for functional layers and not having adhesive properties. |
Plasticiser | Organic compound which reduces the glass transition temperature of the interlayer, usually an interlayer of PVB. |
Glazing | A transparent closure of an opening such as the glass of a window. |
Composite interlayer | A composite laminate that binds the inorganic glass layer to another inorganic glass layer or the durable polymeric sheet or film of the laminated safety glass or glazing. The composite interlayer comprises at least one interlayer and may also comprise an intermediate layer and/or a functional layer. |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PVB | Polyvinyl butyral |
PHR | Parts per hundred of resin - amount of plasticiser per 100 parts of PVB |
IG | Insulation glass |
FRP | Fibre-reinforced plastic |
PCB | Printed circuit board |
PWB | Printed wiring board |
In the case that a layered product comprises a layer of glass fibres without any layer of sheet glass, classification is done in B32B 5/02, the presence of glass fibres being classified by the indexing symbol B32B 2262/101.
B32B 17/00 requires that the layered product comprises at least one glass layer and at least one layer of another material; a layered product comprising both a glass layer and a glass fibre layer is classified in both B32B 17/02 (or B32B 17/04) and B32B 17/06.
This place covers:
Layered products comprising an inorganic glass layer in sheet or film form next to another layer of generic material.
The layers need not be permanently secured, such as a releasable protective layer.
Various materials are used in combination with sheets of glass for the enhancement of the properties of one of the layer, for instance, for protection or reinforcement of natural stone, for architectural purposes in general (E06B 3/54 or E04F 13/14), or for displays in a variety of devices.
B32B 17/06 is given in the case that an inorganic glass layer is present next to another glass layer with no further information.
This place covers:
Layered products comprising inorganic glass in sheet or film form next to a layer of a cellulose derivative or gelatin as polymeric substance.
This place covers:
Layered products comprising at least one inorganic glass layer in sheet or film form next to a layer of synthetic resin; the synthetic resin layer can be used as a glue layer to bond the glass layer with another glass layer or another material layer or can be used as a removable protective film.
In this group, a layer of organic glass is not considered as a glass layer but as a synthetic resin layer. The nature of the synthetic resin material is classified using the appropriate orthogonal symbols from groups B32B 2319/00 - B32B 2386/00 as a single symbol(s).
This place covers:
Layered products comprising at least one inorganic glass layer in sheet form next to a layer of synthetic resin; wherein the glass sheet is permanently bonded to at least one further glass layer in sheet form or a durable polymeric sheet or film via the layer of synthetic resin as a resin interlayer, and wherein the interlayer keeps the laminated safety glass or glazing bonded even when struck or broken, preventing the glass from shattering.
Laminated safety glass or glazing is used for automotive and transport applications (automotive windows in general B60J 1/00), for architectural purposes (E06B 3/54 or E04F 13/15), transparent armour (F41H 5/0407), head-up displays (G02B 27/01) and photovoltaic modules (H01L 31/048).
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Automotive windows | |
Railway windows | |
Aircraft windows | |
Antiballistic glazings | |
Head-up displays | |
Photovoltaic modules | |
Heating windshields |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Glass compositions | |
Coatings on glass | |
Joining pieces of glass to pieces of other inorganic material | |
Sky-lights | |
Coverings or linings of glass, e.g. for walls or ceilings | |
Layout of fixed or moving closures, e.g. windows | |
Insulating glass windows | |
Optical devices made from glass | |
Alarm windows | |
Transparent shielding materials against electric or magnetic fields |
Laminated safety glass comprising at least one layer of inorganic glass, a resin interlayer and an external layer of a synthetic polymeric sheet or film is classified using the appropriate group selected from B32B 17/10009 - B32B 17/1099 together with the B32B 2319/00 - B32B 2386/00 orthogonal Indexing symbol that designates the polymeric material of said external polymer layer as a single symbol.
The presence of resin interlayers, their properties and/or their compositions are further specified in groups B32B 17/1055 - B32B 17/10798.
The resin interlayer or all components of a composite interlayer are to be considered a layer proper for B32B and can be made by any process, including a coating process.
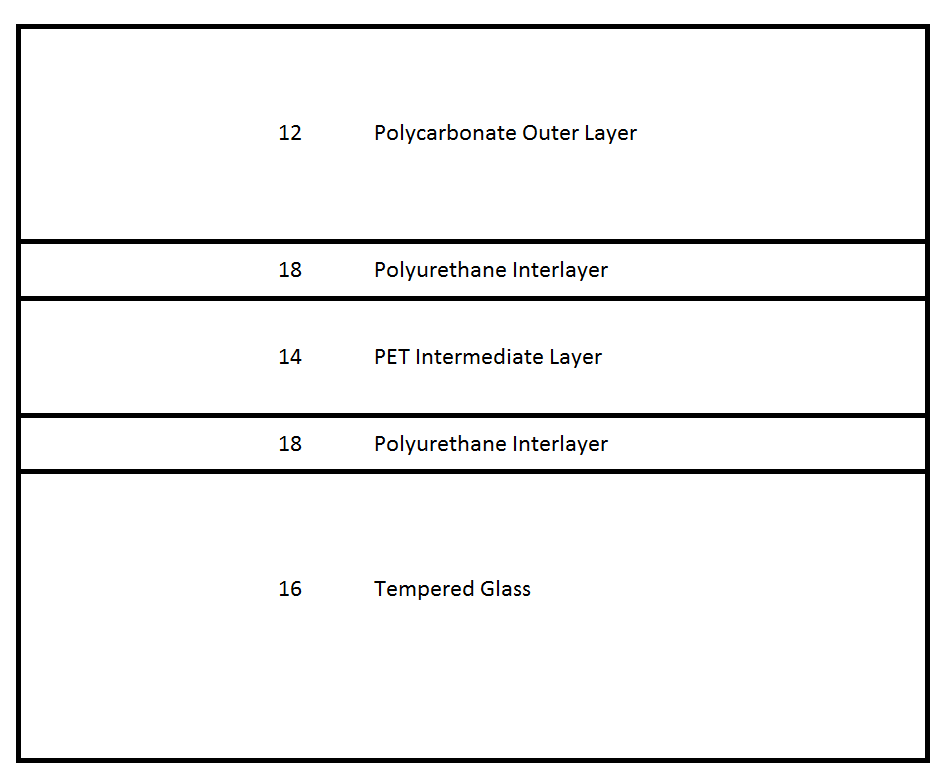
If relevant, an allocation in B32B 2250/02 - B32B 2250/05 may be applied to classify the total number of layers in the composite interlayer, i.e. the total number of interlayers, intermediate layers and functional layers. For example, the laminated glazing shown in the figure of the third C-set example would be proper for B32B 2250/03, which covers three layers, not B32B 2250/05, which covers five layers, because of the three layers of the composite interlayer.
A laminated safety glass or glazing to be used in a head-up display should be classified in B32B 2457/20 and not B32B 2551/00.
If relevant, particles that are present in the glass layers, the durable polymer sheet, the intermediate layers and/or the resin interlayers can be classified in B32B 2264/00-B32B 2264/504.
A laminated safety glass or glazing proper for B32B 17/10009 - B32B 17/1099 should not be separately classified in B32B 27/00 - B32B 27/42. Additional classification in B32B 27/00 - B32B 27/42 is only required when the laminated safety glass or glazing has (1) a further polymeric layer externally attached to the laminated safety glass or glazing; or (2) the composite interlayer is disclosed for separate use not in the form of a laminated safety glass or glazing.
If relevant, classification in B32B 37/00 - B32B 43/006 may be allocated in addition to B32B 17/10807 - B32B 17/1099 in order to capture invention information for the lamination process or apparatus that are not specifically provided for in the B32B 17/10807 - B32B 17/1099 subgroups.
If groups in B32B 37/00 - B32B 43/006 are to be allocated, the materials of the inorganic glass layer, interlayer or composite interlayer should not be separately classified as a single orthogonal indexing symbol. For example, the laminated glazing shown in the figure of the third C-set example should not have a single symbol allocated in B32B 2315/08, B32B 2367/00 or B32B 2375/00.
Classification is applied as Invention (I) information for the subgroups corresponding to the materials indicated in the examples and disclosed as Inventive. In the absence of examples, the pertinent more general main groups or subgroups are allocated.
When B32B 17/10005 is used as a base symbol in C-Sets, it is not allocated as a separate single symbol.
Combination sets (C-Sets):
C-Sets statement: #B32Ba
- In subgroup B32B 17/10005, the polymeric material of an intermediate layer sandwiched between interlayers of a laminated safety glass or glazing is classified in the form of C-Sets.
- In #B32Ba, the base symbol, representing the laminated safety glass structure comprising an interlayer adjacent the glass, is taken from subgroup B32B 17/10005, whereas the subsequent symbol representing the nature of the polymeric material of the intermediate layer sandwiched between interlayers is taken from the groups B32B 2319/00 - B32B 2386/00.
- When the polymeric intermediate layer comprises a mixture of polymeric materials taken from B32B 2319/00 - B32B 2386/00, separate C-Sets are given based on each polymeric material as the subsequent symbol.
- B32B 17/10005 is not allocated as a separate single symbol when it is allocated as a base symbol in a C-Set.
- In #B32Ba C-Sets are always allocated as Invention information (I).
C-Sets syntax rules:
- Each C-Set shall contain exactly two symbols.
- Duplicate symbols are not allowed in these C-Sets.
- The order of symbols in these C-Sets is relevant as it reflects the laminated safety glass structure as the base symbol, followed by the polymeric material forming the intermediate layer as the subsequent symbol.
C-Sets examples:
- #B32Ba: In a safety glass laminate (B32B 17/10005) comprising outer glass panes and a composite interlayer comprising a polycarbonate sheet, the polycarbonate (B32B 2369/00) sandwiched between two polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayers is classified as (B32B 17/10005, B32B 2369/00) and the PVB interlayers are classified as B32B 17/10761.
- #B32Ba: In a safety glass (B32B 17/10005) comprising a first outer layer of glass, a second outer layer of rigid polymer and a composite interlayer adhering the first outer layer to the second outer layer, wherein composite interlayer has the layer structure: polyurethane/polyacrylate/polyurethane, the polyacrylate (B32B 2333/08) is the intermediate film is classified as (B32B 17/10005, B32B 2333/08) and the polyurethane interlayers are classified as B32B 17/1077.
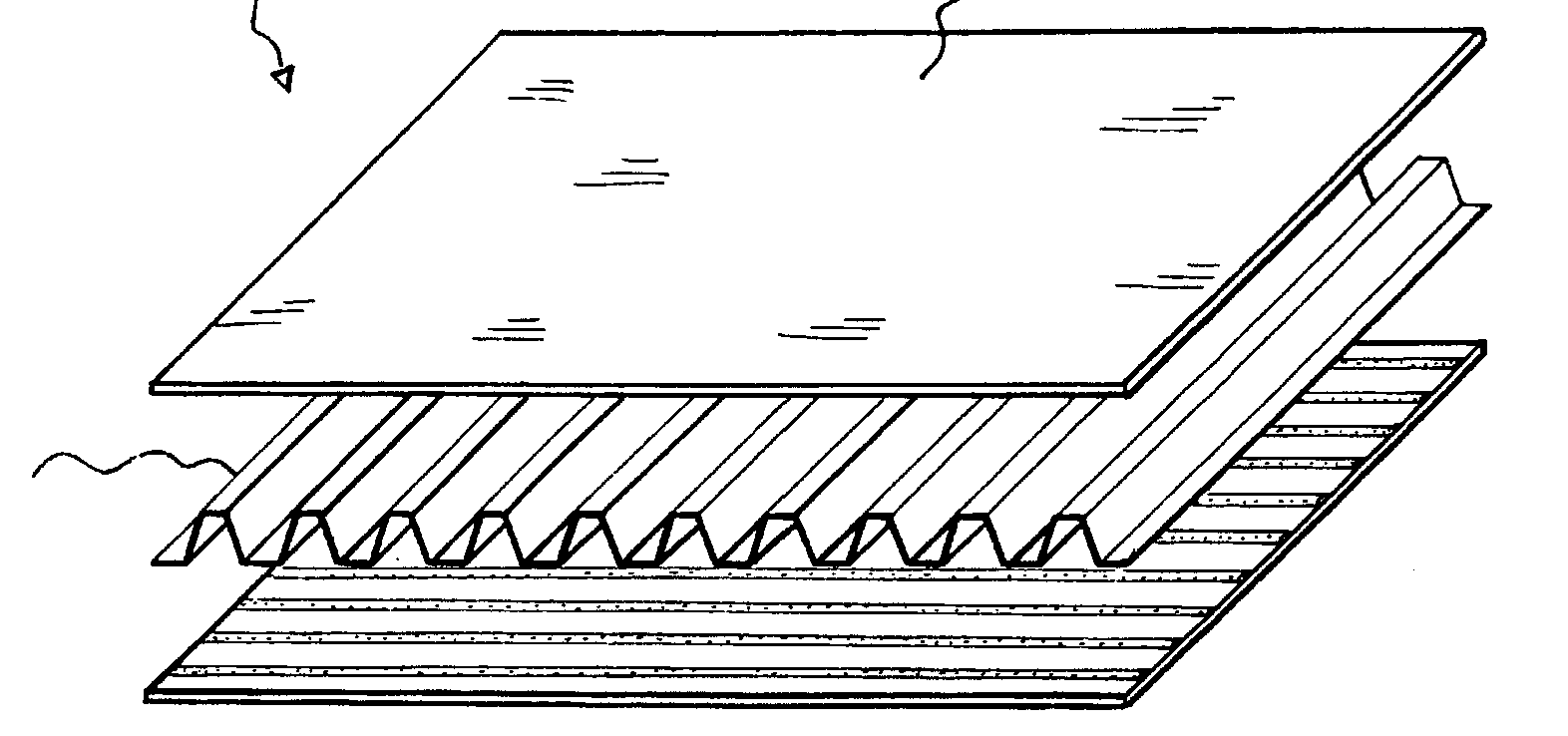
- #B32Ba: In a glass laminate (see figure below) there is a thermoplastic top layer 12 of polycarbonate (B32B 2369/00), a bottom layer 16 formed of tempered glass, and a composite interlayer comprising an intermediate layer 14 of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) (B32B 2367/00) and two polyurethane adhesive (interlayers) 18 positioned between the top 12 and bottom 16 layers, and wherein the glass laminate is a laminated safety glass or glazing (B32B 17/10005). In this laminated safety glass or glazing, the PET intermediate layer 14 is classified as (B32B 17/10005, B32B 2367/00), the polyurethane adhesive layers (interlayers) 18 are classified as B32B 17/1077, and the polycarbonate top (outer) layer 12 is classified as B32B 2369/00 as a single symbol.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Laminated safety glass or glazing, safety glazing, laminated glazing | Inorganic glass layer in sheet form bonded to another inorganic glass layer in sheet form or to a durable polymeric sheet or film via a resin interlayer, and wherein the interlayer keeps the laminated safety glass or glazing bonded even when struck or broken, preventing the glass from shattering. |
Interlayer | An internal layer of thermoplastic polymer bonding the components of a laminated safety glass or glazing to one another. |
Intermediate layer, intermediate film | An internal layer or film used as a barrier or as a carrier for functional layers and not having adhesive properties. |
Plasticiser | Organic compound which reduces the glass transition temperature of the interlayer, usually an interlayer of PVB. |
Composite interlayer | A composite laminate that binds the inorganic glass layer to another inorganic glass layer or the durable polymeric sheet or film of the laminated safety glass or glazing. The composite interlayer comprises at least one interlayer and may also comprise an intermediate layer and/or a functional layer. |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
PVB | Polyvinyl butyral |
phr | Parts per hundred of resin - amount of plasticizer per 100 parts of PVB |
IG | Insulation glass |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical filters | |
Polarising elements | |
Devices for the control of the intensity of light based on liquid crystals | |
Devices for the control of the intensity of light based on electrochromic elements | |
Devices for the control of the intensity of light based on electrophoresis | |
Devices for the control of the intensity of light based on suspension of oriented dipolar particles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical brightening agents | |
Luminescent agents |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Making multi-layered products between preformed layers in general | |
Spacing elements for window units comprising two or more parallel panes |
This place covers:
At least two pre-shaped green ceramic, ceramic pre-form (e.g. a ceramic fiber pre-form) or sintered ceramic layers are joined together, where the emphasis is not on the joining method. It also encompasses two layers of ceramic powders that are pressed together in a press. If after joining the two ceramic layers other type of layers, e.g. metallic or plastic layers are joined to the initial ceramic laminate, classification under other main groups of B32B will be necessary as well, but classification in B32B 18/00 remains. If in between the two ceramic layers there is a thin, non-essential layer of another material, e.g. a metallic electrode, it is still classified in B32B 18/00, but classification in other groups of B32B should be considered. B32B 18/00 is normally not used for laminates containing identical ceramic layers, such as in multilayer capacitors.
B32B 18/00 also contains cold bonding of ceramic substrates.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Laminates containing only one ceramic layer | |
layered structures comprising at least one glass sheet | |
Printing on laminates | |
semi-permeable membranes made of inorganic material | |
ceramic coatings on glass | |
Clay-wares | |
ceramic layers characterised by their composition | |
Joining a ceramic layer to another layer | |
porous ceramic products | |
Coatings of ceramics | |
Aspects relating to ceramic starting mixtures or sintered ceramic products | |
Aspects relating to ceramic laminates or to joining of ceramic articles with other articles by heating | |
sensor elements of laminated structure containing a solid electrolyte | |
Stacked fixed capacitors, e.g. multilayer ceramic capacitors |
Under C04B 37/00 the emphasis is on how the articles are joined. If two ceramic layers are joined, but the emphasis is not on how they are joined, classification would be in B32B 18/00.
Secondary aspects of making ceramic laminates (B32B 18/00) and of joining ceramic articles with other articles through heating (C04B 37/00) are classified with Indexing Code C04B 2237/00, e.g. the composition of the layers or articles that are laminated or joined.
Aspects regarding the heat treatments that are used for laminating are classified in C04B 35/64 and with Indexing Code C04B 2235/65, where the heat treatment of the laminating step should be considered as a sintering step. If for instance pressure is exerted during heating to laminate the articles, C04B 35/645 should be given. Aspects regarding the atmosphere of the heating step, possible annealing steps, heating rate, cooling rate, etc. are given Indexing Code C04B 2235/65.
If much detail regarding the composition and/or synthesis of one or more ceramic layers or articles is given, classification in C04B 35/00 should be considered.
Electrode and electrodes layers that are inserted between ceramic substrate layers are normally not seen as interlayers, since they normally do not have the function of joining the two ceramic substrates. They therefore do not receive a C04B 2237/12 Indexing Code. Only if it is clear that the electrode does have a joining effect, would it be regarded as an interlayer, and an Indexing Code under C04B 2237/12 would be allocated. In that case C04B 37/006 has to be used and there is no classification in B32B 18/00.
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by having a layer made of naturally occurring mineral fibres or particles.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products characterised by having a layer of rockwool fibres |
Product features classified in this group are also classified in B32B 5/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Products characterised by a plastic layer with natural mineral fibres or particles being present as additives |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
- Coating on a wood layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00.
- Impregnation of a wood layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2260/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Products characterised by having fibrous or filamentary layer made of a cellulosic plastic substance | |
Layered products characterised by having a particulate layer made of a cellulosic plastic substance |
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by a layer of thermosetting synthetic rubber.
- Layered products characterised by having a fibrous or filamentary layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2262/00 – B32B 2262/14.
- Layered products characterised by having a particulate layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2264/0207.
- Layered products characterised by having a foamed layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2266/0207.
This place does not cover:
Layered products characterised by having a fibrous or filamentary layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber | |
Layered products characterised by having a particulate layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber | |
Layered products characterised by having a foamed layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered product having a layer comprised of a thermoplastic elastomer | |
Manufacture of polymeric films or sheets | |
Compositions of macromolecular compounds |
- Layered products wherein all layers are polymeric are classified in B32B 2250/24.
- Coating on a layer of natural or synthetic rubber is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Thermosetting Rubber | Vulcanized rubber that cannot be re-melted or remolded without destroying its original characteristics. |
Vulcanization | An irreversible process during which a rubber compound through a change in its chemical structure (for example, cross-linking) becomes less plastic and more resistant to swelling by organic liquids and elastic properties are conferred, improved, or extended over a greater range of temperature. |
- Products characterised by a fibrous or filamentary layer embedded or impregnated in a natural or synthetic rubber are classified in B32B 5/02 and B32B 2260/048.
- Products characterised by a particulate layer embedded or impregnated in a natural or synthetic rubber are classified in B32B 5/16 and B32B 2260/048.
- The nature of the fibres or filaments present as additives is classified in B32B 2262/00.
- The nature of the particles present as additives is classified in B32B 2264/00.
This place covers:
Layered products characterised by a layer of a synthetic resin other than a cellulosic plastic resin or a thermosetting synthetic rubber.
- Layered products characterised by having a fibrous or filamentary layer made of synthetic resin are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2262/00 - B32B 2262/14.
- Layered products characterised by having a particulate layer made of a synthetic resin are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2264/00 - B32B 2264/12.
- Layered products characterised by having a foamed layer made of a synthetic resin are classified in B32B 5/00 and in B32B 2266/00 -B32B 2266/14.
This place does not cover:
Layered products characterised by having a fibrous or filamentary layer made of synthetic resin | |
Layered products characterised by having a particulate layer made of a synthetic resin | |
Layered products characterised by having a foamed layer made of a natural or synthetic rubber |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
- A layer of thermoplastic elastomer is classified in B32B 2274/00 and also at the appropriate place in B32B 27/00 if the nature of the polymer is also known or specified.
- Layered products wherein all layers are polymeric are classified in B32B 2250/24.
- Coating on a layer of synthetic resin is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
Layered products wherein all layers are made of polymers belonging to B32B 27/30 and B32B 27/32 are classified in B32B 2250/246.
This place does not cover:
Layer comprising a layer of synthetic resin comprising vinyl (co)polymers or acrylic (co)polymers |
- Layered products wherein all layers are made of polymers belonging to B32B 27/32 are classified in B32B 2250/242.
- Layered products wherein all layers are made of polymers belonging to B32B 27/30 and B32B 27/32 are classified in B32B 2250/246.
Layered products wherein all layers are made of polymers belonging to B32B 27/36 are classified in B32B 2250/244.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Impregnation or coating of paper; special paper |
- Layered products wherein all layers are made of paper or paperboard are classified in B32B 2250/26.
- Coating on a paper or paperboard layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2255/00.
- Impregnation of a paper or paperboard layer is classified with an appropriate Indexing symbol in B32B 2260/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surface unevennesses or non-uniformities |
Properties should as far as possible be classified in B32B 2307/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Making layered products containing glass and synthetic resin layers | |
Applying liquids or other fluent materials to surface, e.g. coating | |
Extrusion moulding, e.g. coextrusion | |
Lining or sheathing with preformed layers of plastic an object which cannot be seen as a layer | |
Joining or sealing of preformed plastic parts | |
Joining a relatively small portion of the surface of plastic articles | |
Making composites | |
Corrugating paper combined with laminating | |
Associating two or more webs |
Coextrusion steps are classified in B32B 37/153 or B32B 37/156 as long as the coextruded layers are joined with at least one additional layer.
Coating steps are classified in B32B 2037/243 as long as the coated layers are joined with at least one additional layer.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Applying liquids in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Labelling |
Particular aspects directed to removing the carrier layers are classified in B32B 38/10.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pressing means with cooperating endless bands in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Discrete sheets or panels | Dimension of sheets or panels is determined at the instant when sheets or panels come into contact. |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Continuous webs | Dimension of webs or layers is determined at the instant when webs or layers come into contact. |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Discrete and continuous layers | Dimension of layers is determined at the instant when layers come into contact. |
Operations implemented on layered products not in connection with the lamination process are classified in B32B 43/00 or in fields related to said operations.
This place does not cover:
Heat treatment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surface shaping |
Laminate treatment is additionally classified in groups B32B 2310/00 - B32B 2310/14.
This place does not cover:
Punching, slitting or perforating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Permeability to gases | |
Permeability to liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Punching, slitting or perforating without removing material | |
Delamination of layered products not in connection with the lamination process | |
Removing scrap from containers, e.g. removing labels | |
Removing applied preformed layers or sheets used as a coating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Printing |
This place covers:
The layout of stations in a manufacturing line.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional aspects of laminating apparatus |
This place covers:
- Arrangements for controlling or monitoring lamination parameters;
- Arrangements for detecting defaults and taking corrective measures;
- Arrangements for controlling quality.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Operations carried out during or in connection with lamination process |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Specially adapted for layered products | The layered structure of the product governs the operations or the apparatus structure. |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Removing layers or parts of layers carried out during or in connection with the lamination process | |
Removing scrap from containers, e.g. removing labels | |
Removing applied preformed layers or sheets used as a coating |
This place covers:
Inorganic particles in compositions which form a particulate layer or being present as additives.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Layered products comprising a layer of natural mineral particles |