CPC Definition - Subclass A61B
This place covers:
Apparatus, instruments, implements, or processes that are either specially adapted or intended to be solely utilized utilised for evaluating, examining, measuring, monitoring, studying, or testing particular characteristics and aspects of either living or dead human and animal bodies for medical purposes (i.e. diagnosis). Diagnosis consists of scrutinizing scrutinising the following characteristics or aspects of bodies:
- internal or external portions of the bodies (e.g. lungs),
- abnormal bodily conditions (e.g. sickness, broken bones, detecting foreign bodies, pregnancy),
- mental conditions (e.g. psychotechniques), and
- bodily functions (e.g. heart beat, vision).
Apparatus, instruments, implements, or processes that are either specially adapted or intended to be solely utilised for medical procedures employing physical actions (e.g. laser cutting, pressure of fluid) on portions of human or animal bodies to correct, enhance, or inspect (e.g. autopsies) them for medical purposes (i.e. surgery). Surgery consists of the following medical procedures:
- repositioning (e.g. aligning broken bones, opening wounds) parts of bodies,
- stabilising (e.g. inserting bone pins) to prevent harmful movement of parts of bodies,
- repairing (e.g. fastening skin together, removing cancerous tissue) bodies,
- facilitating the occurrence of naturally occurring bodily functions (e.g. child birth, passing kidney stones) that are out of the ordinary,
- introducing, collecting, or removing cells and organs (e.g. inseminations, tissue sampling, hair transplants, skin grafting, biopsies, organ harvesting) to or from bodies, and
- introducing or taking out foreign objects (e.g. replacement heart valves, bullets) to or from bodies.
Apparatus, instruments, implements, or processes that are either specially adapted or intended to be solely utilised in procedures for identifying individual human beings (e.g. finger printing, by recognition of shape or dimension of body part) using unique characteristics of their bodies (i.e. identification). Adjunct or supplementary means specially adapted for use in, or intended for exclusive use in, diagnosis, surgery, or identification. These adjunct or supplementary means contribute to the effectiveness (e.g. surgical drapes) or safety (e.g. operating gloves) of a medical procedure, but may or may not (e.g. protective covers for scalpels) themselves involve any direct contact with a body.
Components of diagnosis, surgery, or identification means with structural features limiting their usefulness to medical procedures.
The prosthesis assessment or monitoring may produce an input signal useful for the control of prosthetics found in A61F 2/482, A61F 2/70 or A61F 2/72.
Several subclasses provide for subject matter that is used for 'diagnosis'. The relationship between these subclasses with regard to the type of 'diagnosis' covered by each is as follows:
Subclass A61B provides for diagnosis in general. A61B also provides for any surgical or identification apparatus or methods when
- the apparatus or methods are combined with diagnosis means or
- the apparatus can be used for diagnosis and either surgery or identification.
A61B additionally provides for any diagnostic apparatus or methods combined with therapy apparatus or method normally covered by subclass A61H or A61N when
- the same apparatus or methods are used for both purposes or
- combined together but only useable separately.
Subclass A61H provides for diagnostic means or steps that are combined with massage and physical therapy apparatus or methods used for the treatment of disease or disability (i.e. an abnormal condition of the body) by utilisation of direct mechanical energy; when the diagnostic means or step is used solely for operational feedback purposes to enhance therapy.
Subclass A61N provides for diagnostic means or steps that are combined with medical treatment therapy apparatus or methods used for the treatment of disease or disability by utilisation of forms of energy other than direct mechanical energy; when the means or step is used solely for operational feedback purposes to enhance therapy.
This place does not cover:
Tools or instruments for operating on the mouth portion of a human being (e.g. tooth saws) | |
Saliva removers combined with instruments for opening or keeping open the mouth (e.g. mouth props, tongue guards, tongue depressors, cheek spreaders) | |
Medical instruments, implements, tools, or methods specially adapted so as to limit their usefulness to only animals | |
Methods or devices for treatment of eyes, putting in contact lenses, or correcting squinting | |
Eye surgery | |
Ear surgery | |
Physical therapy apparatus that includes diagnostic feedback means for influencing operation | |
Syringes and suction, pumping or atomising devices for medical use (e.g. cups, breast relievers, irrigators, sprays, powder insufflators, atomisers, inhalers), apparatus for general or local anesthetics, devices or methods for causing a change in the state of consciousness, catheters, dilators, and apparatus for introducing medicines into the body other than orally | |
Non-surgical treatment of medical conditions or physical injuries by utilisation of forms of energy not directly generated by mechanical apparatus, devices, or means that includes diagnostic feedback means for influencing its operation | |
Protective devices for clinical contact thermometers | |
Recognizing, identifying, or verifying the identity of human beings by analyzing their voice or speech |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric signals of the body or parts thereof | |
Arrangements of measuring, detecting or recording means, e.g. sensors, on external prosthesis | |
Arrangements of measuring, detecting or recording means, e.g. sensors, specially adapted to be brought in contact with an internal body part, i.e. invasive | |
Electrical control of prostheses not implantable in the body | |
Bioelectrical control of prostheses not implantable in the body, i.e. relying on physiological signals, such as myoelectric | |
Operating tables and auxiliary devices for these tables | |
Operating chairs | |
Apparatus for artificial respiration or heart stimulation | |
Containers specially adapted for medical or pharmaceutical purposes | |
Devices for administering medicines orally | |
Materials for surgical sutures or for ligaturing blood vessels | |
Surgical adhesives or cements and adhesives for colostomy devices | |
Materials for colostomy devices | |
Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes or microorganisms | |
Analysing samples of biological material |
This place does not cover:
Illuminating arrangements for the eyes | |
Examination of body cavities or body tracts using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves | |
Endoscopic instruments for taking cell samples or for biopsy | |
Endoscopic surgical instruments | |
Surgical instruments using a laser beam being directed along or through a flexible conduit |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical probes as there is no visual/image channel | |
Catheters, e.g. flexible tubes | |
Industrial endoscopes, e.g. borescopes; optical details thereof, e.g. particularly lens and optical fibre details |
A61B 1/00 - A61B 1/127 deal with technical features of endoscopes. From A61B 1/227 - A61B 1/32 endoscopes are classified according to the body cavity where they are intended to be used.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Rod-lens | A number of glass rods with specially shaped ends, that are used in rigid endoscopes instead of several thin glass lenses to improve image transmission properties and widen the field of view |
This place covers:
Operational signal transmission and data processing related with endoscopes if not provided in other, more specific technical fields.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Automatic control of imaging devices | |
Automatic control of illumination devices |
This place covers:
Operational image processing for display during use of the endoscope, e.g. on-chip or by the camera control unit.
This place covers:
Extracting and/or emphasizing biological structures by image processing e.g. blood vessels for assessing depth, thickness, shape or patterns.
This place covers:
Enhancement processing of live image output quality, e.g. denoising, artifact removal, deblurring, edge enhancement.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Image fusion, information overlay or enrichment | |
Image enhancement or restoration |
This place covers:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning, e.g. details of AI model and its implementation, the training process, or training data generation.
This place covers:
All types of signal transmission.
This place covers:
Wireless data transmission between probe within the body and external receiver.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoradiosondes |
This place covers:
Wire based data transmission by electrical signals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical cables as such |
This place covers:
Exchangeable memory like memory cards, e.g. for image recording or changing endoscope function.
This place covers:
Power source integral with the endoscope, e.g. batteries.
This place covers:
- Power saving features, e.g. in capsule endoscopes or displays
- Sleep/stand-by modes or varying sampling/transmission rates.
This place covers:
All types of user input/interface means.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Deflection control handles |
This place covers:
Data input means, e.g. keyboards, touch screens, GUIs or voice recording.
This place covers:
Control means, e.g. knobs, switches, joysticks, remote or voice control.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Deflection control handles | |
Handles for tip steering devices of catheters |
This place covers:
All types of output means, e.g. visual or acoustic.
This place covers:
Display construction, e.g. portable, head mounted displays, supports for displays.
This place covers:
Display of images obtained by endoscopes, combinations of images, combination of images and other data, e.g. graphs, ECG curves, pulse waveforms, alphanumeric data.
This place covers:
Small display screen at the proximal end of the endoscope shaft, e.g. mounted on the handle.
This place covers:
Alerting/indicating to user of an operative condition/fault, e.g. by voice synthesiser, indicator lights. Includes physiological parameter of patient during endoscopic examination.
This place covers:
All types of endoscope testing, e.g. optical performance, leak detection. Testing operation of endoscope, fault detection.
This place covers:
Endoscope provided with identification means, e.g. barcode, memory chip (ROM), coded resistor etc. May also include other data, e.g. operating data, manufacturer's serial number etc.
This place covers:
Limiting the number and/or duration of uses of an endoscope, e.g. by a counter/timer. Also limiting use to one patient by configuring endoscope to patient ID. Counting usage for payment.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Identification means |
This place covers:
Structural or operational features of the handle, e.g. control elements.
This place does not cover:
Control elements, e.g. on the handle for controlled bending of the shaft |
This place covers:
Construction of valve switches for controlling suction/water/air supply.
This place covers:
Details of endoscope shaft/sheath construction, e.g. layers.
This place does not cover:
Constructional details of flexible insertion parts, e.g. vertebral elements |
This place covers:
Groove(s) on external surface of endoscope to receive additional channel(s), e.g. for tools, suction, rinsing etc.
This place covers:
Details of endoscope shaft/sheath construction, including oversleeves, for stiffening.
This place covers:
Distal tip features not separately provided for below, e.g. distal tips with certain shapes, protective caps, strengthening means, vibrating elements, heating etc.
This place covers:
Distal fluid inflatable balloons, e.g. for retaining endoscope in a fixed position within a body cavity or for enlarging visual field etc.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Balloon catheters |
This place covers:
Distal expandable basket/cage structure, e.g. for retaining endoscope at a fixed position within the body cavity or for spacing the imaging lens from the tissue surface.
This place covers:
Distal tip tool as part of, mounted on or attached to the endoscope shaft or oversleeve, e.g. for displacing/cutting tissue.
This place does not cover:
Tools for introduction through a working channel |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Working channel for introduction of, e.g. surgical tools |
This place covers:
Distal hood, e.g. projecting beyond the lens/window plane, for restricting field of view.
This place covers:
Distal nozzles/baffles/fluid deflectors, e.g. for directing rinsing fluid on to the distal lens/window.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tool deflectors |
This place covers:
Distal suction openings for removing fluid/debris; openings may be in an endoscope oversleeve.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Suction openings for propulsion |
This place covers:
Distal optical features, e.g. window shapes, lens arrangements, mirrors, prisms or filters arranged in the distal tip of an insertion section.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For variation of viewing angle |
This place covers:
Additional non-imaging sensor(s) in the vicinity of the distal tip, e.g. force/pressure sensors for contact detection, distance/time-of-flight sensors for depth/distance detection of objects, temperature sensors for thermal control or patient safety; light/CO2 detection for endotracheal navigation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring for diagnostic purposes |
This place covers:
Distal deflector for a tool/instrument/optical fibre introduced through an endoscope channel.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tool/instrument channels |
This place covers:
Disposable endoscope or endoscope parts explicitly intended for single use only and usually not sterilizable.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prevention of overuse | |
Modular construction |
This place covers:
Modular construction of endoscope allows parts to be exchanged/replaced, e.g. different shafts used with the same handle. Also for disassembly of parts for easier cleaning. Multiple endoscopes interchangeably connected to a monitor unit.
This place covers:
Portable endoscopes not requiring a physical connection to further supply or monitor units, e.g. including integrated power supply, light source and video controller, suction and fluid supply, telemetry and/or display means.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wireless data transmission | |
Integrated data storages | |
Integrated power supply | |
Integral display units |
This place covers:
All types of steps/processes in manufacturing / assembling endoscopes or parts thereof.
This place covers:
All types of couplings are included here, e.g. optical, mechanical, electrical.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Medical aspects of connections | |
Details of coupling devices |
This place covers:
Details of electrical cables. Includes cable construction and cable arrangements.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical conductors and cables in general |
This place covers:
Details of optical cables, e.g. light supply cables for connection to an external light source.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connectors as such |
This place covers:
Also universal cables for combined water/air/suction supply.
This place covers:
Details of any type of electrical connector used with endoscopes, includes connectors at the distal end of a cable projecting from the operation portion and connectors mounted on the operation portion.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical couplings in general |
This place covers:
Details of any type of mechanical connector used with endoscopes, includes connectors or adaptors at the proximal end of the working channel.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Forceps plugs for sealing or closing of working channels | |
Surgical tool connectors |
This place covers:
Drive unit for attachment to an endoscope for driving/introducing a tool/instrument. May be manual or motor driven.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Holding or positioning of the endoscope | |
Guiding of flexible endoscopes as such | |
Operating/actuating an endoscopic tool | |
Introducing catheters | |
Introducing guidewires |
This place covers:
Separate oversleeve tube and optical assembly. The optical assembly is inserted into the oversleeve prior to use in a body cavity. The oversleeve may have features like additional working channels for instruments, rinsing or suction channels, illumination channels or further distal tools.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sanitary sheaths for hygiene mainly | |
Guide tubes to aid endoscope insertion | |
Guiding flexible endoscopes |
In patent documents, the word/expression in the first column is often used instead of the word/expression in the second column, which is used in the classification scheme of this place:
"sheath" | "oversleeve" |
This place covers:
For closing or sealing openings at both ends of an endoscope, e.g. forceps plugs for the proximal end of a working channel.
This place covers:
Any type of fastening element to attach an accessory/tool/channel to the outside of the endoscope shaft, e.g. clip, clamp, loop, band.
This place covers:
Prevention of contamination with bodily fluids of a patient, e.g. by a hygienic sheath covering the insertion tube of an endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Oversleeves or sheaths not mainly for hygiene, but comprising additional technical features like working channels | |
Drapes for protection of surgical instruments |
This place covers:
Packages for keeping endoscope sterile before use/in storage.
This place covers:
Means for holding and/or changing the position (advancing, rotating, pivoting etc.) of an endoscope with respect to the patient/cavity.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locating endoscope position inside of the body | |
Tracking endoscopes with NMR |
This place covers:
Propelling, advancing or securing of an endoscope in direct physical contact with tissue or anatomical structures of a patient, e.g. by balloons or tissue anchors provided on/with the endoscope.
This place covers:
Articulated arms for holding and positioning an endoscope.
This place covers:
Propelling/advancing endoscope by everted tube means, e.g. by turning the tube inside out.
This place covers:
Guiding arrangements positioned at the opening of a body cavity to aid insertion of the endoscope along the guiding arrangement and into the cavity, e.g. guide tubes or wires not fixed or attached to the endoscope shaft.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Oversleeve to cover an endoscope prior to insertion | |
Access ports for surgical instruments |
This place covers:
Probe operating inside the body without physical contact with the external environment.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capsule endoscopes |
This place covers:
The probe, e.g. a capsule endoscope, is guided by a magnetic field controlled by the operator. Also for controlled bending of endoscope insertion tube by magnetic forces.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determining endoscope position using magnetic field | |
Manipulators for magnetic surgery |
This place covers:
Drive unit, e.g. proximal motor, for insertion of an endoscope into the body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Drive unit for introduction of an endoscopic tool into the endoscope | |
Pumps for everted tubes | |
Guiding arrangements for flexible endoscopes in general | |
Introducing catheters | |
Introducing guidewires |
This place covers:
Details of optical arrangements for transmitting image within the endoscope not covered by any lower ranking class. Includes jointed image paths using mirrors/prisms.
This place does not cover:
Rod-lens arrangements | |
Illuminating arrangements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distal optical elements |
This place covers:
Guiding light from distal to proximal end of the endoscope, not limited to imaging.
This place does not cover:
Guiding in particular illumination light from proximal to distal end of the endoscope |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Light guides per se | |
Light guides for industrial endoscopes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical fibre arrangements for illumination |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical fibres for illumination |
This place covers:
2D/3D scanning of illumination and/or imaging light beams.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distal mechanical or optical elements | |
Optical coherence tomography | |
Confocal scanning | |
Optical scanning systems in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distal optical features in general | |
Detachable distal elements |
This place covers:
Optical element at distal end of endoscope allows side-viewing.
This place covers:
Optical element at distal end of endoscope sets the field-of-view at an angle to the longitudinal axis of the endoscope i.e. between 0-90 degrees, in forward or rearward direction.
This place covers:
Optical elements allow multiple different fixed views, e.g. combining either alternative or simultaneous 0 degree frontal and 90 degrees side-viewing.
This place does not cover:
Stereoscopic viewing |
This place covers:
Optical element at distal end of endoscope allows variable field of view, e.g. by rotation or deflection of a distal optical element.
This place covers:
Filters in the optical imaging path of an endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters in the optical illumination path of an endoscope |
This place covers:
Optical and/or mechanical arrangements for adjusting the focal point or magnification of an endoscope, e.g. for auto-focus or endo-microscopy.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Confocal scanning |
This place covers:
Lens with variable refractive properties, e.g. fluid filled lens, Alvarez lens.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Variable lenses as such |
This place covers:
Stereoscopic or three dimensional imaging, e.g. by combining images from two laterally spaced cameras.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stereoscopic vision for industrial endoscopes |
This place covers:
Image acquisition and related image processing for three-dimensional imaging (3D), e.g. based on passive or active triangulation.
This place covers:
Features of the eyepiece, e.g. lens arrangement, attachment to endoscope shaft/camera etc. Includes binocular eyepieces.
This place covers:
Multiple eyepieces allowing more than one observer to view the image.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Binocular eyepieces |
This place does not cover:
Rod-lens arrangements in combination with a camera |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "Rod lens" and "Hopkins optics"
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catheters without visualisation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tip steering of catheters | |
Articulated or flexible manipulators | |
Crawling robots for pipe lines |
This place covers:
Operating elements for active control of bending, e.g. mechanical levers, dials or pulleys, but also electrical switches usually mounted on the handle.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscope handles in general | |
Force transmission elements, e.g. control wires | |
Controlled bending of the insertion part using shape memory elements | |
Handles for tip steering devices of catheters |
This place covers:
Backbone elements repetitively aligned and movably connected to each other to provide stability and flexibility to the insertion tube.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Articulations |
This place covers:
Operating elements for transmission of forces for the purpose of e.g. bending, flexing, twisting, pivoting or rotation of a flexible portion of the insertion tube.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control elements, e.g. on the handle | |
Articulations |
This place covers:
Means for interconnecting (rigid) backbone elements of the shaft to provide flexibility, e.g. hinges, joints or pivots.
This place covers:
Determining the bending state, curvature or shape of the insertion part by features inherent to the endoscope, not for locating or tracking the endoscope with respect to the body.
This place covers:
Guiding means, which are independent from the flexible endoscope and its integrated tip steering mechanisms, e.g. guide wires or insertion aids.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guide tubes | |
Guiding arrangements for catheters |
This place covers:
Combination of at least 2 endoscopes, where one endoscope is introduced into the body cavity, e.g. by passing it through a channel of another endoscope.
This place covers:
Controlling fluid supply or evacuation to or from cavities of the human body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fluid supply or evacuation to distal balloons | |
Fluid supply or evacuation for cleaning purposes post-use | |
Fluid supply or evacuation for cleaning purposes in-use |
This place covers:
All kind of working channels for insertion of medical instruments thought the endoscope shaft, e.g. for minimally invasive surgery.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Camera adapters | |
Television cameras |
This place covers:
Small mostly capsule type cameras, usually but not necessarily swallowed for minimally invasive visual documentation e.g. of the gastroenterologic tract or blood vessels. Often in combination with miniaturized on-board diagnostic or therapeutic tools.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wireless transmission of control or image signals | |
Internal power supply, e.g. by batteries | |
Capsule type diagnostic sensors without visualization |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "Capsule endoscope" and "Pill camera"
This place covers:
Endoscopic cameras integrated into or detachably fixed to the proximal end of an endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cameras in the distal end portion of an endoscope | |
Image processing e.g. | |
Details of the TV cameras |
This place covers:
Visual imaging of tissue fluorescence induced e.g. by exogenously administered fluorophores or endogenous autofluorescence.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters in the imaging path | |
Monochromatic illumination | |
Polychromatic illumination | |
Filters in the illumination path | |
Detection of tissue fluorescence not resulting in an image |
This place covers:
Visual imaging of tissue absorbance with or without contrast agents, e.g. using infrared light.
This place covers:
Infrared (IR) or near infrared (NIR) imaging indent from the used light source.
This place covers:
Details of mounting the CCD chip in the distal tip of the endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Illumination arrangements for industrial endoscopes |
This place covers:
Illumination arrangements with spatially modulated light patterns, e.g. LCDs or spatially arranged illumination fibers.
This place covers:
Illumination arrangements where light exits the endoscope forwardly in multiple points or circularly, including illumination sources for the oral cavity not incorporated in the endoscope shaft.
This place covers:
Illumination arrangements where light exits the endoscope radially (perpendicularly to the longitudinal axis). Single or multiple illumination ports.
This place covers:
Illumination of cavity at an angle to the longitudinal axis of the endoscope other than at 90 degrees.
This place covers:
Optical elements allow multiple different fixed illumination angles, e.g. combining either alternative or simultaneous 0 degrees frontal and 90 degrees side illumination.
This place covers:
Optical element at distal end of endoscope allows variable illumination angles, e.g. by rotation or deflection of a distal optical element.
This place covers:
- Lasers or laser diodes
- Quasi-monochromatic light sources like narrow-band filtered lamps or LEDs.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Illumination filters |
This place covers:
Illumination with multiple spectral bands, e.g. for fluorescence endoscopy.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fluorescence spectroscopy without visual imaging |
This place covers:
Optical filters provided in the illumination path of the endoscope, e.g. for fluorescence endoscopy.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Filters in the optical imaging path of an endoscope |
This place covers:
Endoscope comprising one or several light source(s), e.g. semiconductor light source or LEDs, that illuminate(s) a fluorescent material, e.g. phosphor, to emit light at a different wavelength than the exciting light.
This place covers:
Automatic control of illumination-related settings such as intensity, spectral, geometric or pulse properties e.g. of the light source, apertures or other optical elements in the illumination path and based e.g. on measured parameters or image processing.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lightning devices in general |
This place covers:
External or internal light sources coupled to or positioned at the proximal end of an endoscope for illumination.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cables to couple a light source to an endoscope | |
Connectors to couple a light source to an endoscope |
This place covers:
Headlamps, e.g. used for dental or ENT applications.
This place covers:
Guiding illumination light from proximal to distal end of the endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guiding light from distal to proximal end of the endoscope, not limited to imaging | |
Details of optical fibre bundles | |
Details of single optical fibre structure | |
Light guides per se | |
Light guides for illumination in industrial endoscopes |
This place covers:
Fluid supply or evacuation for functional purposes of the endoscope.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Fluid supply or evacuation to or from cavities of the human body |
This place covers:
Cleaning, e.g. physically, of endoscopes and/or parts thereof after use.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cleaning of endoscopes in-use | |
Cleaning of surgical instruments | |
Cleaning of dental instruments | |
Disinfection or sterilisation | |
Cleaning of hollow articles in general |
This place covers:
Tools for cleaning endoscopes after use, e.g. cleaning swabs or brushes inserted into endoscope channel.
This place covers:
Washing machines specially adapted for cleaning endoscopes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Disinfection or sterilisation |
This place covers:
Fluid circulation in the endoscope during endoscope cleaning cycle.
This place covers:
Active cleaning of endoscope parts during use, e.g. of distal windows to maintain vision.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Distal nozzles | |
Cleaning of endoscopes post-use |
This place covers:
Prevention of fogging, e.g. by dedicated covers or coatings.
This place does not cover:
Active cleaning of endoscopes in-use | |
Means for preventing fogging of dentists mirrors |
This place covers:
Monitoring/controlling/regulation of temperature in an endoscope (shaft or handle) and related units like proximal light sources.
This place does not cover:
Light based diagnosis of oral or dental tissue |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tongue depressors per se | |
Combined with saliva removers | |
Mouth openers for animals |
This place covers:
Devices for enlarging natural openings of the human body for visual inspection, e.g. specula or the like.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tractors for holding wounds open | |
Surgical trocars for introduction into natural body openings | |
Dilators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
A61B 3/02 - A61B 3/09 for subjective testing i.e. with patient feedback and A61B 3/10 - A61B 3/158 for objective testing i.e. without patient feedback
The breakdown symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" or non "mirror" symbols) and "orthogonal" symbols are to be used for classifying the invention information (in addition to the invention symbols) in case the invention is insufficiently classified by an invention information symbol. They are also to be used for classifying the additional information. They are stored in the additional information field.
This place covers:
Illuminating means for examining the eyes (not related to a specific measuring instrument)
This place does not cover:
Illumination for examining the anterior chamber or the anterior chamber angle | |
Illumination for objective testing apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Goniolenses used for laser treatment | |
Illuminating means for optical instruments |
This place covers:
Use of any type of eye model, e.g. to aid in measurement of visual function or checking correct prescription of corrective lens.
Determination of parameters of contact lenses or of intraocular lenses on the basis of ophthalmic measurements
Correlation of eye images taken at different times
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Planning of eye laser surgery | |
Computer processing of eye images | |
Medical models |
This place covers:
All types of user input/interface means, e.g. particular keyboard/switch layouts, control desks/panels, voice-controlled, light pen, touch screen, joysticks, cursors etc.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjusting devices, e.g. operated by control lever |
This place covers:
Display construction, e.g. portable, supports for displays.
This place covers:
Display of images obtained by all types of apparatus in A61B 3/00, combinations of images, e.g. side-by-side, superimposed, tiled etc., combination of images and/or other data, e.g. graphs, waveforms, alphanumeric data, questionnaires, patient reports etc.
This place covers:
Identification of apparatus or component parts of the apparatus by any means, e.g. RFID, bar code, coded resistors, EPROM etc.
This place covers:
Control levers for ophthalmic apparatus
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Manipulators as such |
This place covers:
Means for positioning of a patient with respect to apparatus, e.g. head-rests, chin-rests, seats etc. Adjustable positioning, e.g. sliding elements or motor driven structures.
This place covers:
Details or arrangements of fixation targets or lights.
The fixation light 16 includes a plurality of LEDs arranged in a lattice shape. By lighting one LED, the fixation light 16 can guide a sight line of the subject's eye E to a direction of the LED lighting.
Also to relax the accommodation power
This place covers:
Examination or measurement of the contrast sensitivity of the eye.
This place covers:
Determining the field of vision
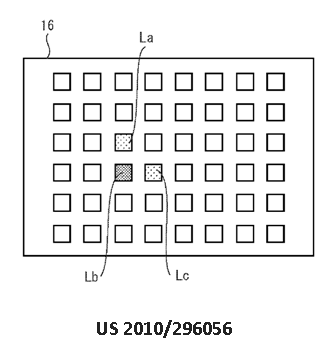
This place does not cover:
For testing astigmatism |
This place covers:
Measurements on the eye without the patient's feedback.
Besides the below-listed fields, the following is included:
- detect the features (e.g., position, fitting) of a contact lens or an intraocular lens
- examining the eyelid
- evaluate a contrast agent on the eye surface
- fluorescence examination
- scanning laser ophthalmoscope
- examination of light scattering
This place does not cover:
For measuring interpupillary distance or diameter of pupils |
This place covers:
Measurement of any quantity related to tear secretion or tear film production, e.g. volume, flow, or film thickness.
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used with the meaning indicated:
Examining | Measuring. |
This place covers:
Measuring optical aberrations of the eye or corneal topography with wavefront sensor.
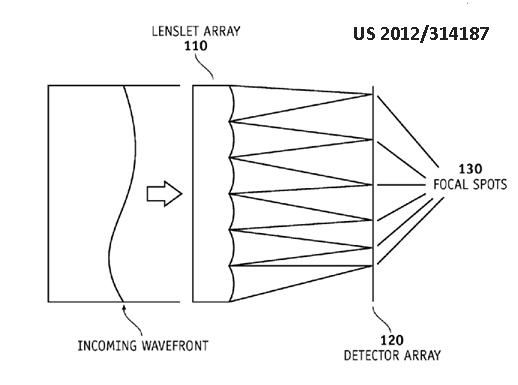
wavefront sensor, Hartmann sensor, shack sensor, lenslet array, microlens array
This place covers:
By optical coherence tomography, also in combination and sharing optical components with scanning laser ophthalmoscopy.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical coherence tomography of body tissue in general | |
Optical coherence tomography as such |
In patent documents, the following words/expressions are often used as synonyms:
- "optical coherence tomography", "OCT", "OCDR", "optical coherence domain relectometry", "optical coherence imaging", "low coherence interferometry" and "partial coherence tomography"
This place covers:
Scanning the eye wherein a detector receives only the reflected light focussed on a single point in the eye tissue, e.g. cornea or retina.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Confocal scanning of body tissue in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wavefront analyzer | |
Intraocular lenses | |
Eye surgery | A61F9/01 |
Lenses | |
Contact lenses | |
Spectacles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Computation of astigmatism based on input values | |
Testing astigmatism |
This field mostly relates to processing of ophthalmic data in order to estimate astigmatism.
This place covers:
Measurement of corneal topography.
E.g. by projecting a light pattern (moiré, placido rings) on the cornea
Examination of limbus
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wavefront analyzer | |
Examination of anterior and posterior chambers | |
Eye surgery | A61F9/01 |
Measuring curvature by projecting a pattern |
This place covers:
Measurement of interpupillary distance in the context of diagnostic procedures.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring geometric parameters required to locate ophthalmic lenses in spectacles frames |
This place covers:
Eye tracking mainly for diagnostic purposes.
Example: Using imagine processing.
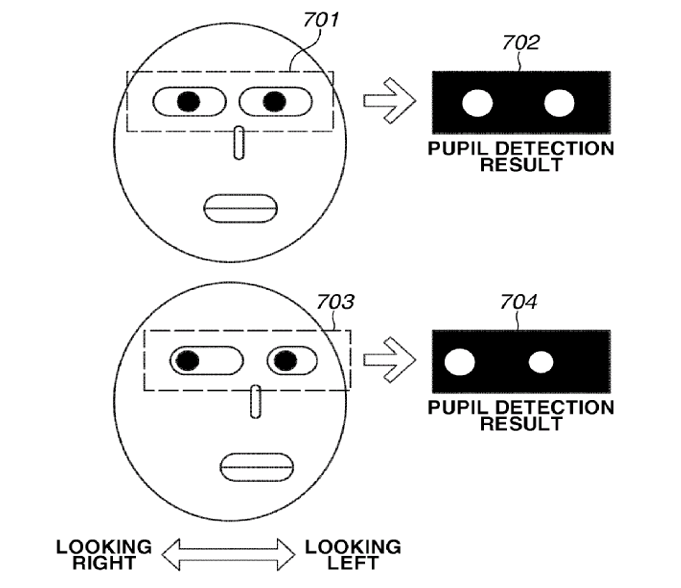
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrooculography [EOG], e.g. detecting nystagmus | |
Tracking eye movements during eye surgery | |
Means for monitoring data relating to the user, e.g. head-tracking, eye-tracking | |
Man-machine interfaces | |
For photography |
This place covers:
Examination of the anterior chamber: Space between the cornea and the iris
Examination of the posterior chamber: Iris, ciliary body, lens
This place does not cover:
Examination of the cornea |
This place covers:
Any type of apparatus for determining, measuring or examining the opacity of the lens, e.g. due to cataract.
This place does not cover:
Ophthalmic microscopes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Documentation by photo or video means |
This place covers:
Lens adapted to be placed on the cornea for direct observation of the retina
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Contact lenses per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Operation microscopes | |
Surgical microscopes |
This place covers:
Means for focussing an eye image detector:
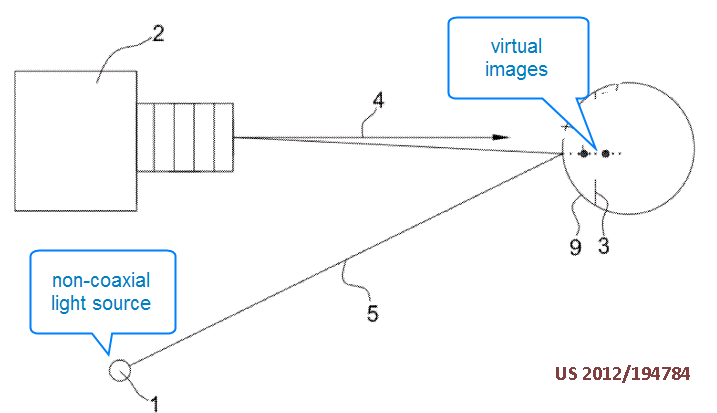
Also:
- Adaptive optics
- Camera adapters
- Focussing features
- Eye spectrometry
- Evaluation of eye-detector distance
This place covers:
Means for stopping, e.g. polarised light reflected from the cornea to enhance detection of light reflected from the retina, e.g. in eye fundus examinations.
This place covers:
Detect intraocular pressure.
E.g., using a deformable element in contact with the cornea
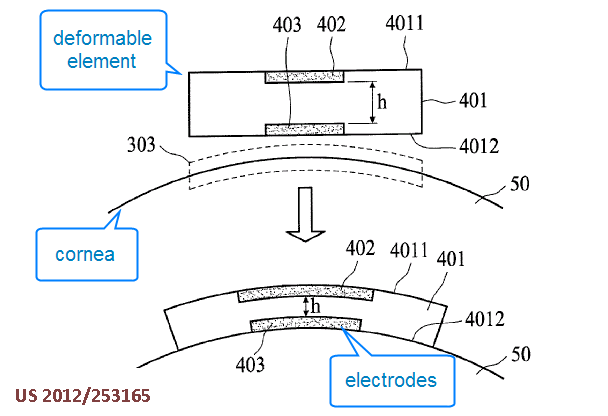
Also:
- using deformable item on the eye surface
- causing eye deformation using ultrasound waves
- using implanted sensor
This place covers:
Detect intraocular pressure by deforming the eye surface with a gas jet a measuring the deformation of the eye surface
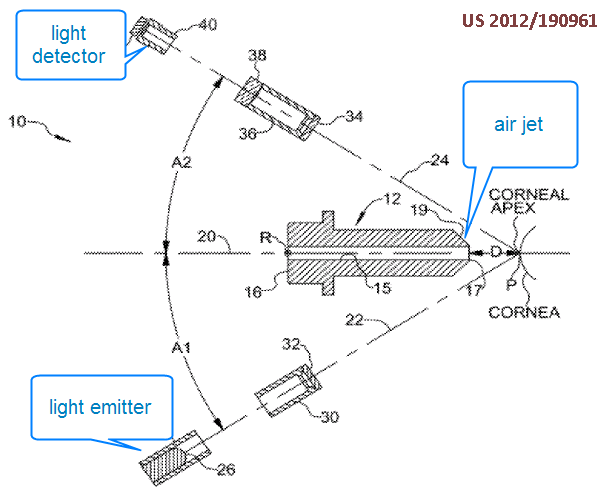
This place covers:
Combinations of eye-testing apparatus in a single workstation, e.g. at a test station.
This place covers:
Apparatus may be modified for different applications by exchanging component parts.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Attachment of cameras or photography equipment |
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring or recording in general |
The breakdown symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" or non "mirror" symbols) and "orthogonal" symbols are to be used for classifying the invention information (in addition to the invention symbols) in case the invention is insufficiently classified by an invention information symbol. They are also to be used for classifying the additional information. They are stored in the additional information field.
This place does not cover:
Endoradiosondes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission by light |
Documents in this subgroup should be also be classified according to type of imaging apparatus in other subgroups of A61B 5/00.
This place covers:
Imaging apparatus, for example employing electron or nuclear magnetic resonance, including surgical and therapeutic techniques to facilitate healing.
Implantable medical device may include pacemakers. Ablating includes cutting, eroding, melting, evaporating, or vaporizing. Ventilating includes oxygenating, aerating.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis combined with treatment in closed-loop systems or methods | |
Monitoring or testing the effects of treatment, e.g. of medication | |
for verifying the position of the patient with respect to the therapeutic radiation beam |
This place covers:
Testing or evaluating the body or part of the body by applying mechanical forces or stimuli and measuring the response of the body or tissue to the mechanical force or stimulus.
This place does not cover:
Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels | |
Stress testing | |
Examination by percussion |
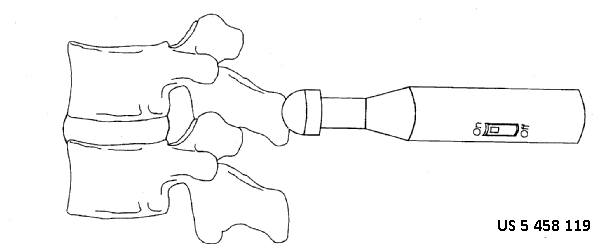
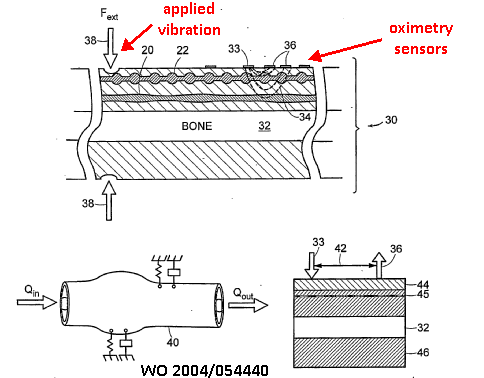
This place covers:
1) Vibration stimulator, e.g. for detecting pain threshold
2) Apply stimulation while carrying out measurements, e.g. oximetry:
This place does not cover:
Applying ultrasound vibrations |
This place covers:
Applying compression during a measurement:
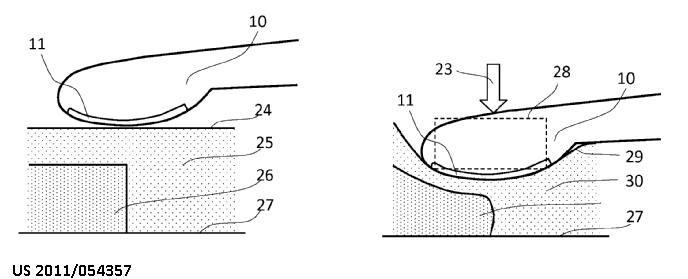
Holding skin for skin gauges, palpation, indentation
This place covers:
Applying suction or vacuum at the measurement area during the measurement, e.g. to increase blood pressure:
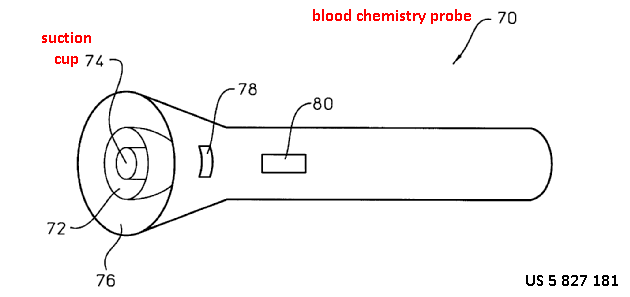
This place does not cover:
Apply suction to enhance body fluid extraction | |
Apply suction to attach sensor to the body surface |
This place covers:
Applying torque, friction etc. to a body part during the measurement of an effect of this force
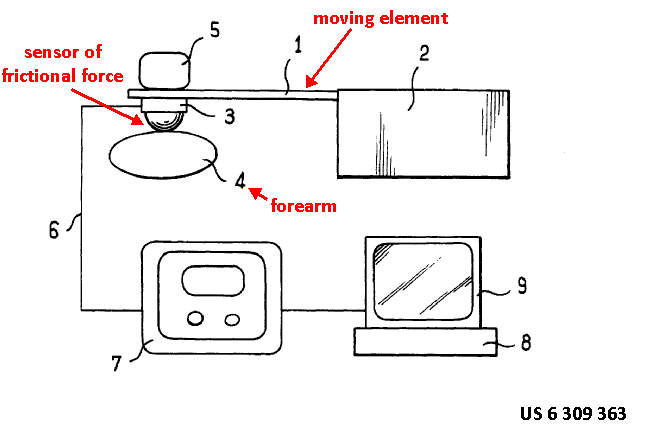
This place covers:
Testing or evaluating the body, parts of the body or body tissues by applying light and measuring the change in light characteristics caused by the interaction of the light with the body or tissue.
This place does not cover:
Optoacoustic or acoustooptic imaging | |
Optical probes for detecting heart rate | |
Optical probes for blood flow measurement | |
Optical probes for detecting blood characteristics |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus | |
Medical imaging apparatus involving image processing or analysis | |
Spectrometry | |
Optical measurment in general |
This place covers:
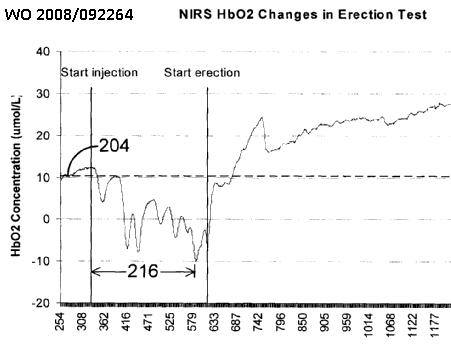
Diagnosis using scanned light, e.g.:
Laser speckle imaging
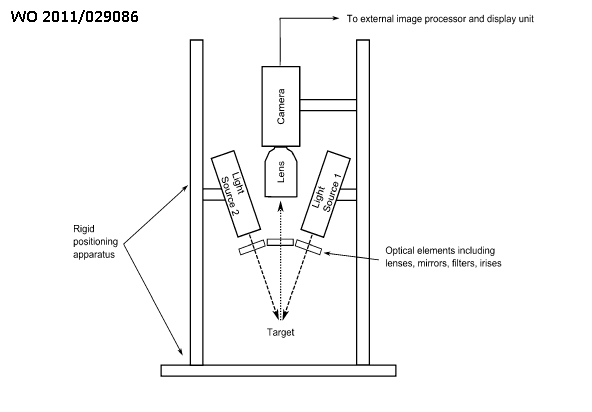
This place covers:
Apparatus for optical scanning of the external body surface:
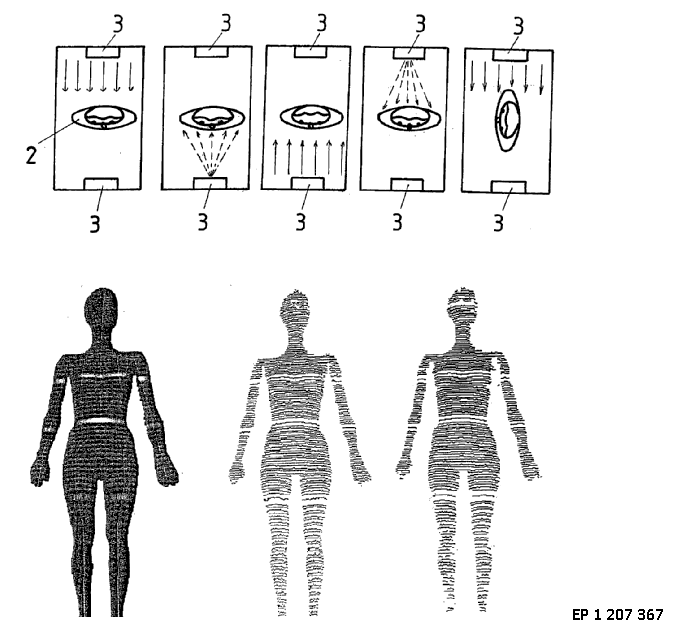
This place covers:
Detection using coherent light emission
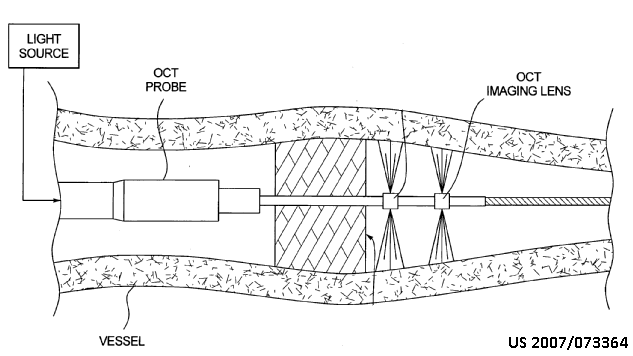
This place does not cover:
OCT for eye diagnosis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
OCT in general |
This place covers:
The use of confocal scanning techniques, e.g. confocal laser scanning microscopy in order to obtain images at selected depths of body tissue.
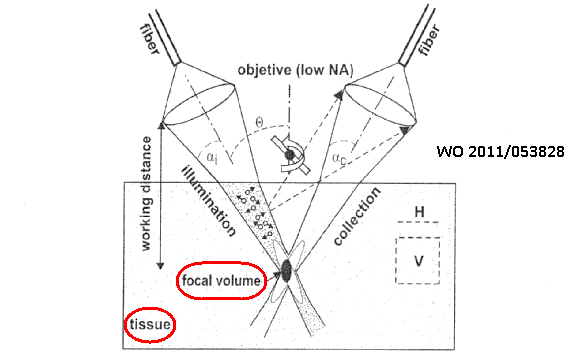
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Confocal scanning surgical probes |
This place covers:
Detecting fluorescence emission as a result of irradiating excitation light
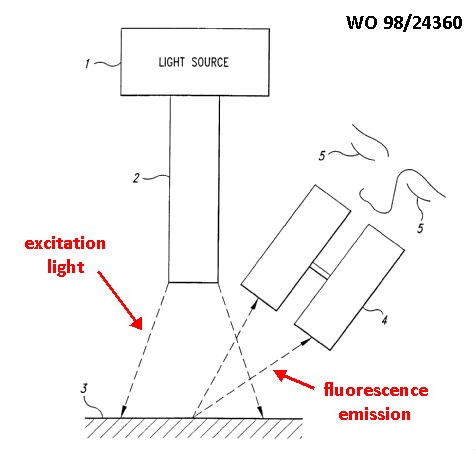
This place covers:
Reconstructing volumes using light irradiated into the body and scattered outside the body
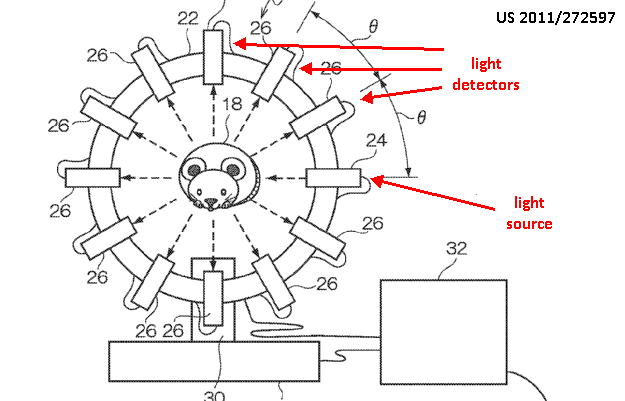
This place does not cover:
Optical coherence tomography |
This place covers:
Evaluating spectral properties of body parts
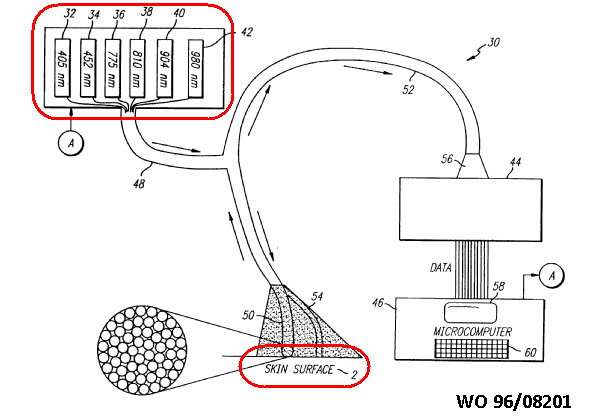
This place does not cover:
Measuring fluorescence emission |
This place covers:
Apparatus for viewing and taking images of the surface of the body. Documents may include diagnostic evaluation of images, e.g. evaluation of images taken with a camera at different times
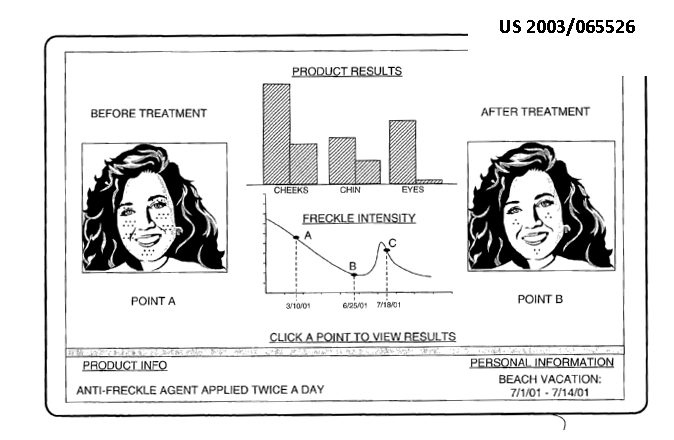
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for image acquisition of a particular organ of body part |
This place covers:
Devices using light adapted for a particular medical procedure, e.g. dentistry, mammography, insertion into the body
This place covers:
Inspecting the composition of body tissues using light probes introduced into the body
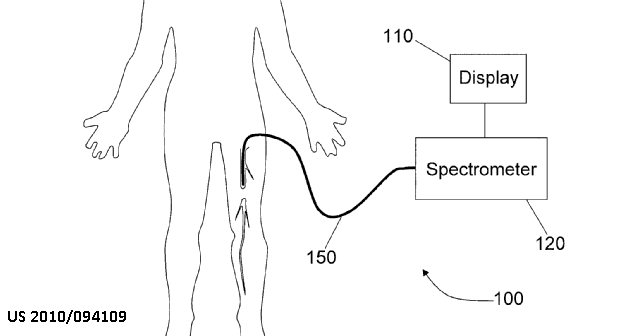
This place does not cover:
Invasive probes for taking images (i.e. endoscopes) | |
Invasive optical sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Probes mounted on invasive devices |
This place covers:
Detecting properties of all types of oral or dental tissue, e.g. teeth, gums, tongue
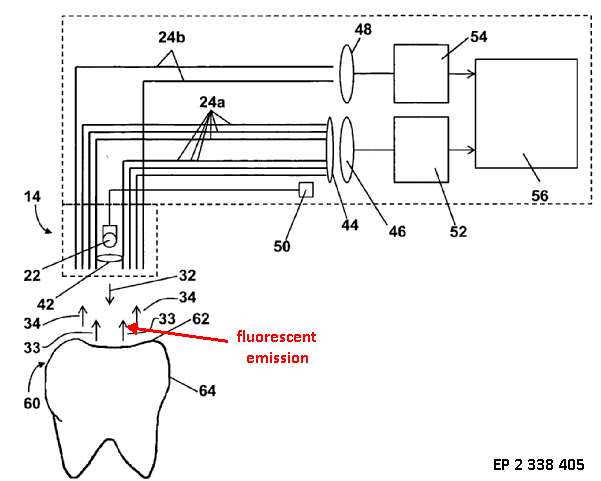
This place does not cover:
Imaging the oral region |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments specially adapted for dentistry |
This place covers:
Detection of breast cancer or other properties using light
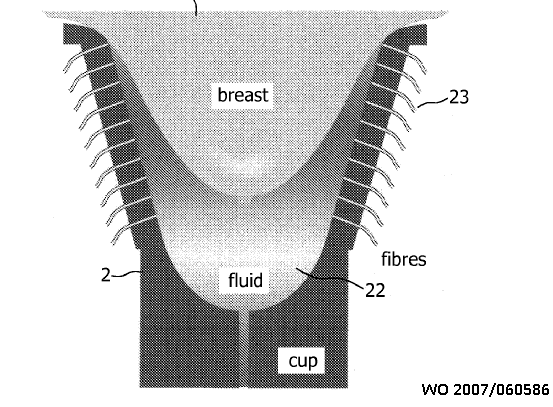
This place does not cover:
X-ray mammography | |
Ultrasound mammography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Breast evaluation in general | |
Biopsy instruments for the breast |
This place covers:
E.g., magnetoacoustic examination: apply magnetic energy, detect resulting acoustic radiation
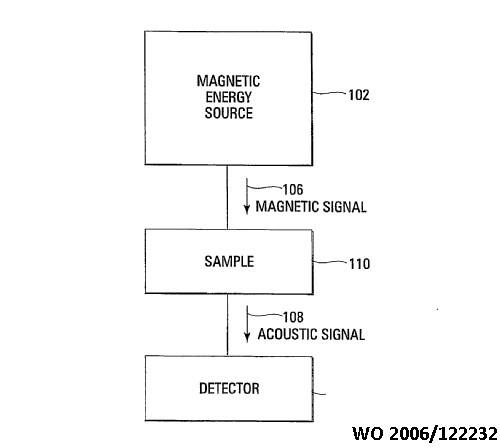
This place covers:
Apply light, detect resulting acoustic emission
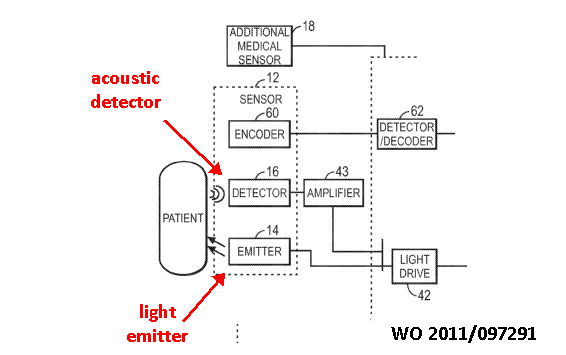
This place covers:
Apply acoustic (e.g. ultrasonic) energy, detect resulting light emission
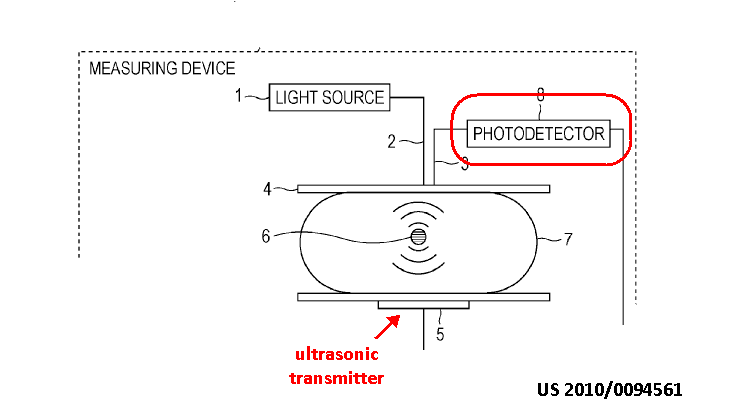
This place does not cover:
Clinical contact thermometers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission of temperature signals |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording physiological parameters related to diagnosis of the cardiovascular system. It includes apparatus where calculation of health indices, e.g. an arterial index, are made or apparatus for monitoring trends in the patient's condition by analysis of the physiological data, e.g. ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring a physiological parameter of a patient undergoing therapy, e.g. for controlling the administration of therapy | |
Controlling electrotherapy using a measured physiological parameter | |
Electrotherapy combined with monitoring a physiological parameter | |
Measuring a physiological parameter of a user of sports apparatus |
Multiple subgroups may be allocated if the particular physiological parameter is essential for the determination of a diagnosis or calculation of a health index.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating flow properties of materials, e.g. viscosity |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording multiple physiological parameters where at least one parameter is a cardiovascular parameter. Combinations with any other physiological parameters, not only a respiratory condition, are allowed, e.g. measurement of heart rate, movement activity and blood glucose concentration. Multiparameter vital signs monitoring.
Indexing Codes added for specific parameters to show the combination of physiological parameters measured, e.g. A61B 5/024, A61B 5/0816 and A61B 5/14532.
This place covers:
Simultaneously evaluating both cardiovascular condition and body temperature. Multiple vital signs monitoring where at least one cardiovascular parameter is measured with body temperature, e.g. heart rate and temperature.
This place does not cover:
Remote monitoring of patients by using telemetry of temperature signals | |
Details of apparatus calibration for compensation or correction of the measured physiological value using ambient temperature | |
Clinical thermometers | |
Special purpose thermometers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring temperature of a patient undergoing therapy, e.g. for controlling administration of therapy | |
Controlling electrotherapy using body or blood temperature | |
Measuring temperature of a user of sports apparatus |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording blood pressure, diastolic pressure, systolic pressure, arterial pressure, venous pressure. Includes measuring pressure in specific blood vessels, e.g. aortic pressure.
This place does not cover:
Simultaneously evaluating both cardiovascular conditions and different types of body conditions | |
Detecting, measuring or recording fluid pressure within the body other than blood pressure | |
Measuring fluid pressure by mechanical pressure-sensitive elements in general | |
Measuring fluid pressure by electric or magnetic pressure-sensitive elements in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for maintaining contact with the body by monitoring or controlling sensor contact pressure | |
Details of pressure sensors specially adapted for sensing pressure in-vivo | |
Measuring blood pressure during the administration of therapy | |
Controlling electrotherapy by using blood pressure | |
Measuring blood pressure of a user of sports apparatus |
IPC precedence does not apply in the case where the blood pressure in combination with another physiological parameter is essential for the invention, e.g. in calculation of a particular arterial index.
This place covers:
All types of apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording blood pressure invasively including catheters, needle probes, guidewires and implanted devices. Blood pressure may be measured in blood vessels or in the heart itself.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring pressure in other body cavities | |
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices | |
Solid probes | |
Catheters, e.g. for introducing media or drainage |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording blood pressure in a blood vessel or the heart comprising optical means for transmitting the pressure change, e.g. deflection of a pressure sensitive membrane is detected optically.
This place does not cover:
Optical transmission of a pressure signal from the patient to a remote site |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmitting or indicating the displacement of pressure sensitive flexible diaphragms using photoelectric means |
This place covers:
Methods or apparatus for calibrating the pressure sensor repsonse. May include correction or compensation of the measured value, e.g. due to drift.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of apparatus for calibration, e.g. calibration protocols | |
Sensors provided with means for identification combined with means for recording calibration data, e.g. on memory chip | |
Testing or calibrating of apparatus for measuring fluid pressure |
This place covers:
Apparatus provided with two or more pressure sensors for measuring the blood pressure in the body, e.g. two pressure transducers mounted on a catheter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of pressure sensors, e.g. in a linear arrangement |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording blood pressure where the blood vessel is fully occluded during part of the measurement cycle and then released to allow blood flow.
This place does not cover:
Partial compression of blood vessel to allow blood pressure measurement |
This place covers:
Details of occluders, e.g. construction of inflatable cuffs, adjustable clamps.
This place does not cover:
Tourniquets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring pressure of a fluid using liquid as a pressure sensitive medium, e.g. liquid-column gauges |
This place covers:
Details of valves specially adapted for use in blood pressure measuring apparatus, e.g. valves for releasing air from an inflatable cuff. Includes valves used in any part of the apparatus..
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Valves for medical use |
This subgroup is not restricted to apparatus where the blood vessel is occluded.
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording pulse rate or heart rate, e.g. given in beats per minute.
This place does not cover:
Evaluating a cardiovascular condition not otherwise provided for, e.g. pulse waveform shape analysis | |
Simultaneously evaluating both cardiovascular conditions and different types of body conditions | |
Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels | |
Ballistocardiography, detecting chest motion due to heart beat | |
Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring a physiological parameter to provide biofeedback to patient, e.g. measuring heart rate to allow patient to control the heart rate | |
Measuring heart rate of a patient during administration of therapy | |
Measuring heart rate of a user of sports apparatus |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording pulse rate or heart rate using an optical sensor for detecting photoplethysmograph signals.
This place does not cover:
Measuring blood flow using plethysmography | |
Using optical sensors for measuring blood gases, e.g. details of photometrical oximeters |
This place covers:
Details of optical sensors for detecting photoplethysmograph signals. Includes constructional details of sensors, arrangements of sensors in housings or probes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of optical sensors specially adapted for measuring blood gases | |
Details of optical sensors specially adapted for in-vivo measurements |
This place covers:
All types of portable devices for detecting, measuring or recording pulse or heart rate. Heart rate devices may be worn on any part of the body or be incorporated in a portable device providing a non-medical function, e.g. a music player.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements of detecting, measuring or recording means where the sensors are mounted on worn items | |
Arrangements of detecting, measuring or recording means where the sensors are mounted on a non-medical device | |
Constructional details of apparatus, low-profile patch shaped housings | |
Apparatus with built-in sensors |
This place covers:
Details of sensors for measuring heart or pulse rate not covered by A61B 5/02416 or A61B 5/0245. For example, pressure sensors, strain gauges or accelerometers for measuring the tissue deformation due to the pulse wave. Inlcudes sensor construction and arrangements of sensors in housings or probes.
This place does not cover:
Details of optical sensors for measuring heart rate | |
Details of ECG sensors for measuring heart rate |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of sensors specially adapted for in-vivo measurements |
This place covers:
Apparatus for measuring, detecting or recording the heart rate using the detection ECG signals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bioelectric electrodes therefor | |
Detecting specific parameters of the electrocardiograph cycle | |
Apparatus with built-in electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electric stethoscopes |
This place covers:
Apparatus for measuring, detecting or recording blood flow or perfusion of blood in tissue. The extent of blood flow detected is not always given as a flow rate, e.g. in ml/s.
This place does not cover:
Apparatus, instrument for testing the eyes | |
Measuring volume flow or mass flow in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling therapy by using blood flow rate |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring volume flow or mass flow using electromagnetic flowmeters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of catheters for measuring | |
Catheters, e.g. for introducing media or drainage |
This place does not cover:
Measuring blood output from the heart using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling electrotherapy by using blood flow rate, e.g. blood velocity or cardiac output |
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording devices for evaluating the respiratory organs by impedance pneumography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Impedance plethysmography not specifically for determining blood flow or perfusion | |
Measuring volume of limbs, e.g. by plethysmography |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording fluid pressure within any part of the body other than blood pressure of the heart or blood vessels.
This place does not cover:
Determining bladder or urethral pressure | |
Measuring fluid pressure by electric or magnetic pressure-sensitive elements in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of pressure sensors specially adapted for in-vivo measurements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood pressure by means inserted into the body | |
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices, e.g. burr holes | |
Catheters, e.g. for introducing media or drainage | |
Devices for cerebrospinal drainage |
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording spinal fluid pressure | |
Detecting, measuring or recording uterine pressure using intra-uterine probes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood pressure by means inserted into the body | |
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices | |
Catheters, e.g. for introducing media or drainage |
This place covers:
Measurements carried out while applying a magnetic field, an electric field or an electromagnetic field, e.g.:
1) Magnetic induction tomography, note figure showing measurement coils, or
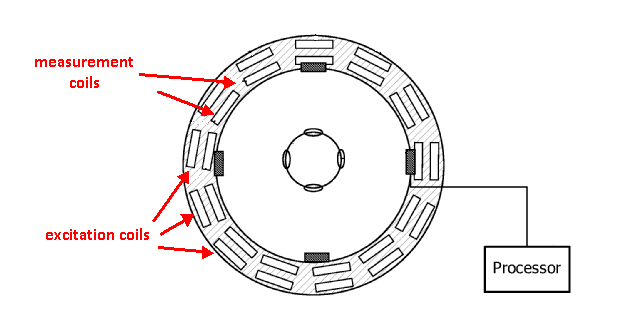
2) Measurements of microwaves modified by parts of the body.
This place does not cover:
Impedance plethysmography | |
Detecting movement of the body | |
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus | |
Dental radiography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determining position of an invasive probe using impedance measurements | |
Measuring impedance in general |
This place covers:
Measuring skin impedance, conductance or resistance by applying a current or voltage to the skin.
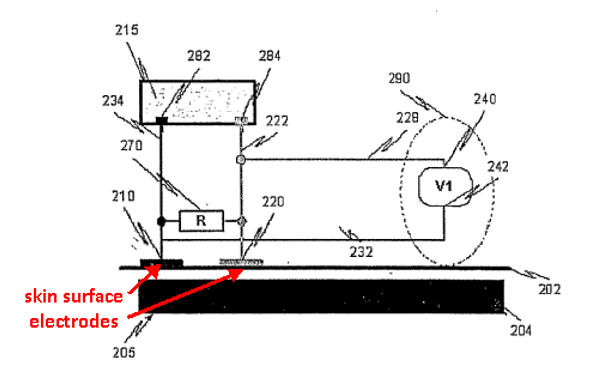
This place covers:
Using skin conductance measurement to detect acupuncture points
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating the autonomic nervous system |
This place covers:
Measurements are carried out while presenting a stimulus (visual, auditory, auditive, etc.) to the subject of the examination
This place covers:
Conductance / impedance measurement on teeth
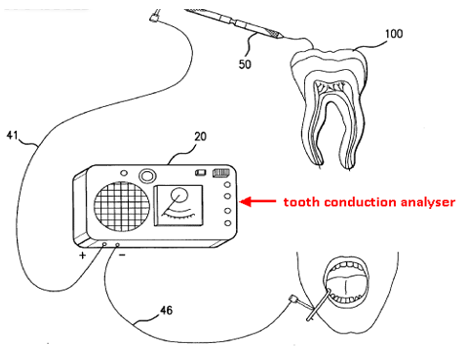
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluation of teeth in general | |
Sensors adapted for attachment to the mouth | |
Dental radiography | |
Measuring instruments specially adapted for dentistry |
This place covers:
Detection of volume changes by impedance measurements
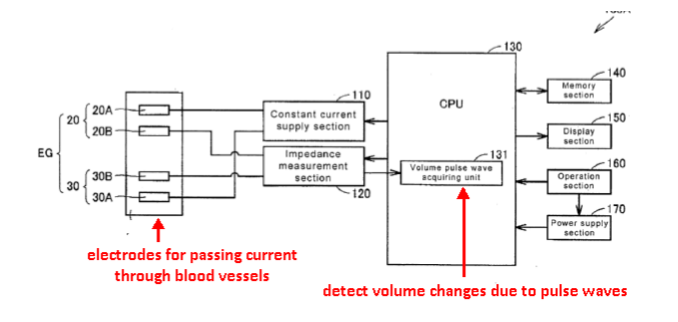
This place does not cover:
Impedance plethysmogaphy for measuring blood flow |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detection of electrical impedance of respiratory organs |
This place covers:
Reconstruction of images of parts of the body by means of impedance measurements:
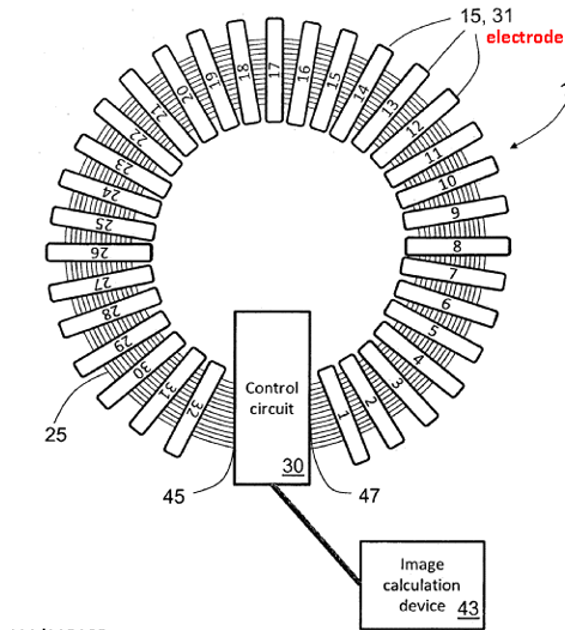
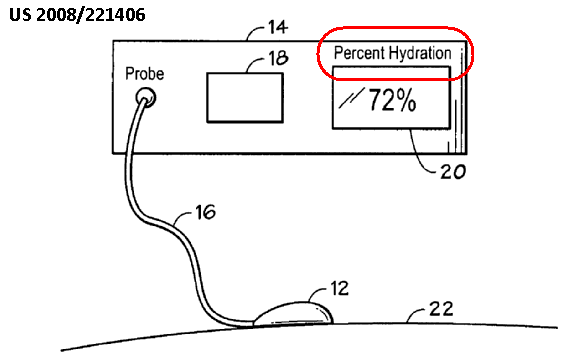
This place covers:
Fat content evaluation: measuring various parameters of body composition including body fat composition, lean body mass, body-fat ratio, tissue hydration, total body water, extracellular fluid volume etc..
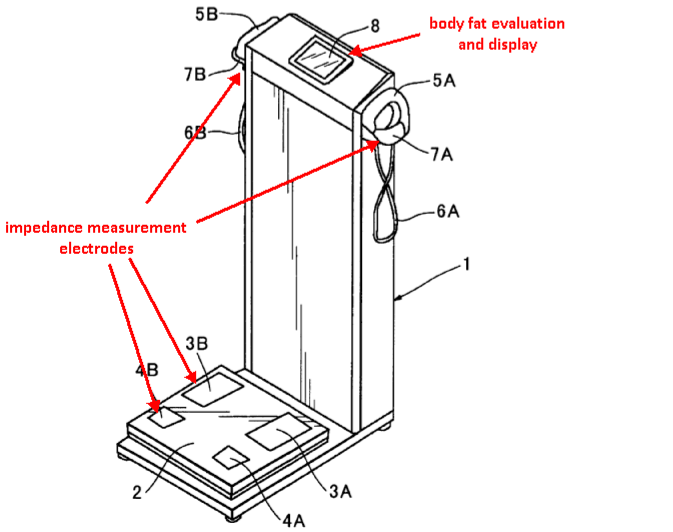
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Weighing apparatus for diet control | |
ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans (e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance) relating to nutrition control (e.g. diets) |
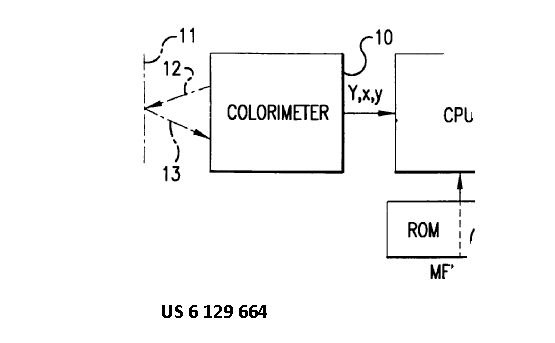
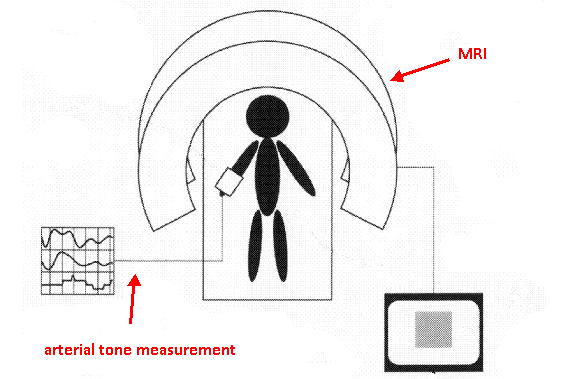
This place covers:
A61B 5/055 mainly covers the relationship between magnetic resonance apparatus (NMR, MRS, MRI, fMRI etc.) and other devices classified in A61B 5/00. This subgroup does not include specific MR arrangements and MR processes as such which are already covered in G01R 33/20, however includes documents where the diagnostic application of MR predominates rather than the system details or the details of the MR process. The following image shows an example of an MRI device with arterial tone measurement output.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus | |
Adapted for image acquisition of a particular organ or body part | |
Diagnosing of monitoring cognitive diseases, e.g. Alzheimer, prion diseases or dementia | |
Touch or pain perception evaluation | |
Surgical systems with NMR or MRI images on a monitor during operation | |
In vivo contrast agents | |
Arrangements or instruments for measuring magnetic variables involving electronic or nuclear magnetic resonance, in general | |
Invasive instruments, e.g. catheters or biopsy needles, specially adapted for tracking, guiding or visualization by NMR | |
Using nuclear magnetic resonance [NMR] | |
With selection of signals or spectra from particular regions of the volume, e.g. in vivo spectroscopy | |
Signal processing systems, e.g. using pulse sequences | |
Image enhancement or correction, e.g. subtraction or averaging techniques, e.g. improvement of signal-to-noise ratio and resolution |
There is an overlap between the scope of G01R 33/20 (or its relevant subgroup) and A61B 5/055 in the sense that, depending on the disclosure of a given document, the document may have to be classified in G01R 33/20 (or its relevant subgroup) only, in A61B 5/055 only or in both places.
For instance:
- if the invention information of a document to be classified is primarily directed to the MR process as such (e.g. a novel pulse sequence which, according to the document, facilitates the diagnosis of a disease on the basis of the resulting MR images wherein the document merely mentions the diagnosis but does not specifically disclose its implementation in detail), the document should be classified in G01R 33/20 (or its relevant subgroup) only and the additional information related to the diagnosis may be classified using the appropriate Indexing Code corresponding to A61B 5/055.
- if the invention information of the document is primarily directed to the diagnosis as such (e.g. a novel way of processing MRI data in order to enable the diagnosis of a disease wherein the MRI data was acquired using a commonly known standard MRI technique), the document should be classified in A61B 5/055 only.
- documents where the focus lies in diagnostic features as well as in technical details of the MR apparatus or details of the MR process should be classified in both A61B 5/055 and G01R 33/20.
This place covers:
Position sensors on a probe to detect relative positions of different components
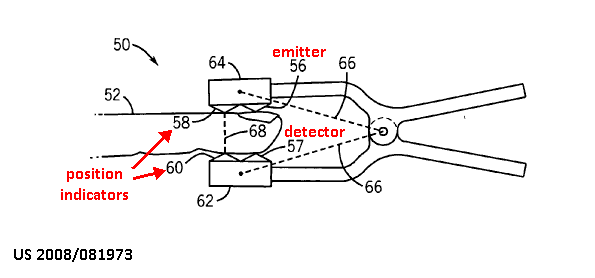
Sensor 50 is configured to provide position data for the emitter 56 and detector 57.
Sensor 50 comprises a sensor body that includes the emitter 56, detector 57, and one or more position indicators 58 and 60
This place does not cover:
Tracking foreign bodies using x-ray | |
Tracking foreign bodies using ultrasound | |
Instruments for removing foreign bodies |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Foreign body | 1) Sensing probe inserted in the human or animal body, e.g. catheter, endoscope, implant 2) External sensing probe |
This place covers:
External tracking device detecting position of:
1) Invasive probes comprising position indicating element
2) Markers placed on the surface of the body
This place does not cover:
Endoscope provided with position sensors, e.g. internally mounted |
This place covers:
Probes comprising magnet or electromagnetic coil
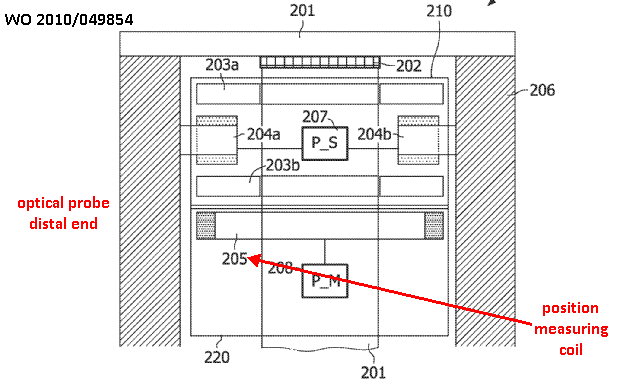
This place does not cover:
MRI tracking of surgical probes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electromagnetic tracking of surgical instruments |
This place covers:
Impedance measurement means for detecting the position of an invasive probe
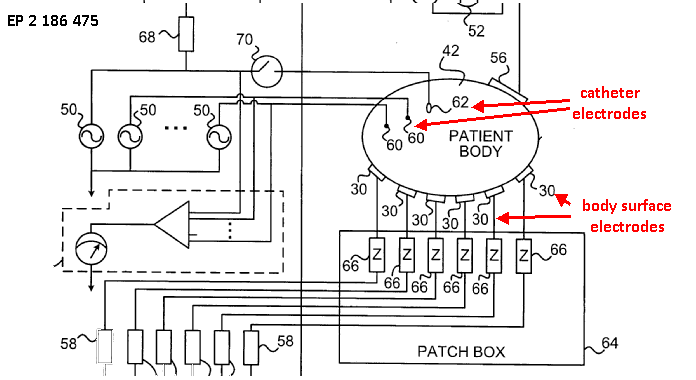
The coordinates of a catheter inside the body are determined by passing currents between catheter electrodes 60, 62 and body surface electrodes 30.
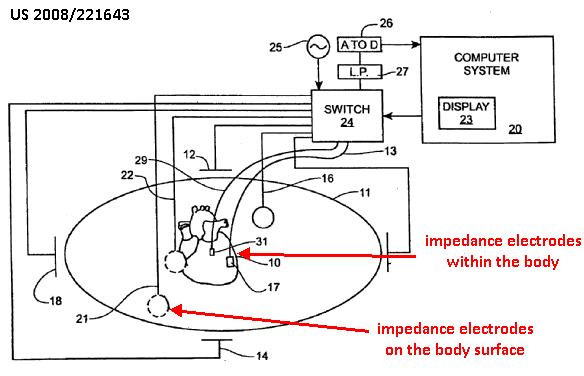
This place covers:
1) Detecting position of markers associated with a sensor, the markers being placed on the surface of the body of the patient.
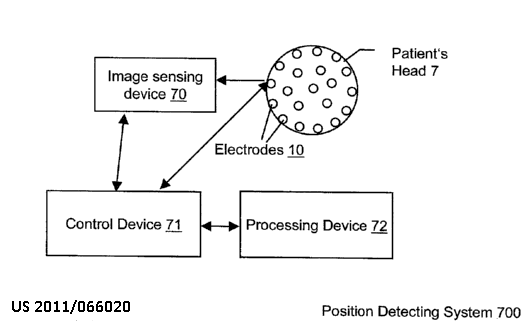
2) Tracking position of markers associated with an invasive probe
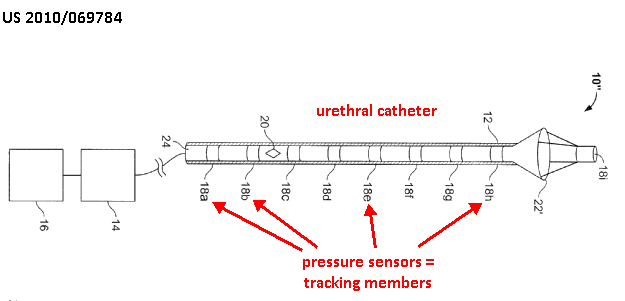
The position and movement of the tracking members are tracked by the control unit 14.
The pressure sensors in rings 18a-18i serve as the tracking members.
This place does not cover:
Using magnetic fields |
This place covers:
The probe is provided with means for detecting its own position within the body
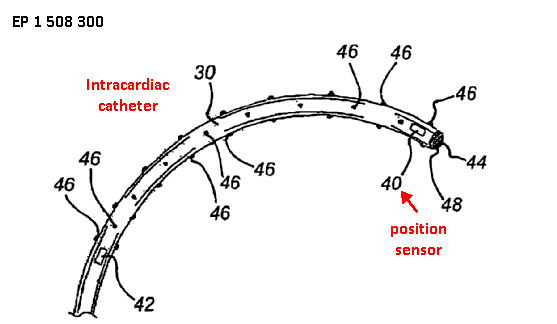
Position sensors detect positions relative to their own reference frame, e.g., gyroscopes, accelerometers
This place covers:
Registration of pre-operative images with detected positions of a probe.
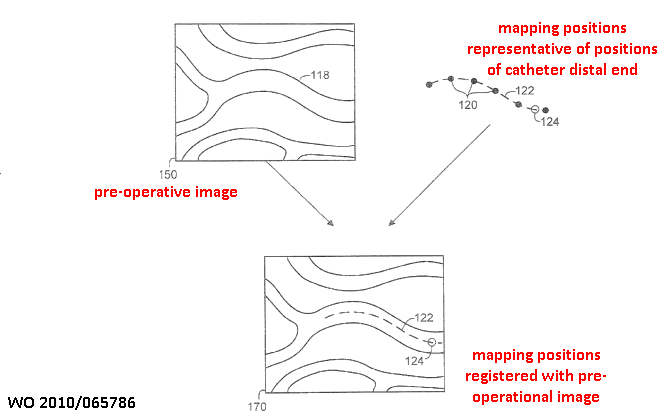
This place does not cover:
MRI tracking of interventional instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
X-ray detection of foreign bodies | |
Ultrasound detection of foreign bodies | |
Visualisation of surgical instruments using MRI |
This place covers:
Wireless data transmission between probe within the body and external monitor
This place does not cover:
Transmission of endoscopic image data | |
Transmission of measured data from implanted circuitry |
This place covers:
Swallowed capsules travelling through the GI system
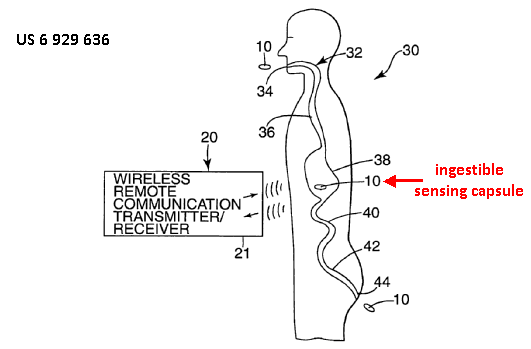
This place covers:
Implanted devices that are attached or anchored to the internal body tissue so that movement of the device from the place of attachment does not occur.
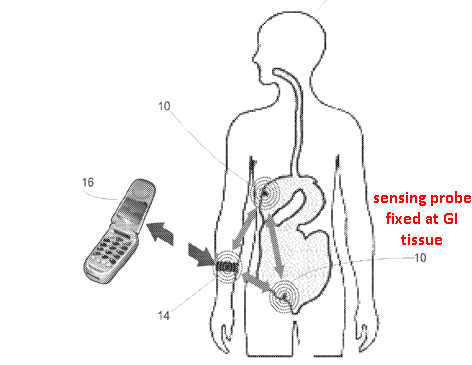
Using clips, sensor 10 may be held at a fixed position in the Gl tract.
Device 10 uses a wireless communication protocol to transmit data to monitor 14
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implants for transcutaneous transmission | |
Evaluation of respiratory rate in general | |
Implanted stimulators |
This place covers:
Evaluation of the respiratory system.
This place does not cover:
Simultaneously evaluating both cardiovascular conditions and different types of body conditions |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Mechanical impedance of respiratory organs | Ratio of the measured air pressure and air flow at the mouth of the patient |
Electrical impedance of respiratory organs | Ratio of voltage applied to respiratory organs and current flow |
This place covers:
Apparatus for recording respiratory parameters, e.g. portable devices for ambulatory recording.
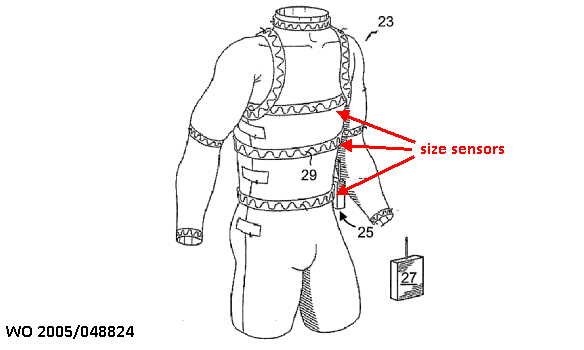
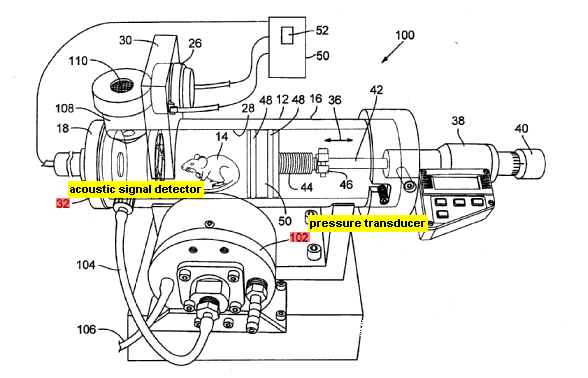
This place covers:
Evaluating volume changes due to respiration
1) by measuring changes of spatial dimensions:
2) by measuring pressure changes in a closed chamber
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluation of respiratory rate in general | |
Measuring movement due to respiration |
This place covers:
Detection of electrical impedance of respiratory organs
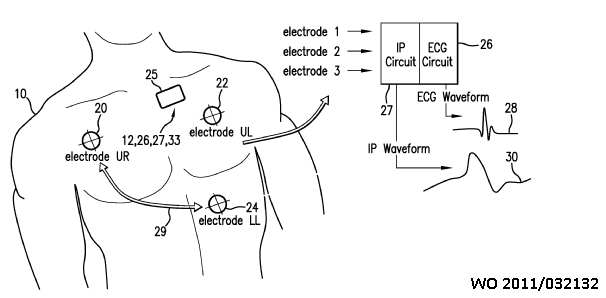
IP (impedance pneumography) circuit 27 25 generates a current that is modulated at a high frequency (typically 50-100 kHz). The current passes through electrode LL 24. It then propagates through the patient's chest, as indicated by the arrow 29, where a respiration-induced capacitance change modulates it according to the RR.
Electrode UR 20 detects the resultant analog signal, which is then processed within the IP circuit to determine an analog IP waveform 30 featuring a low-frequency series of pulses corresponding to RR.
The analog filters in the IP circuit 27 are chosen to filter out high-frequency components that contribute to the ECG QRS complex.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Impedance plethysmography in general | |
Detecting respiration rate in general |
This place covers:
1) Evaluation of tracer quantity absorbed by the lungs
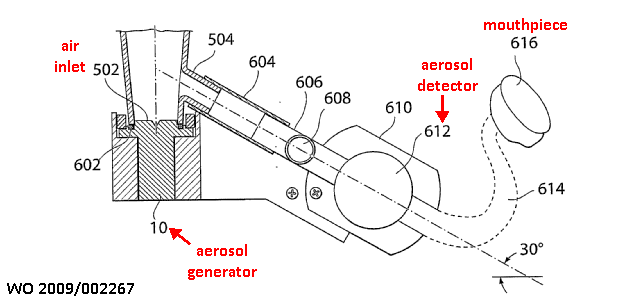 .
.
2) Inhalators for tracers to be detected by imaging devices, e.g. MRI, PET
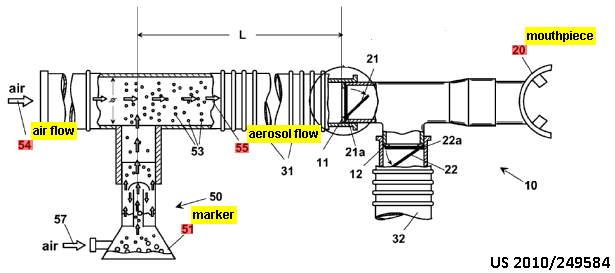
This place does not cover:
Breath analysis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Breath test in general |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Tracer | Composition, e.g. aerosol, which is mixed with inhaled air and detected after exhalation |
This place covers:
Detection of respiratory signals, e.g.:
using photoplethysmography, i.e. a signal provided by a pulse oximeter on a body part, e.g. finger, ear
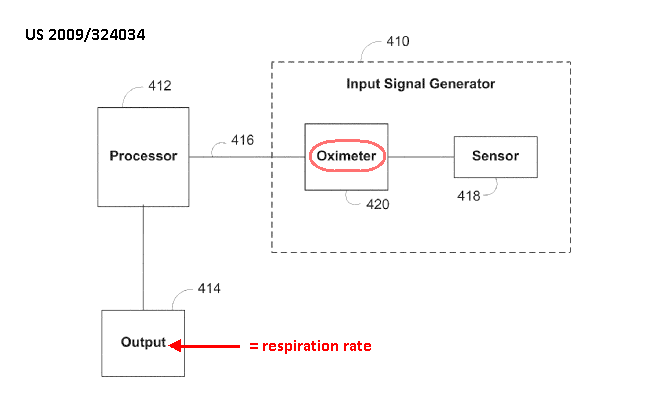
This place does not cover:
Detect changes of body volume due to respiration | |
Detect respiratory signals using electrical impedance measurements | |
Detect respiratory sounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring frequency of electric signals |
This place covers:
Detection of chemical composition of exhaled breath.
Not relating to lung function.
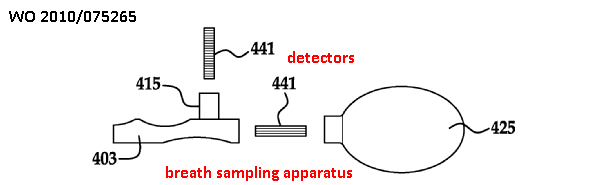
Detector 441 is optionally operable to detect bacteria, virus, fungus, antibody, protein, or chemical such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitric oxide, alcohol and the like
This place does not cover:
Evaluation of lung function | |
Determination of instantaneous concentration of a component of inhaled/exhaled air in order to determine breath flow |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gas analysers | |
Breath analysis in general |
This place covers:
Detect cough events which may be spontaneous coughing events or where the patient is asked to voluntarily cough:
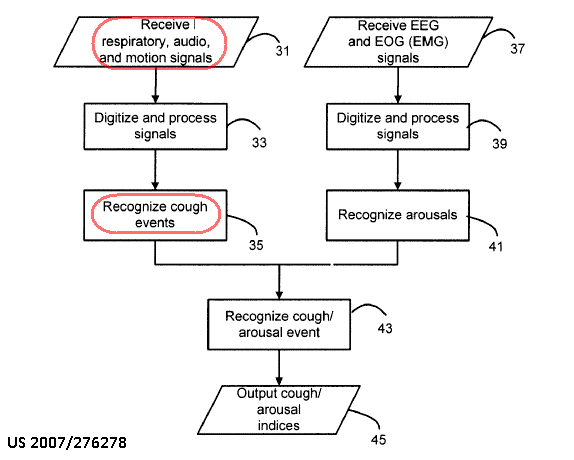
Evaluate cough event:
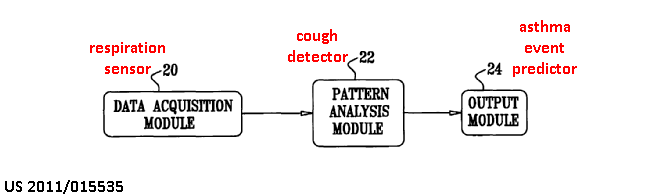
This place covers:
Detection of all types of apnoea events, e.g. cessation of breathing (apnoea), shallow breathing (hypopnea), fast deep breathing (hypernoea), Cheynes-Stokes respiration etc.
This place does not cover:
Detection of sleep apnoea |
This place covers:
Breath test specially adapted to detect rate of metabolism. For example, properties of exhaled gas are compared to properties of inhaled air.
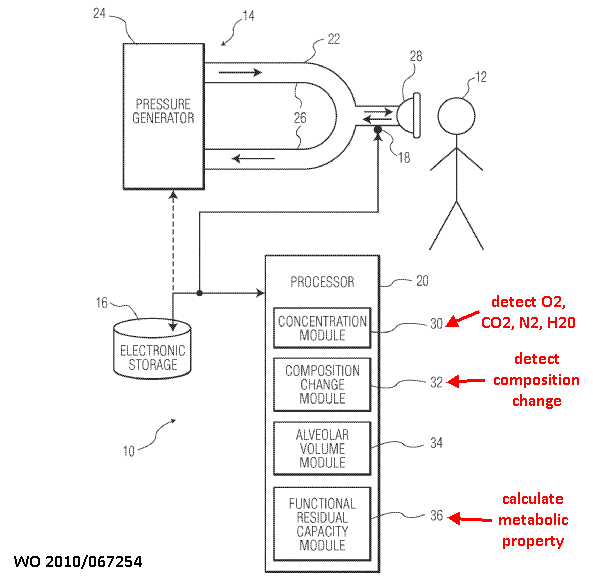
This place does not cover:
Detect a tracer mixed in inhaled gas | |
Determination of instantaneous concentration of a component of inhaled/exhaled air in order to determine breath flow |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detect chemical composition of exhaled gas by breath test in general | |
Gas analysers | |
Breath analysis in general |
This place covers:
Evaluation of O2 uptake from breath analysis.
This place covers:
Evaluation of CO2 release.
This place covers:
Detection of mechanical impedance of respiratory organs.
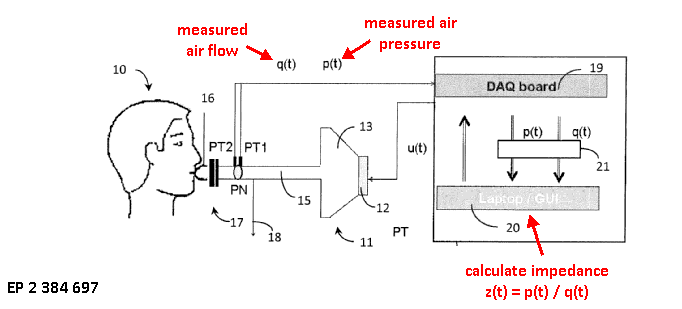
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Mechanical impedance of respiratory organs | Ratio of the measured air pressure and air flow at the mouth of the patient |
Electrical impedance of respiratory organs | Ratio of voltage applied to respiratory organs and current flow |
This place covers:
Evaluate breath flow
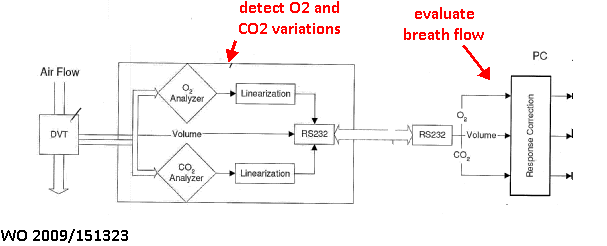 Text1
Text1
This place does not cover:
Detect breath flow in order to evaluate lung impedance parameters | |
Ventilators provided with means for detecting breath flow |
This place covers:
Detectors of maximum air flow
I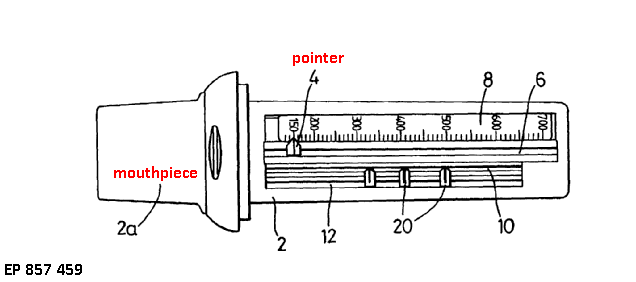
The pointer 4 is entrained along its slot 6 by the exhaled air flow. When the exhalation ends friction retains the pointer 4 in its displaced position to indicate a peak flow value against a scale 8 marked along the slot
This place does not cover:
Spirometers in general, wherein it is possible to calculate peak flow |
This place covers:
Detection of breath flow using optical sensors. The optical sensor is placed in or by the flow path.
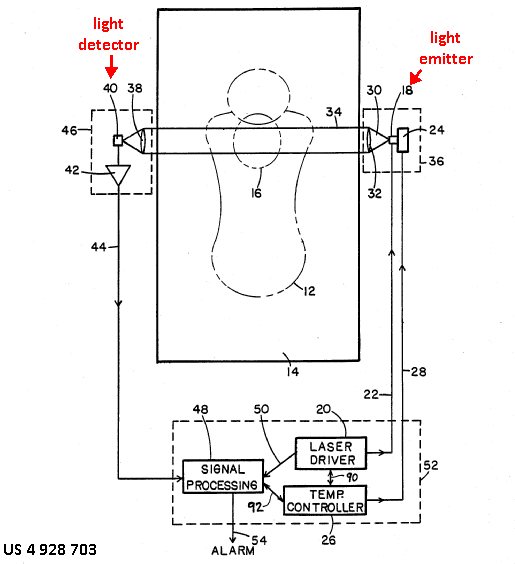
The detector 40 generates an electrical signal that is related to the radiant power falling on it. The detector senses the breath exhaled into the volume 16 close to the patient's mouth and nose.
The signal processing circuit 48 examines the electrical signal 44 to determine whether it varies in a manner that indicates the patient is breathing.
This place covers:
E.g. for indicating flow level for breath training.
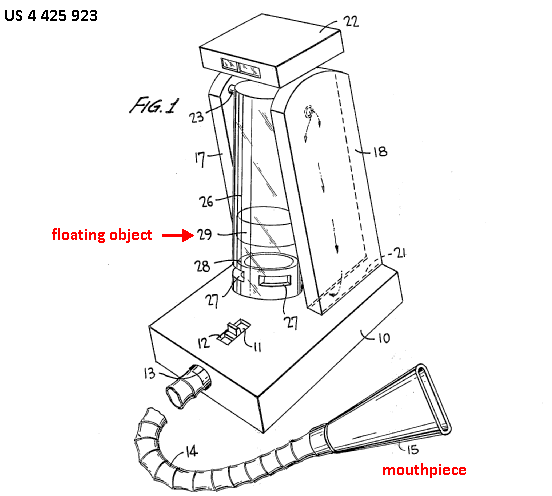
Object 29 is raised in tube 26 according to exhalation effort of the patient.
This place does not cover:
Flow meters adapted to indicate specifically the maximum value |
This place covers:
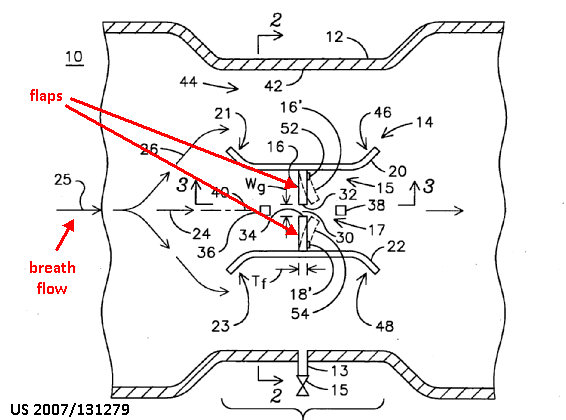
Flaps 16, 18 are deflectable in response to breath flow 25.
This place covers:
A filament 34 is secured to the ends of the four pins 32.
The filament 34 is used to measure the flow rate of the fluid 26 based on its power consumption.
This place covers:
An optical detector detects rotor movement to evaluate air flow
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toys actuated by air current |
This place covers:
This place covers:
Detecting spatial properties of the human or animal body, e.g. lengths, areas, volumes, angles, velocities, accelerations, weights
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording devices for evaluating the respiratory organs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments specially adapted for dentistry | |
Measuring aids for tailors | |
Analysis of geometric features (lengths, area, volume) from images |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring colour in general |
This place covers:
Assessing body features by comparison with colour patterns or atlases
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Colour charts in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gait analysis | |
Apparatus for weighing persons |
This place covers:
Measuring spatial dimensions: distances (e.g. length, depth, thickness), angles, areas, volumes etc.
By detecting marker positions:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring distance in general |
This place covers:
Measurements of angles
Angle measuring device 6 comprising light source 7 and light detector 8
Processing module is enabled to calculate, from the ratio between the power entered into the light source 7 and the power received by the light detector 8, an angle between the first and second member
This place does not cover:
Discriminating types of movement |
This place covers:
Rulers, tapes, height measuring device for direct measurement on the body
This place does not cover:
Measuring interpupillary distance | |
Measuring dimensions inside body cavities |
This place covers:
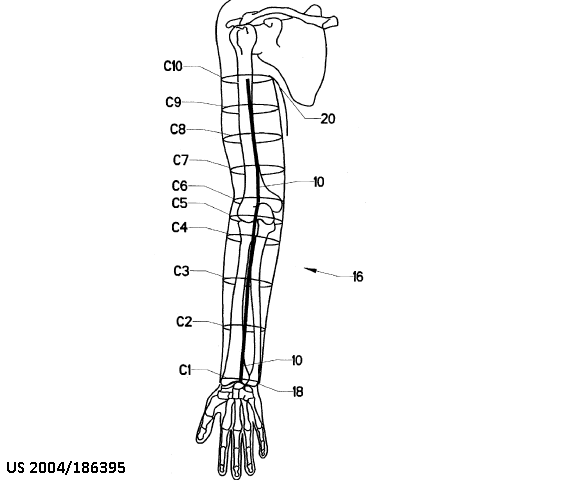
The arm has been segmented into discrete volumes C1-C10
Circumference measurement is taken at the intersection of each linear segment of centerline 10.
Evaluate changes in the arm volume over time.
This place does not cover:
Plethysmography for blood flow assessment based on vessel volume changes | |
Impedance plethysmography | |
Whole-body plethysmography for respiration assessment based on chest volume changes | |
Impedance pneumography | |
Measuring bladder volume |
This place covers:
All types of apparatus for measuring dimensions non-invasively, e.g. calipers, gauges, templates for measuring on patient images. Also, includes imaging apparatus with measuring scales projected on the image or cursors allowing dimensions to be read from an image.
This place does not cover:
Endoradiosondes by impedance pneumography |
This place covers:
Rulers, height measuring devices for direct measurement inside the body
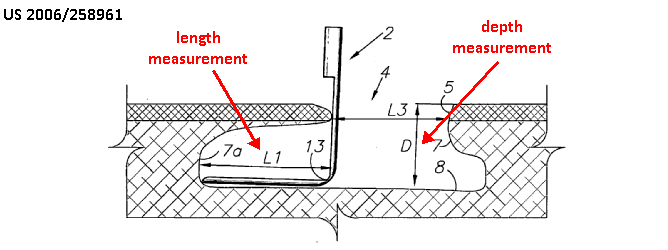
This place does not cover:
Measuring distances inside the eye, e.g. thickness of the cornea | |
Measuring interpupillary distance | |
Measuring dimensions on the body cavities |
This place covers:
Detect 2- or 3-dimensional contour or profile or shape of objects, e.g. using mechanical elements brought into contact with the body surface:
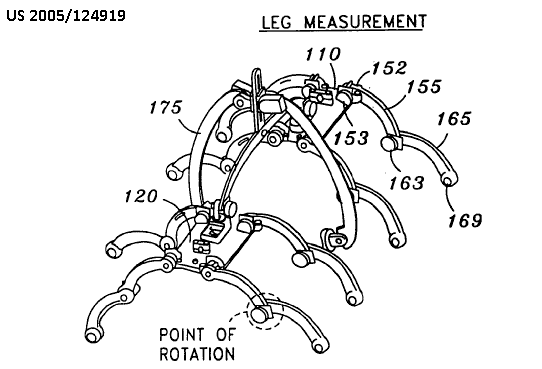
This place does not cover:
Optical shape detection: | |
Measuring volumes of body parts |
This place covers:
Measurement of movement includes the determination of any change in position or orientation, it is not mandatory that a velocity or acceleration is measured.
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording pulse rate or heart rate | |
Measuring for testing the shape, pattern, size or movement of the body or parts thereof for podologic studies during locomotion | |
Measuring movement for compensation of motion artefacts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring eye movement, e.g. using eye trackers | |
Measuring circulation of blood, e.g. blood flow | |
Plethysmography | |
Measuring movement of foreign bodies, e.g. tracking of catheters | |
Detecting, measuring or recording respiratory frequency | |
Testing reaction times | |
Ergometry or measuring muscular strength | |
Bioelectric electrodes for electrooculography [EOG]: for electroretinography [ERG] | |
Measuring or inducing nystagmus | |
Detecting organic movements or changes using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves | |
Pleximeters | |
Measuring movement in general |
This place does not cover:
Ballistocardiography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating medicinal preparations |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for measuring work or force in general |
This place covers:
Patient monitors including means for global position determination, localizing a patient world-wide.
This place covers:
Patient monitors including means for local position determination, e.g. in hospitals, rooms, imaging apparatus.
This place covers:
Includes posture transitions from standing to sitting to lying down, etc.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling electrical heart stimulation by body motion |
This place covers:
Patient position sensing/monitoring with sensors, e.g. carried on the patient, e.g. 3D sensors, mercury switches, for indicating (change to) prone/lying position probably from a fall. May be combined with a timer/physiological sensors/alarm (to remote station). Includes devices for monitoring fall from bed.
This place covers:
Determining a parameter indicative of the degree of overall activity of a subject, e.g. for use in determining caloric consumption.
When metabolism is evaluated, e.g. caloric expenditure determined, A61B 5/4866 should additionally be given.
This place does not cover:
Gait analysis |
This place does not cover:
Determining posture transition | |
Gait analysis |
This place covers:
Evaluating the degree of mastering a particular task in the form of a specific movement or sequence of movements. In particular for rehabilitation or assessing development of infants.
This place covers:
Details of sensing techniques adapted for measuring movement other than those mentioned in A61B 5/1127 and A61B 5/1128.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
inertial sensors used for measuring movement |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Markers for medical use |
This place does not cover:
Using markers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Analysis of motion in images | |
Extraction of features from images |
This place covers:
Means for distinguishing one person from another
This place does not cover:
Methods or arrangements for reading or recognising patterns, e.g. fingerprints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dental impression cups or articulators | |
Identification tags |
This place covers:
Apparatus and methods for taking fingerprints from a person. Includes developing latent fingerprints for forensic purposes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Recognition of fingerprints or palmprints |
This place covers:
Evaluating the hearing system
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Otoscopes | |
Electroencephalography using acoustic or auditory stimuli | |
Evaluating sense of balance | |
Tinnitus treatment | |
Testing of hearing device using in-hear measurements |
This place covers:
Evaluation of the hearing without technical means for detecting an auditory characteristics, e.g.:
Vibrating unit for stimulating the ear canal. No sensor is provided:
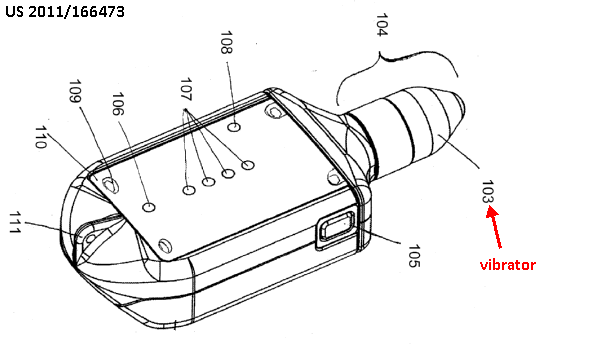
Feedback is provided by the patient by, e.g., a response button:
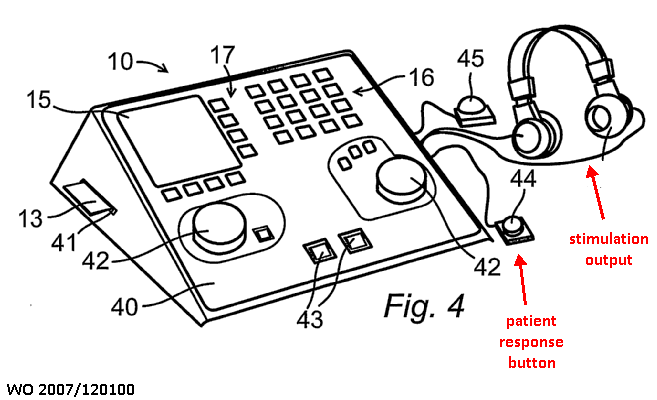
This place covers:
Detecting physiological response, e.g. EEG, to auditory stimuli:
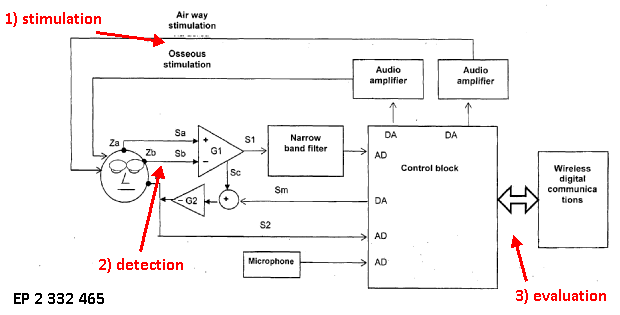
This place covers:
Tympanometer (detects acoustic response to a sound generated into the ear canal)
Measuring acoustic impedance (frequency response) of the outer ear in general:
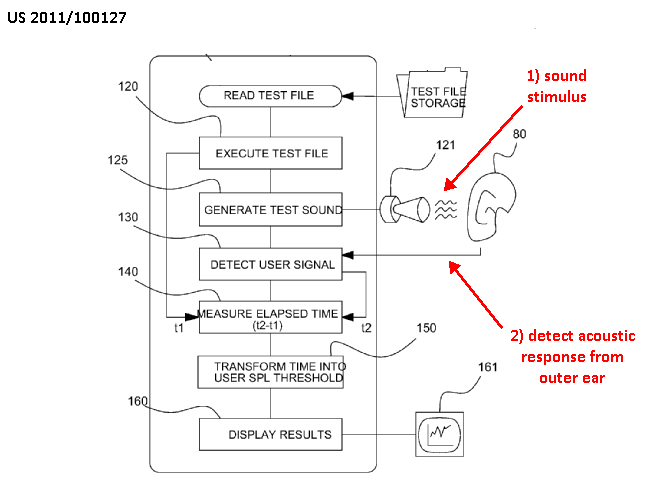
This place covers:
Detecting, testing, evaluating or measuring tinnitus to determine frequency, frequency range, bandwidth or other tinnitus features, e.g. by using a generator for generating tinnitus masking sound based on the detected tinnitus features.
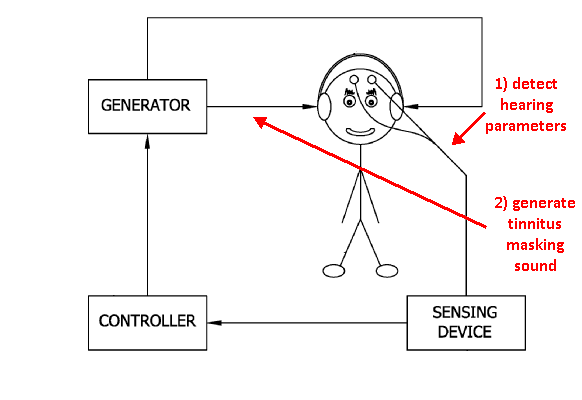
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Masking sound in general | |
Deaf-aid sets that provide electric tinnitus maskers |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording characteristics of blood, body fluids or tissues in-vivo. Determining chemical characteristics, e.g. measuring the concentration of an analyte. Determining constituents of blood or body fluids, e.g. haematocrit. The measurement is performed on the body, i.e. in-vivo, or immediately after a sample of body fluid has been obtained, e.g. by lancet.
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording for diagnosis using light, e.g. detecting cancer, fatty tissue | |
Measuring blood pressure or blood flow | |
Non-radiation detecting or locating of foreign bodies in blood | |
Investigating or analysing materials by determining their chemical or physical properties in general | |
Investigating or analysing biological material in vitro, physical analysis | |
Chemical analysis of biological material |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood composition characteristics of a patient undergoing therapy, e.g. for controlling the administration of therapy | |
Controlling electrotherapy using a parameter of a chemical substance in blood | |
Measuring blood composition characteristics of a user of sports apparatus |
Combinations of several characteristics are common. Classification in more than one EC subgroup takes place if the apparatus is specially adapted for detecting, measuring or recording a particular characteristic. An indexing code is used where a characteristic is explicitly mentioned, but no details of specially adapted apparatus are given.
This place does not cover:
Using invasive optical sensors | |
Optical sensors specially adapted for foetal tissue | |
Using invasive chemical or electrochemical sensors | |
Chemical or electrochemical sensors specially adapted for foetal tissue | |
Using invasive enzyme electrodes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices | |
Catheters, e.g. for introducing media or for drainage |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording glucose. Apparatus for continual monitoring of glucose with analysis of glucose data to determine trends, e.g. to optimise insulin administration. Apparatus for measuring glucose in combination with an insulin pump. Apparatus for glucose measurement in-vivo or combination with fluid or blood sampling where the measurement is made immediately after sampling the fluid, e.g. by lancet.
A61B 5/14532 is given for glucose, and the corresponding subgroup for the measurement technique, e.g. A61B 5/14532 and A61B 5/1486. Classification of glucose measurement in combination with blood or fluid sampling is covered by A61B 5/15-A61B 5/157 (apparatus for blood sampling). Test strips with no further disclosure of interaction with the patient is covered by G01N.
This place does not cover:
Devices for bringing media into the body in a subcutaneous, intravascular or intramuscular way | |
Measuring or testing processes involving enzymes, enzyme electrodes for glucose | |
Investigating or analysing biological material in vitro by physical analysis using electrical means for determining glucose content | |
Details, e.g. test element handling, dispensing or storage not specific to a particular test method |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for taking samples of blood characterised by integrated means for measuring characteristics of blood | |
Other medical applications, combined with drug delivery | |
Measuring blood glucose of a patient undergoing therapy, e.g. for controlling the administration of therapy | |
Measuring blood glucose of a user of sports apparatus |
This place does not cover:
Measuring blood gases using optical sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood gases of a patient undergoing therapy, e.g. for controlling the administration of therapy | A61M 2230/202; K61B230/20D |
Measuring blood gases of a user of sports apparatus | K61B230/20C; A63B 2230/207 |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording chemical characteristics of blood, body fluids or tissue using optical sensors, where the measurement is made in-vivo or on a blood of fluid sample immediately after sampling, e.g. measurement is made immediately after sampling by lancet.
This place does not cover:
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording for diagnostic purposes using light, e.g. for detection of tumour | |
Detecting, measuring or recording heart rate using photoplethysmograph signals |
This place covers:
Details of optical sensor construction for pulse oximetry. Sensors particularly adapted for attachment to parts of the body, e.g. earlobe clips, finger clips, adhesive patches etc.. Arrangements of optical sensors in housing or probes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording heart rate using photoplethysmograph signals, details of sensor | |
Details of optical sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating the central nervous system | |
Sensors mounted on head worn items, e.g. helmet or cap |
This place covers:
Apparatus for making pulse oximetry measurements at the eye fundus, comprising optical sensors for detecting changes in light characteristics reflected from the eye fundus.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for looking at the eye fundus |
This place covers:
Pulse oximetry using measured change in the fluoresence of light. Includes the use of fluorescent agents.
This place does not cover:
Measuring blood gases specially adapted for the eye fundus | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of light, optically excited fluorescence |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording chemical characteristics of blood, body fluids or tissue where the measurement is made in an extracorporeal circuit attached to the patient, e.g. a blood dialysis machine attached to a patient by a catheter. Apparatus for measuring in an external fluid line, e.g. measurement cassette connected to the patient's blood circulation by a catheter.
This place does not cover:
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, flow through cuvettes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other treatment of blood in extracorporeal circuits | |
Measuring blood gas characteristics of a patient undergoing therapy |
This place covers:
Pulse oximetry using the measured change in the polarisation characteristic of light.
This place does not cover:
Investigation or analysing materials by the use of optical means, using polarisation-affecting properties |
This place does not cover:
Using optical sensors specially adapted for foetal tissue |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording of characteristics of blood, body fluid or tissue using optical sensors specially adapted for foetal or neonatal monitoring.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using chemical or electrochemical methods specially adapted for foetal tissue |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording chemical characteristics of blood, body fluids or tissue using chemical or electrochemical sensors, where the measurement is made in-vivo or on a blood or fluid sample immediately after sampling, e.g. sampling by lancet. Includes apparatus for measuring in an external fluid line, e.g. measurement cassette connected to the patient's blood circulation.
This place does not cover:
Using enzyme electrodes | |
Investigating or analysing biological material in vitro by using electrochemistry |
This place does not cover:
Using chemical or electrochemical methods specially adapted for foetal tissue |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices |
This place does not cover:
Using optical methods specially adapted for foetal tissue |
This place does not cover:
Measuring or testing processing involving enzymes, enzyme electrodes | |
Investigating or analysing biological material in vitro by using electrochemistry |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of apparatus for calibration, e.g. calibration protocols | |
Sensors provided with means for identification combined with means for recording calibration data, e.g. on memory chip | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, detection standards or calibrating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hypodermic syringes |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Piercing element | skin penetrating component, e.g. blade, needle, lancet, laser beam |
piercing or lancing device | device ready to be used for lancing |
driving device | device for driving a piercing element, e.g. spring |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording the psychological state of a subject from physiological measurements. Any type of measurement may be applied, e.g. skin resistance, motion activity.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting using light | |
Detecting using MRI | |
Measuring movement of the body or parts thereof for determining motor skills | |
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof | |
Devices or methods to cause a change in the state of consciousness |
Classification is made in A61B 5/16 and in the particular physiological measurement, e.g. A61B 5/16 and A61B 5/0531, when appropriate.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Eye testing |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Reaction-time training with a substantial physical effort |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determining motor skills | |
Reaction-time games |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for examining the eye | |
Processing of images of the eye | |
Acquiring or recognizing eyes, e.g. iris verification |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording the state of alertness or consciousness of drivers or machine operators from physiological measurements. Any type of measurement may be applied, e.g. tracking eye motion, measuring heart rate.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Safety devices for propulsion-unit control responsive to incapacity of driver | |
Alarms responsive to an undesired or abnormal condition indicating sleep |
This place covers:
Evaluation of the urinary system.
Urine collection bags comprising urine sensors
This place does not cover:
Evaluating the male reproductive system |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring contraction of body parts | |
Measuring constituents of body fluids other than blood | |
Devices for taking urine samples |
This place covers:
Evaluate renal function, e.g. detect renal failure
1) By urine analysis:
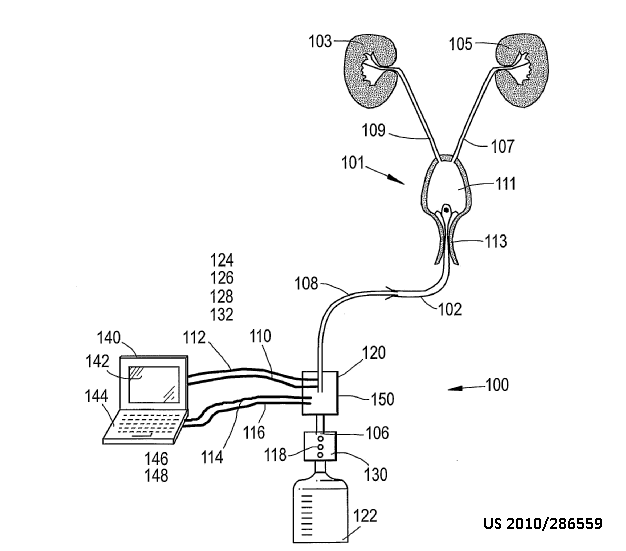
detecting a change in a urinary parameter indicative of a kidney malfunction, e.g. pH, a sodium level, an oxygen level, a potassium level.
2) By blood analysis:
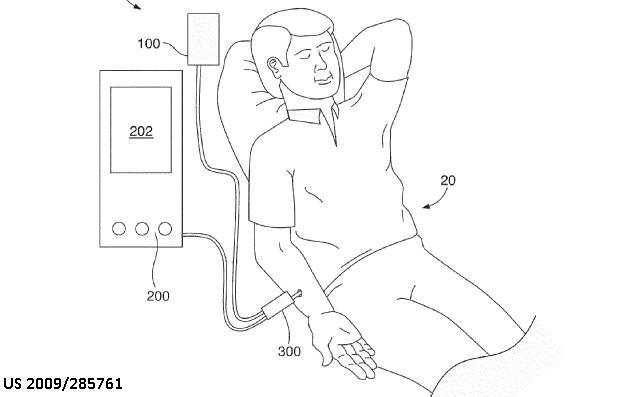
Fluorescent molecules are introduced into the blood stream.
Over a period of time, a measurement of the intensities of the reporter and marker fluorescent molecules is taken.
A ratio is calculated to determine a glomerular filtration rate and therefore the health of the subject's kidney.
This place does not cover:
Dialysis systems |
This place covers:
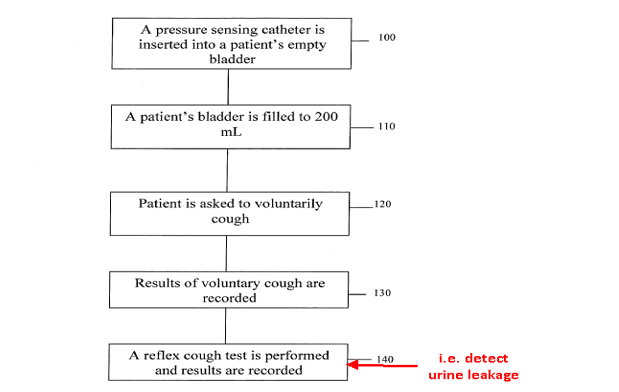
Detection of urine flow:
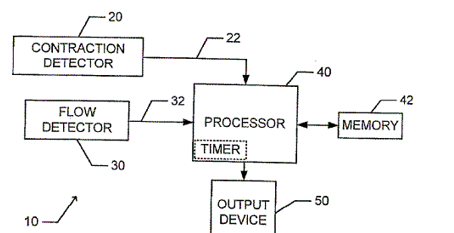
Flow detector 30 is configured to detect the onset of urination. For example, flow detector 30 generates a flow signal 32 upon detecting a flow of urine.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Assessing bladder internal pressure | |
Electromyography of genito-urinary organ | |
Electrical stimulation of urinary organs to alleviate incontinence |
This place covers:
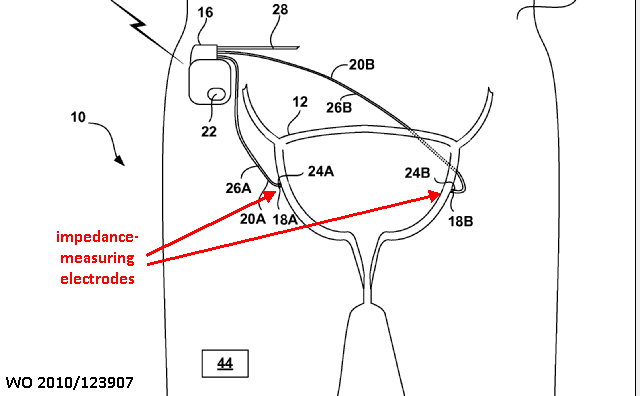
System 10 determines the filling status of a urinary bladder 12 of a patient 14 based on electrical impedance of the bladder
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring contraction of body parts |
This place covers:
Measuring quantity of urine
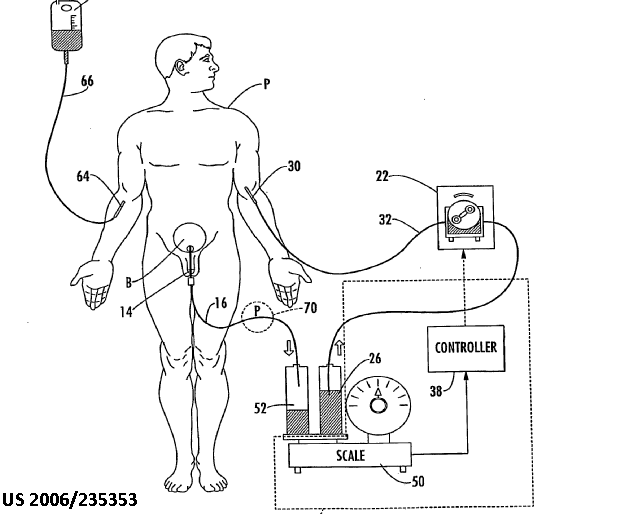
This place does not cover:
Measuring contraction of parts of the body, e.g. organ, muscle |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exercising apparatus | |
Measuring of work or force in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments for dentigraphy |
This place covers:
Apparatus for measuring, detecting or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals generated by the body or parts thereof. The measurement does not require application of an electric current or voltage nor application of an electromagnetic or magnetic field. Apparatus for ambulatory or long-term monitoring of bioelectric signals. Apparatus for measuring combined with analysis of bioelectric signals for diagnosis.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of electrodes specially adapted for in-vivo measurements, e.g. for impedance measurements | |
Medicinal preparations involving or responsive to electricity, magnetism or acoustic waves | |
Electrodes for electrotherapy implanted or inserted into the body; for stimulating the brain; spinal or peripheral nerve electrodes; nerve electrodes not otherwise provided for | |
Controlling electrotherapy using a physiological parameter, e.g. heart potential | |
Electrotherapy combined with monitoring a physiological parameter | |
Electrically-conducting adhesives | |
Indicating or recording in connection with measuring in general | |
Measuring or recording or electrical currents of voltages in general | |
Recording with possibility of play-back | |
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices | |
ICT specially adapted for mining of medical data, e.g. analysing previous cases of other patients | |
Emergency protective circuit arrangements | |
Amplifiers | |
Interference or noise suppression in transmissions systems |
This place covers:
Apparatus and methods for detecting electromagnetic fields generated by the body or biomagnetic signals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring magnetic variables in general |
This place covers:
Constructional details of electrodes
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrodes for bioimpedance measurements | |
Probe or electrodes for electrosurgery | |
Manufacturing methods specially adapted for producing electrodes | |
Electrodes for stimulation in electrotherapy |
Where the electrode(s) is(are) adapted for both measuring and applying therapy classification in this group and the corresponding therapy or electrosurgical group takes place.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for maintaining contact with the body by using a vacuum |
This place covers:
Conductive adhesive or gels for improving the electrical contact between the electrode and the skin or body surface
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adhesives characterised by being electroconductive |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting electrode failure or electrode disconnection from patient. Also called lead failure.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Monitoring or maintaining sensor contact pressure |
This place covers:
Arrangements of multiple ECG electrodes mounted on a single substrate, e.g. a flexible strap. Arrangements of multiple electrodes joined by a cable. Arrangements of multiple ECG electrodes mounted or fixed on an item of clothing, e.g. vest.
This place does not cover:
For introduction into the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Patient cord assembly, e.g. cable harness |
This place covers:
Details of ECG electrodes specially adapted to be introduced into the body. All types of apparatus, e.g. catheters, guidewires, probes or implanted devices for introducing ECG electrodes into the body. Electrodes for epicardial or endocardial measurements of ECG or electrograms.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details of invasive sensing devices | |
Electrodes for electrotherapy for implantation or insertion into the body, epicardial or endocardial electrodes |
This place covers:
Multiple electrods on a single holder, e.g. multiple electrodes on a catheter.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors mounted on catheters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors for measuring characteristics of blood specially adapted for foetal tissue | |
Anchoring means for maintaining sensor contact with the body, e.g. barbs |
This place covers:
Input circuits specially adapted for EEG, ECG or EMG signals, e.g. for filtering, amplification, switching.
This place covers:
Means for the electrical isolation of the patient side electrodes from the mains power supply, e.g. using an isolation transformer or optocoupler.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coupling light guides with opto-electronic elements | |
Adaptations of transformers for specific applications of functions | |
Amplifiers using electroluminescent element or photocell |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements of sensors with cables or leads, e.g. cable harnesses |
This place covers:
Apparatus for switching the connection of ECG leads to the monitor or analysis unit, e.g. using a multiplexer.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Modular apparatus with a separable interface unit, e.g. for transmission or switching signals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating the central nervous system for particular diseases | |
Evaluating the musculoskeletal system | |
Arrangements for analysing frequency spectra in general |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording ECG signals on the surface of the body. Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording electrograms from the heart surface or from within the heart. Apparatus for long-term or ambulatory monitoring of ECG. Apparatus for measuring ECG combined with analysis of the ECG to obtain a diagnosis.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Remote monitoring of patient with the measured ECG signals being transmitted from the patient to a remote monitor or site | |
Controlling electrotherapy using a physiological parameter, e.g. heart potential |
This place covers:
Hand-held or portable apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand-held or portable apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording |
This place covers:
Recording apparatus specially adapted for long-term or ambulatory recording of ECG, e.g. 24 hour recording, Holter monitors.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Recording measured values |
This place covers:
Integrated circuit memory devices may be built into the device or may comprise removable memory chips, e.g. flash memory stick.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Solid state data loggers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for displaying electric variables or waveforms, e.g. cathode-ray oscilloscopes | |
Output arrangements for digital computers, output to a display device |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording ECG in combination with analysis of specific parameters of the electrocardiograph cycle in order to determine a diagnosis, e.g. analysis of ST segment elevation for determining ischaemia. Includes analysis of epicardial or endocardial electrograms for diagnosis.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Controlling electrotherapy by using a physiological parameter, e.g. heart potential | |
Pattern recognition in time domain, e.g. time-series data |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Physiological signal analysis for synchronising or triggering a measurement or image acquisition | |
Circuit arrangements for obtaining a series of X-ray photographs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices provided with high/low alarm device |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording electroencephalographic signals (EEG) for diagnosis. Apparatus for measuring combined with analysis of signals for determining a diagnosis, e.g. for determining a seizure.
This place does not cover:
Devices for psychotechnics, e.g. for determining the psychological state |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating the central nervous system | |
Devices or methods to cause a change in the state of consciousness | |
Evaluating the central nervous system | |
Measuring EEG of a user of sports apparatus | |
Input arrangements for computers based on nervous system activity, e.g. brain machine interfaces using EEG | |
Pattern recognition in time domain, e.g. time-series data |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Analysing frequency spectra in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Biofeedback per se |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording EEG that has been evoked in response to the application of a stimulus.
This place covers:
Using a sound, acoustic or audible stimulus to evoke an EEG response.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Audiometering with electric or electronic apparatus, e.g. using evoked EEG response |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrical operating or control means of prostheses implantable into the body | |
Electrical operating or control means of prostheses not implantable in the body, e.g. myoelectric |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording electro-oculographic signals or electroretinographic signals.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring or inducing nystagmus |
This place does not cover:
Evaluation of sleep, anaesthesia, pain |
This place covers:
Evaluate sensations, e.g.:
Temperature sensitivity:
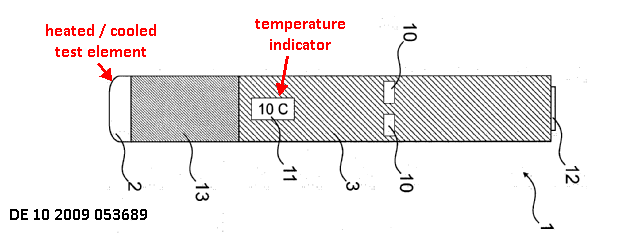
This place does not cover:
Diagnostic temperature sensing | |
Audiometry | |
Evaluating the central nervous system |
This place covers:
1) Manual odour test using odour samples
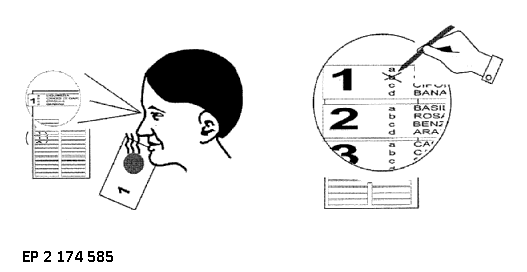
2) Automatic test device
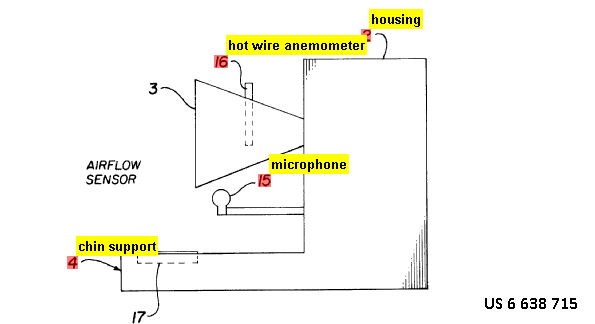
- Dispensing a controlled amount of volatile fluid
- Determining if the patient has sensed the volatile fluid
- Dispensing an increased quantity of volatile fluid if the patient has not sensed the volatile fluid or a reduced quantity of volatile fluid if the patient has sensed the volatile fluid.
This place covers:
1) Manual test using taste samples;
Each strip 22, 32 is comprised of a thin layer 23, 33 of material with a specific taste.
2) Automatic taste sensor
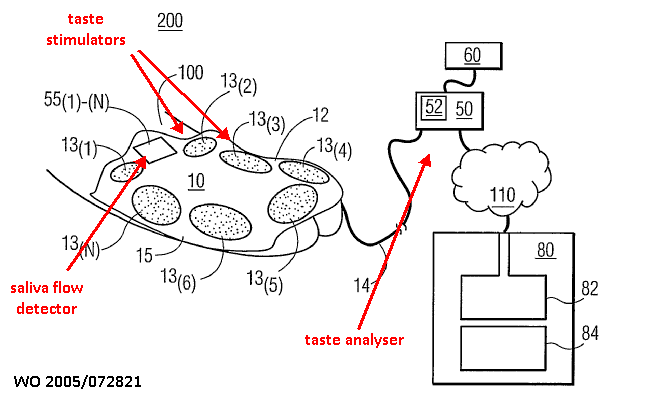
This place covers:
Evaluate forces applied by the patient to maintain balance, possibly while perturbing her balance
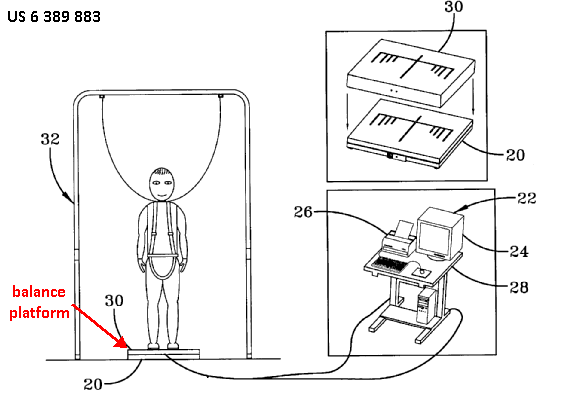
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof |
This place covers:
Evaluate sympathetic/parasympathetic activity
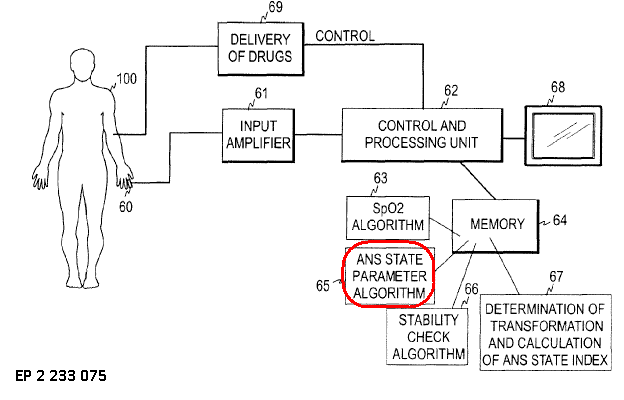
This place does not cover:
Sleep evaluation | |
Pain perception evaluation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electroencephalography [EEG] | |
Using MRI |
This place covers:
Various regions of the brain 108 may be colour coded according to a scale 112 to represent the cortical thickness, or deviation from normal thickness
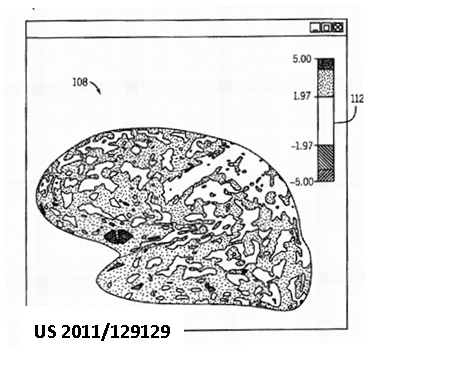
This place does not cover:
Intracranial pressure measurements | |
Using optical sensors, specially adapted for cerebral tissue | |
Electroencephalography [EEG] |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for psychotechnics |
This place covers:
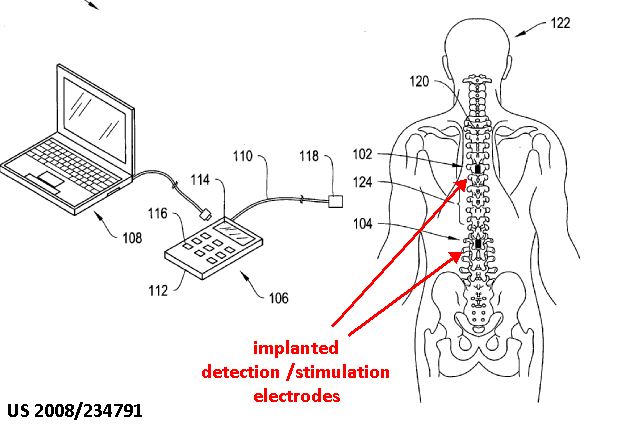
This place does not cover:
Epidural space location |
This place does not cover:
Determining level of anaesthesia | |
Determining pain perception |
This place covers:
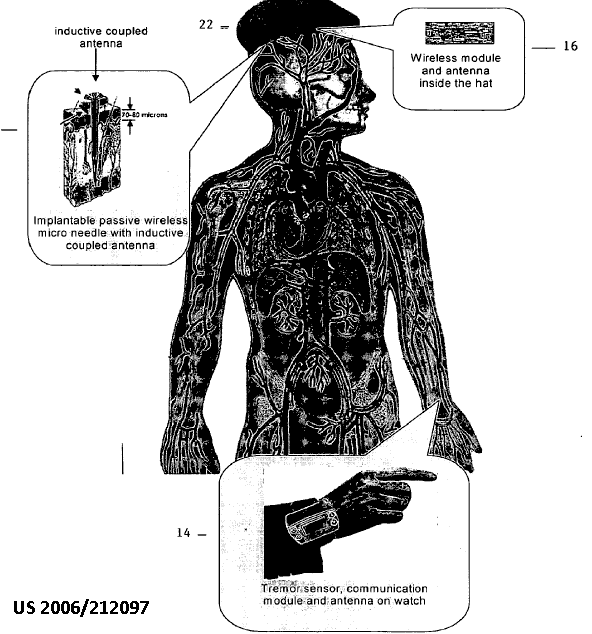
This place covers:
All types of diagnostic apparatus and methods for diagnosing or monitoring cognitive diseases. Includes objective type measurement apparatus, e.g. measuring a physical characteristic of the brain tissue and subjective type apparatus, e.g. for applying cognitive tests to the patient.
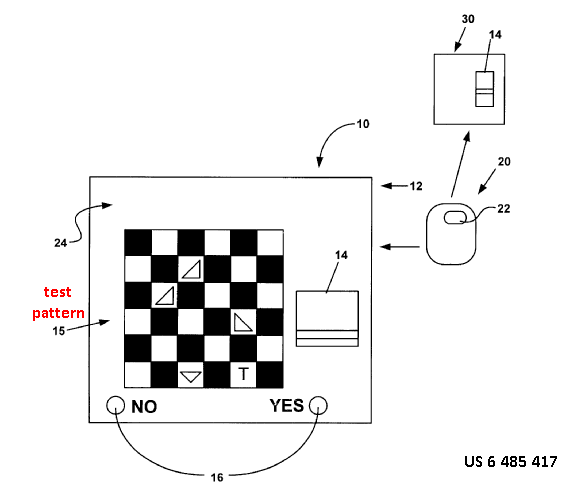
This place covers:
Assess seizures based on detected movement patterns, heart rate variability, EEG etc.
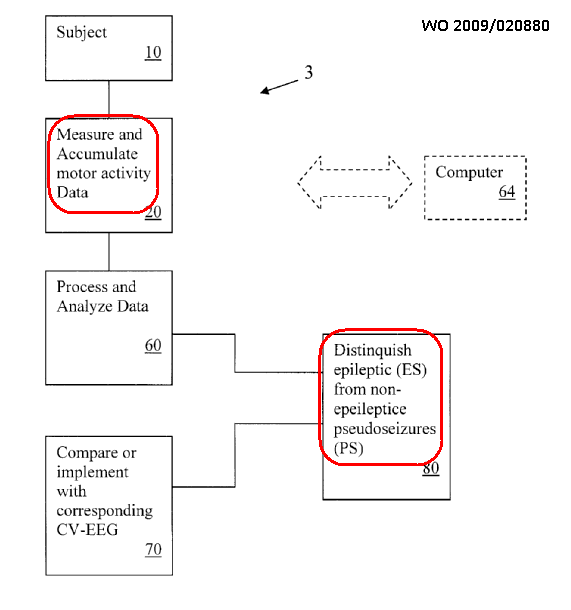
This place covers:
Evaluation of allergies or intolerances, with or without sensors of physiological quantities:
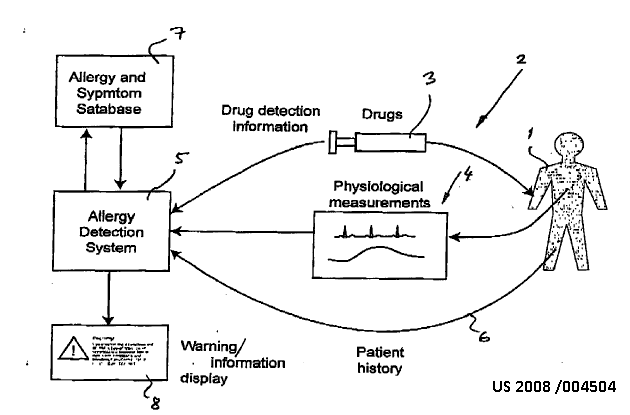
This place does not cover:
Monitoring explanted organs (i.e., between explantation and implantation) |
This place does not cover:
Gastrointestinal endoscopy | |
Biorhythm | |
Measuring sweat production | |
Evaluating metabolism | |
Determining consituents of the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catheters for measuring non-vascular pressure | |
Detecting gastrointestinal contractions | |
Diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonicwaves in body cavities or body tracts, e.g. by usingcatheters |
This place covers:
Backflow detection from stomach to oesophagus, e.g. by impedance measurement with a balloon catheter:
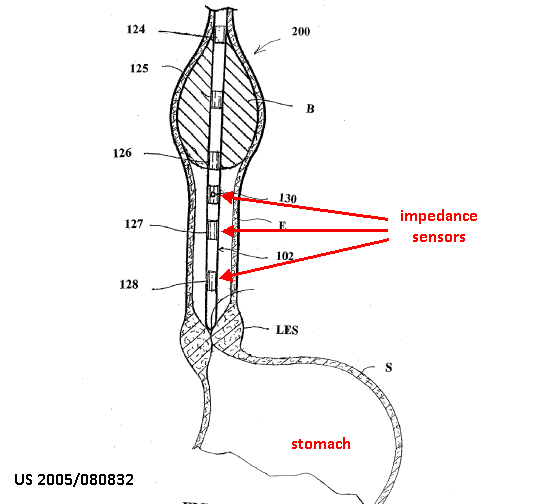
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 5/4216:
by pH measurement in the gastrointestinal system
This place covers:
Evaluating oesophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines, endocrine glands
This place covers:
Determining the activity of endocrine glands, e.g. determining the response of the hypothalamus to stimulation.
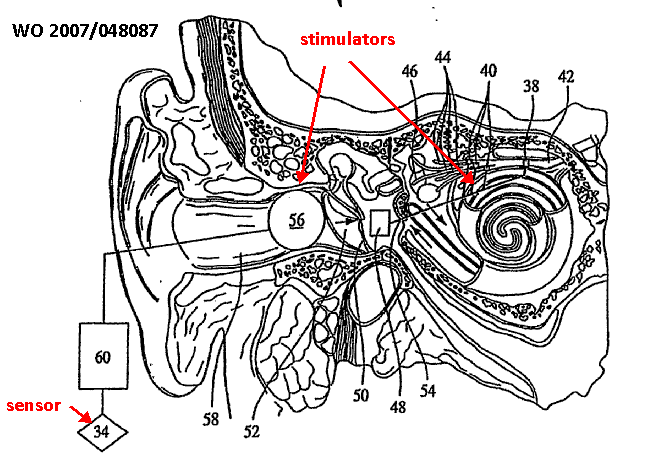
This place covers:
Evaluating the function or state of the stomach, e.g. determining the amount of food or drink ingested.
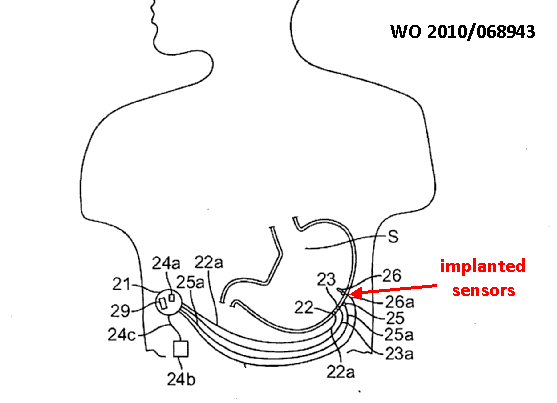
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 5/425
For example, electropancreatography:
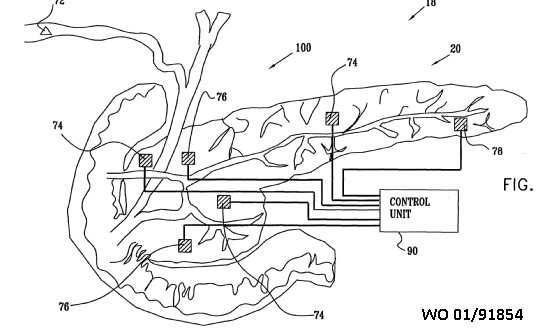
This place covers:
Evaluating the function or state of the intestines, colon or appendix, for example, identification of intestinal ischemia
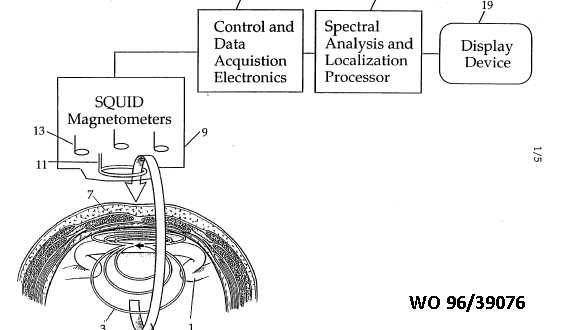
This place covers:
Sweat, sebum, saliva, gastrointestinal secretions, mammary secretions, vaginal secretions
This place does not cover:
Tear secretion |
This place covers:
Detect, e.g., alcohol content in perspiration fluid
This place covers:
Reagent changing colour according to sebum concentration
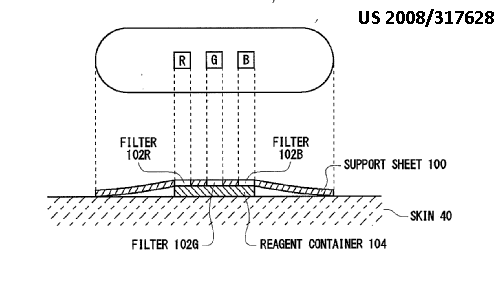
This place covers:
All types of evaluations of vaginal secretion including rate of production, viscosity etc.
For example, evaluating pH of vaginal secretions
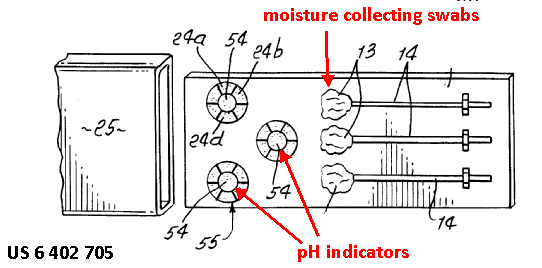
This place covers:
All types of apparatus and methods for evaluating the breasts, including measurement of breast size and diagnosis of breast disorders, e.g. by detecting properties of the breasts
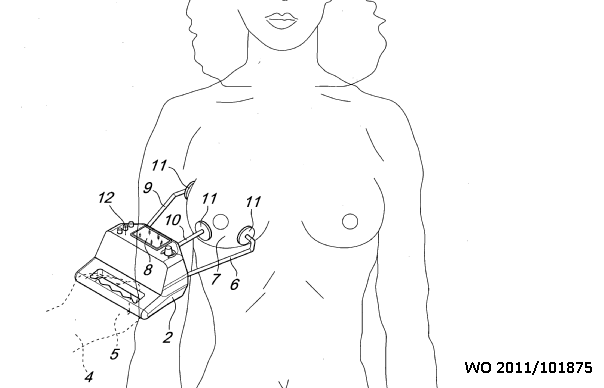
This place does not cover:
Optical mammography | |
X-ray mammography | |
Ultrasound mammography |
This place covers:
Evaluations of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix, vagina
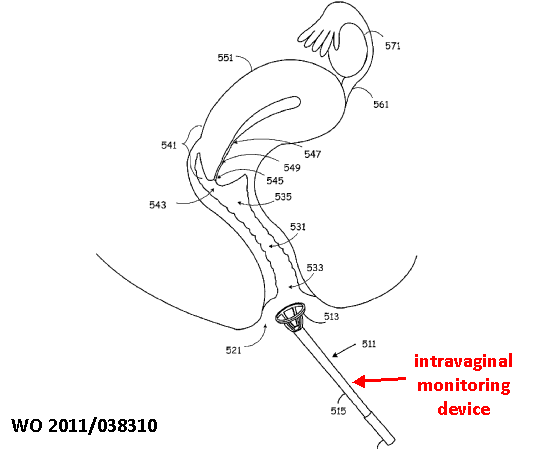
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pregnancy and labour monitoring |
This place does not cover:
Assessing cervix alteration |
This place covers:
Monitoring pregnancy and labour
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting uterine fluid pressure |
This place does not cover:
Measuring pressure of intrauterine fluid |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of a device for examining the prostate
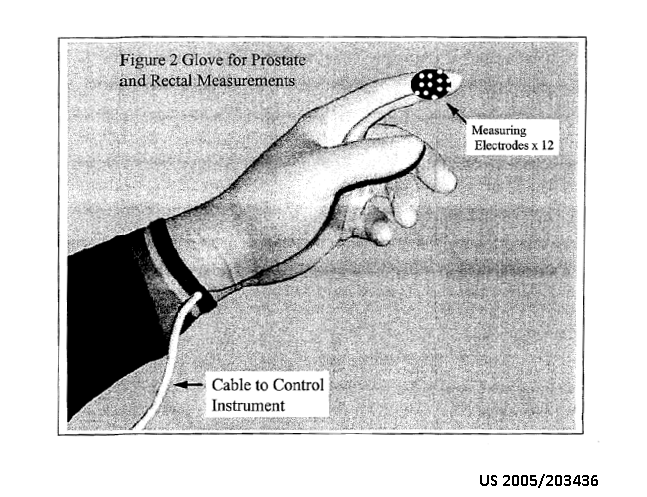
This place does not cover:
Colonoscopes |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 5/4387
E.g. estimate drug dosage as a function of testicle size
This place does not cover:
Identification of persons |
This place does not cover:
Evaluation of skin sensitivity |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determining colour for diagnostic purposes | |
Colour measurement in general |
This place covers:
Determining skin hardness, elasticity, tenderness, stiffness, pliability, laxity, mobility
 .
.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring roughness of surfaces in general |
This place does not cover:
Measuring contraction of wounds |
This place covers:
Evaluate scalp conditions:
This place covers:
All types of apparatus or methods for evaluating the hair and disorders of the hair or hair growth in-vivo.
For example, evaluating hair density:
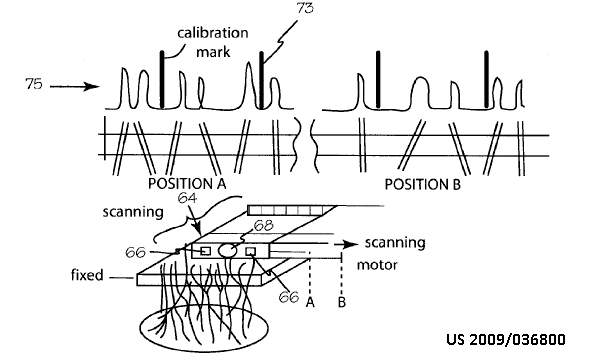
Illustrative example, evaluating hair colour:
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording using colour cards |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Colour evaluation in general |
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording using colour cards |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Colour evaluation in general |
This place does not cover:
Measuring for testing the shape, pattern, size or movement of the body or parts thereof for podologic studies | |
Foot measuring devices | |
Detecting skeletal, cartilage or muscle noise |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Particular body parts of the musculoskeletal system | |
Positioning the sensor in relation to a particular body part of the musculoskeletal system |
This place does not cover:
Evaluating teeth |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Examining bone tissue using radiation diagnosis | |
Examination of bone material using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves |
This place does not cover:
Measuring muscular strength | |
Electromyography [EMG] |
This place covers:
Testing joints for stability or strength, e.g. knee laxity.
This place does not cover:
Evaluating or diagnosing ligaments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Goniometers |
This place does not cover:
Measuring using light, adapted to oral or dental tissue | |
Testing vitality of teeth by means of electric currents or magnetic fields | |
Detecting tooth mobility |
This place covers:
Determining a static posture of the body,e.g. whether a person is standing, sitting or lying. Includes also determination of spinal posture due to curvature or inclination
This place does not cover:
Measuring movement of the entire body or parts thereof for determining posture transitions |
This place covers:
Speech analysis for diagnostic purposes, e.g. evaluating speech disorders, evaluating speech for determining a subject's psychological state.
This place does not cover:
Speech analysis for identification of individuals | A61B 5/117 and G07C 9/37 |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Speech analysis per se |
This place covers:
Apparatus or methods for monitoring or analysis of sleep.
This place does not cover:
Determining level or depth of anaesthesia |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for inducing sleep |
Determining sleep quality may comprise sleep detection as in A61B 5/4809 or detecting sleep stages as in A61B 5/4812. In this case also A61B 5/4809 and/or A61B 5/4812 should be given.
This place covers:
Monitoring or investigating sleep apnoe, e.g. multiparameter monitoring or polysomnography. Also for SIDS.
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
SIDS | sudden infant death syndrome. |
This place covers:
Determining/detecting/monitoring the level of anaesthesia by measuring a physiological parameter, e.g. EEG, EMG, etc.
This place does not cover:
Measuring movement of the entire body or parts thereof to asses neuromuscular blockade | |
Electric apparatus for detecting reflex action | |
Introducing anaesthetics |
This place covers:
Testing/indicating/recording/assessing level of pain for all parts of the body. Includes all types of apparatus, e.g. charts, expert systems, questionnaires etc.
This place does not cover:
Determining level or depth of anaesthesia |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluating the nervous system | |
Testing skin sensitivity |
This place covers:
Measurement of any physiological parameter indicating subject's compliance with drug therapy or treatment regime. Includes detection of drug or marker in breath, blood, urine etc. by non-invasive measurements and fluid samples, but not for laboratory analysis.
This place covers:
Closed-loop control of therapeutic treatment based on measuring a physiological parameter.
This place does not cover:
Features of imaging apparatus including treatment |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensing and controlling the application of energy in surgical instruments. | |
Heart stimulators controlled by a physiological signal |
This place covers:
Measuring a physiological parameter combined with therapeutic drug/medication delivery. Imaging of drug/medication for targeted delivery. Not for delivery of contrast agents/dyes.
This place does not cover:
Delivery of contrast agents or dyes | A61B 5/0275, A61B 5/0813, A61B 6/504, A61B 6/481 , A61B 8/481 . |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of apparatus for drug delivery/infusion | A61N 1/30, A61M 1/00, A61M 5/172, A61M 25/00, A61M 31/00, etc. |
This place covers:
Measuring a physiological parameter to evaluate the progression or development of a disease over time.
This place does not cover:
Monitoring the effects of medication |
This place covers:
Testing the efficacy or side effects of therapeutic medication.
This place does not cover:
Monitoring or testing the effects of anaesthetics |
This place covers:
Assessment or monitoring based on detecting, measuring or recording of or related to the prosthesis, e.g. measuring motion or position of prosthesis or measurement of physiological parameters or signals, such as myoelectric signals. The detecting, measuring or recording means may or may not be located on or in the prosthesis. The measurement, detection or recording may for example be used as an input signal useful for the control of prosthesis.
The prosthesis assessment or monitoring may produce an input signal useful for the control of prosthetics found in A61F 2/482, A61F 2/70 or A61F 2/72.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof | |
Arrangements of measuring, detecting or recording means, e.g. sensors, on external prosthesis | |
Arrangements of measuring, detecting or recording means, e.g. sensors, specially adapted to be brought in contact with an internal body part, i.e. invasive | |
Prostheses as such | |
Electrical control of prostheses not implantable in the body | |
Bioelectrical control of prostheses not implantable in the body, i.e., relying on physiological signals, such as myoelectric |
This place covers:
Includes, e.g. measurement/analysis of physiological parameter, e.g. pulse, according to oriental or other non-orthodox theories of medicine, e.g. Ayurvedic or Chinese
This place does not cover:
Measuring skin impedance specially adapted for acupuncture |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Acupuncture needles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clocks or watches with indicators for biological cycles |
This place covers:
Providing a feedback signal to the subject of a physiological parameter measured from the subject for the purpose of informing the subject to maintain or modify his/her behaviour such that the measured parameter stays within a certain range, e.g. the subject maintains a certain breathing rate.
This place does not cover:
Electroencephalography using biofeedback |
This place covers:
Apparatus and methods for evaluating the metabolism of the body not involving breath test. Includes measuring basal metabolic rate, determining calorific or energy expenditure from physiological parameters, e.g. heart rate or activity, determining level of radioisotope excretion. Also includes evaluating metabolic syndrome.
This place does not cover:
Measuring rate of metabolism by using breath test |
When evaluation is based on measuring movement, A61B 5/1118 should additionally be given.
This place covers:
Determination of tissue type or evaluating tissue characteristics not covered by other subgroups.
Evaluating a particular tissue type, e.g. for detection of cancer, is dealt with in the subgroups A61B 5/0088, A61B 5/0091, A61B 5/02007, A61B 5/40 - A61B 5/45.
Determination of blood, body fluid or tissue analytes, or blood constituents, e.g. red blood cells, is dealt with in A61B 5/145 and subgroups.
For example, evaluating bone is classified in A61B 5/4504; evaluating skin cells is found in A61B 5/441 and subgroups.
This place does not cover:
Using light to evaluate oral or dental tissue | |
Using light for mammography, e.g. for tumour detection | |
Evaluating blood vessel condition, e.g. elasticity, compliance | |
Measuring body composition by impedance | |
Measuring characteristics of blood, body fluids or tissues | |
Evaluating the nervous system | |
Evaluating the immune or lymphatic system | |
Evaluating the gastrointestinal, the endocrine or the exocrine system | |
Evaluating the reproductive system | |
Evaluating the integumentary system | |
Evaluating the musculoskeletal system |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for radiation diagnosis, clinical applications | |
Detecting organ movements or changes, e.g. tumours, cysts, swellings | |
Other methods or instruments for diagnosis, e.g. instruments for taking a cell sample |
This place covers:
Appartus and methods for determining the proportion of fat in the body. Includes determining the ratio of fat to fat free mass, e.g. using ultrasound, optical measurements, calipers, flotation tanks.
This place does not cover:
Skin gauging |
This place covers:
Apparatus and methods for determining the proportion of fluid in the body or hydration status, Includes water compartments, extracellular water, intercellular water.
This place covers:
Patient is subjected to stress situation, e.g. exercise, change of posture, drugs or valsalva manoeuvre during measurement of physiological parameters. e.g. to determine rate of recovery/investigate regulatory mechanism (homeostasis).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring heart rate variability |
This place covers:
Locating blood vessels, e.g. for blood sampling. Applies also to ultrasound location.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Blood vessel location for injecting media |
This place covers:
Detect epidural space, e.g. by means of a pressure drop that occurs while introducing the needle of a syringe into the patient's body. When the needle reaches the epidural space the lower pressure in the space causes the pressure in the needle to drop, which is indicated by movement of the syringe plunger.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring spinal fluid pressure | |
Puncturing needles for the peridural or subarachnoid space or the plexus, e.g. for anaesthesia |
This place covers:
Arrangements for ensuring the correct position for a sensor to detect a physiological quantity on a patient.
It relates to the position of the sensor, independently of the part of the body which is object of the diagnosis. For example, if impedance electrodes are placed on hands and feet to detect an impedance value of the whole body, the corresponding document must be classified in this group even if no diagnosis of hands and feet is carried out.
This place does not cover:
Sensors provided on surgical tools for measuring tool-related quantities, e.g., contact between tool and tissue, tool penetration length | |
Measuring instruments for implanting a prosthesis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Foot-measuring devices | |
Attachments on the body, e.g. for measuring | |
Car sensors for detecting driver's condition | |
Computers with physiological sensor to allow interaction with the user |
This place covers:
Means for attaching a sensor to a patient's body or for positioning a sensor in contact with a patient's body
This place covers:
Any kind of clothing which is specially adapted to position a sensor in contact with the body
This place covers:
Sensors for measurement on the head. Includes headbands, head straps, masks, spectacles, helmets and caps.
This place does not cover:
Measurement on the eye | |
Sensors to be placed on foetus's head |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted in a garment i.e. resembles clothing, not just straps.
Also for sensors in textiles and fabrics.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Garments adapted to accommodate electronic equipment | |
Patients' vests with incorporated sensors | |
Wearable computers, e.g. on a belt |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted in a garment resembling a vest
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Garments; Clothes |
This place covers:
Sensors mounted in a glove/mitten (not all fingers have to be covered)
- for measurement on the hand itself wearing the glove;
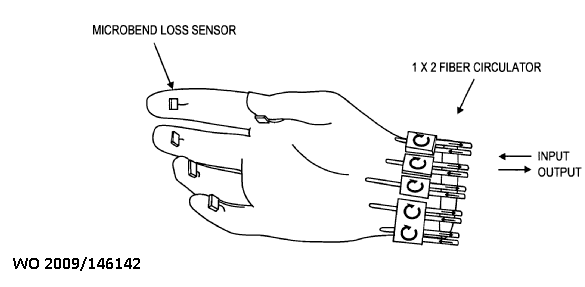
- for measurement on the other hand, another body part or another person or animal:

Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand-worn input devices |
This place covers:
Sensor mounted in footwear, e.g. shoes, socks.
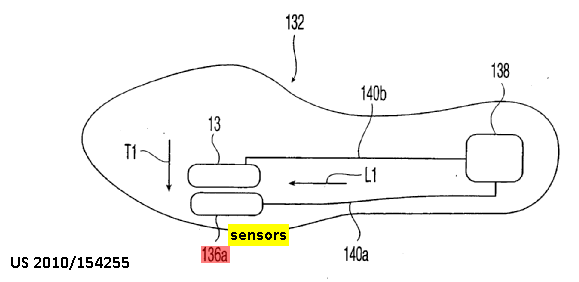
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting podologic data, e.g. load distribution on feet | |
Gait analysis | |
Footwear with electrical or electronic arrangements | |
Pedometers |
This place covers:
Sensors mounted on or in diapers
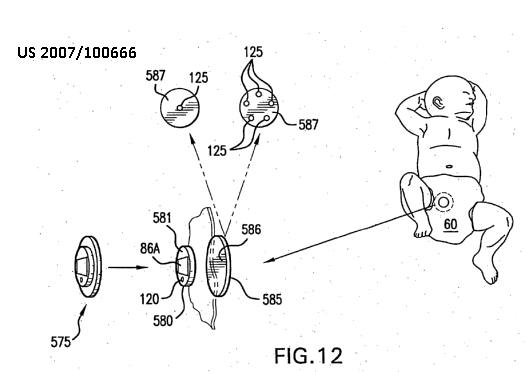
This place does not cover:
Dressings provided with sensor | |
Absorbent pads, e.g. diapers, with wetness indicators |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted in wristwatch type housing.
May not have time keeping function.
Also includes portable devices for receiving data from a sensor separated from the wristwatch housing, e.g. on finger, for data storage/display/further transmission.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable devices for measuring heart rate |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electromyography | |
Control means for non-implantable prostheses | |
Measuring parameters relating to control or test of non-implantable prostheses | |
Input arrangements based on EEG, EMG, ECG, GSR |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on external orthopaedic device
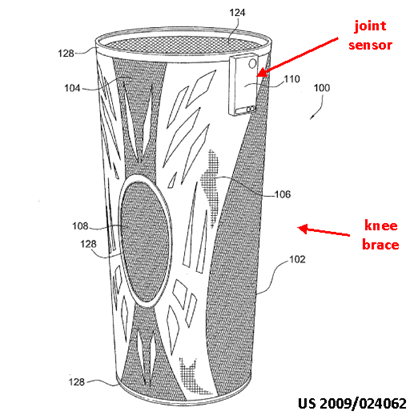
This place covers:
The sensor is suitable for contact with a specific body part, but no particular arrangement is foreseen to provide contact. For example, electrodes to be attached to hands and feet in order to measure whole-body impedance, but no specific attaching means are provided.
This place does not cover:
Arrangements to provide contact with a specific body part |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensor attached to the head of a foetus | |
Sensors mounted on head-worn items, e.g. helmets, headphones or goggles. |
This place covers:
Sensor attached to ear, e.g. as ear clip hooked over the pinna, attached to part of the pinna, not the ear lobe
This place does not cover:
Sensor attached to ear canal or ear lobe |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clips |
This place covers:
Sensor is used for measurement in or close to the ear canal. Shape is adapted to fit in the ear canal. Includes measurement on the ear drum. Includes construction of ear canal probes for audiometry.
This place does not cover:
Instruments for viewing inside the ear canal |
This place covers:
Sensor is attached to the nose.
This place does not cover:
Instruments for viewing inside the nose |
This place covers:
Sensor is held/mounted/fixed for measurement on and in the mouth, e.g. on the lips, tongue, gums and teeth, including snorkel-like mouthpieces.
This place does not cover:
Instruments for viewing inside the mouth | |
Devices using light, specially adapted to mouth and teeth | |
Impedance measurements for testing vitality of teeth | |
Devices for collecting breath | |
Identification by dental data | |
Measuring strength of masticatory organs | |
X-ray for dentistry | |
Depth control for dentistry instruments | |
Mouthpieces in ventilators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring instruments adapted for dentistry |
This place covers:
Sensor is attached to or in the vicinity of the eye.
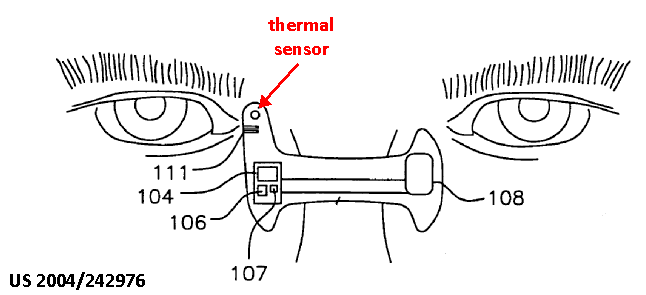
This place does not cover:
Apparatus for testing the sight |
This place does not cover:
Blood pressure cuffs | |
Wristwatch-type devices with sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Portable devices for measuring heart rate |
This place covers:
Sensor is attached/positioned for measurement on the hand. Includes resting hand on shaped surface.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting hand motion | |
Detecting hand force | |
Portable ECG devices | |
Gloves with sensors |
This place covers:
Sensor is used for measurement on the fingers. Includes clamps, wraps, finger receiving cavities, rings. Also for sensors worn by the physician on the fingertips.
This place does not cover:
Blood pressure cuffs adapted for fingers | |
Identification by finger prints | |
Measuring finger strength | |
Gloves with sensors |
This place covers:
Sensor is used for measurement on the foot.
This place does not cover:
Measuring load distribution on feet | |
Measuring dimensions of foot | |
Identification by foot-printing | |
Footwear with sensors |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Foot-measuring devices |
This place covers:
Means specially adapted for maintaining contact between different surfaces, specially adapted to maintain contact between a sensor and the human or animal body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors mounted on worn items |
This place covers:
Sensor is attached to the body, e.g. chest, shoulders, by straps, bands, harnesses
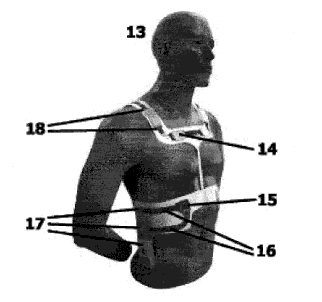
This place covers:
Sensors provided with an adhesive layer for attachment to the skin or body surface that is not a separable or detachable element from the sensor. Includes adhesive applied directly to the skin surface.
This place does not cover:
Using conductive adhesive means, e.g. gels |
This place covers:
Separate adhesive patch or wrap for attaching the sensor to the patient's skin.
This place covers:
Attaching sensor/probe to the skin surface by vacuum.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measurement carried out while applying suction | |
ECG electrodes, including foetal ECG electrodes, attached by suction |
This place covers:
Positioning or holding sensor relative to the body by mechanical arms, e.g. articulated, sliding, swivelling.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Holding arrangements for endoscopes | |
Holding arrangements for ultrasound probes |
This place covers:
Sensors attached to the surface of the body by means of sutures
This place covers:
Sensors affixed to the body by means of clamp, e.g. by elastic force
This place covers:
Means for anchoring the sensor to the body, i.e..with tissue penetration/piercing. Includes prongs, coils, barbs.
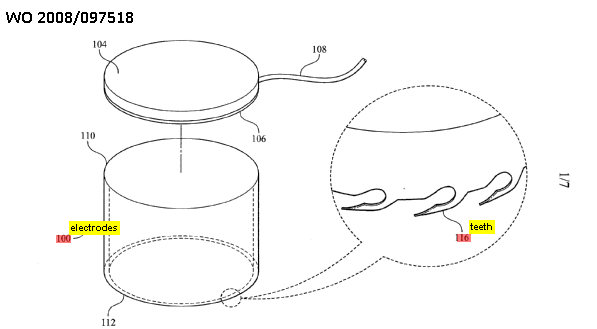
This place covers:
Means for indicating the correct position of a sensor on the body surface
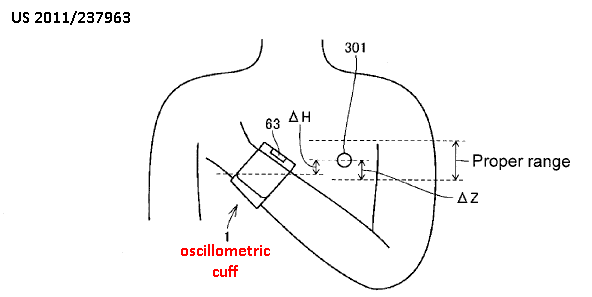
This place covers:
Template/gauge to assist positioning of sensor on the measurement site.
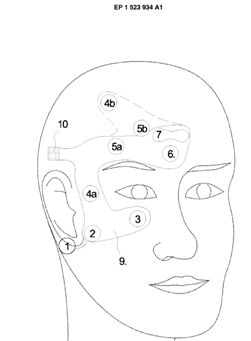
This place does not cover:
Sensors mounted on harnesses |
This place covers:
Site of sensor attachment is marked/referenced (e.g., by marker) so that the sensor may repositioned on the same site. Includes taking an anatomical reference, e.g. palm-print, photograph.
This place covers:
Determining degree of contact between sensor and body surface by any means, e.g. spring bias, inflatable ballons, measuring impedance, measuring applied pressure etc.
This place covers:
Determining, monitoring or controlling the distance between sensor and body surface in order to ensure consistency of measurements taken by the sensor.
This place covers:
Means for attaching or positioning a sensor in contact with an internal part of the patient's body
This place covers:
Sensor is part of an implant (including short-term implants such as needles).
This place does not cover:
Endoscopes |
This place covers:
The sensor is part of a piercing element introduced into the body, e.g. needle, cannula. The sensor is within the body or in the immediate vicinity of its surface.
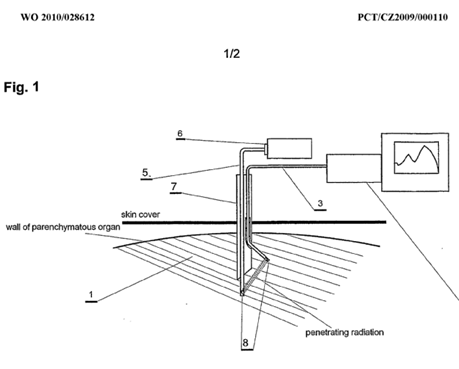
This place covers:
The needle/canula is attached to the skin surface by a base plate.
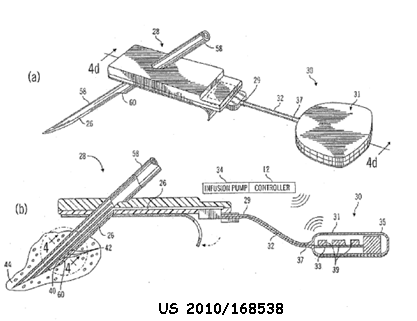
This place covers:
Details of microneedle sensor construction. Includes multiple microneedles, e.g. arrays as electrodes/analyte sensors.
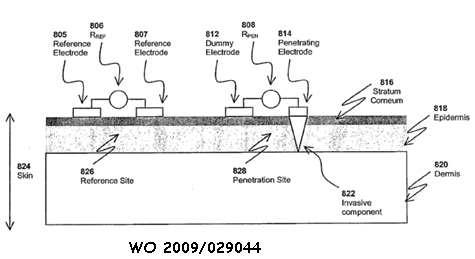
This place covers:
Sensor mounted directly in a guidewire. Guidewire is usually introduced with a catheter.
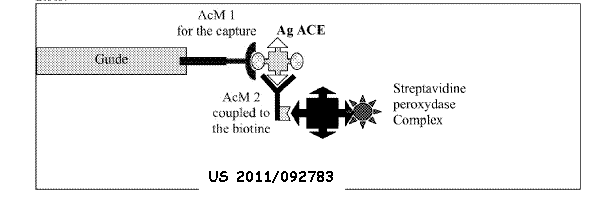
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Catheters with pressure sensors |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a catheter
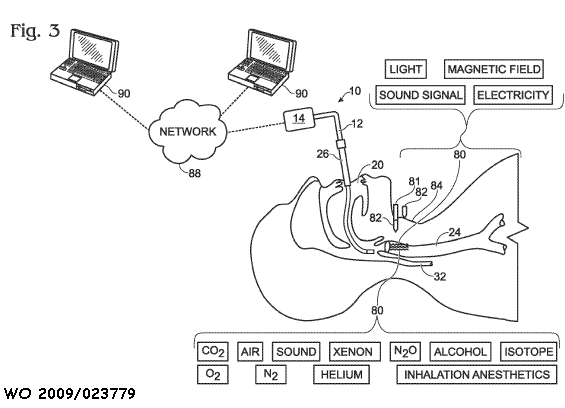
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood pressure by means inserted into the body | |
Invasive optical probe | |
Catheters with pressure sensors |
This place covers:
The sensor is mounted on a balloon catheter
This place covers:
Sensor mounted on a catheter with a curved tip
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a catheter with a looped tip
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a catheter tip with one or more loops, the plane of the loop being perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the catheter
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a catheter with an expandable basket or cage
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a catheter with multiple splines/prongs/tines/spines/arms not joined at their distal tips. Splines are usually expandable from a retracted position.
This place covers:
Specific details of sensors mounted on pacemakers...
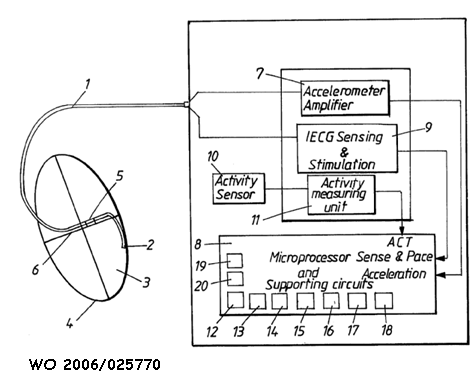
... or on implanted devices comprising a housing like that of a pacemaker
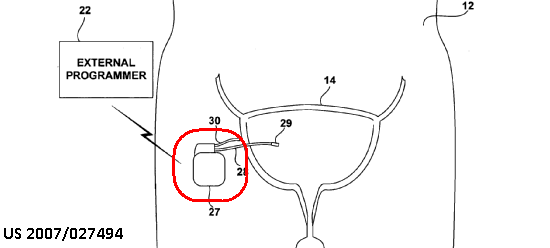 .
.
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on ingestible or implantable capsule, excluding pacemakers.
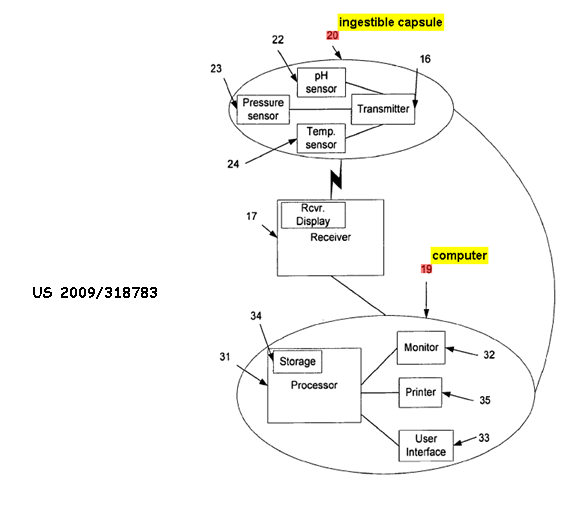
This place does not cover:
Ingestible capsules with imaging means |
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on a device contacting internal blood vessel walls, e.g. stent.
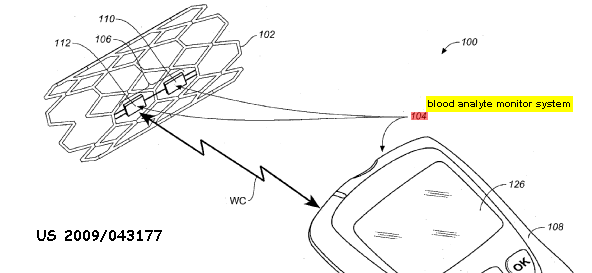
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted in a burr hole, e.g. by cranial bolt.
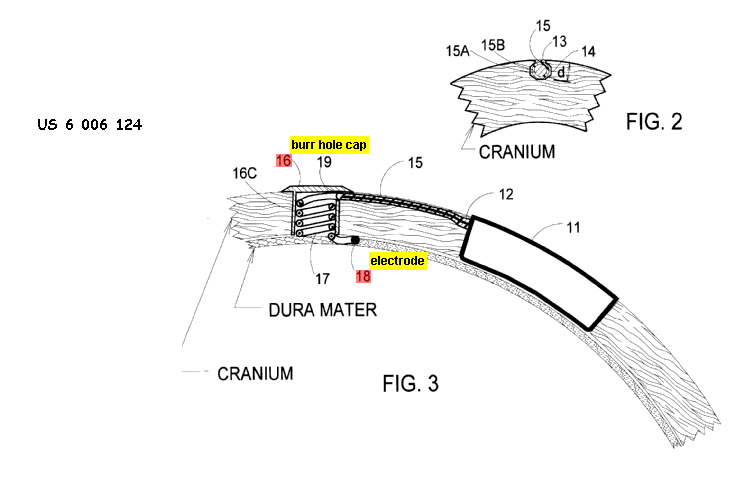
This place covers:
Implants for measuring a physiological parameter with an access port for any application. Includes ports for signal transmission, refilling/replenishing measuring fluid (e.g. enzyme), refilling medication
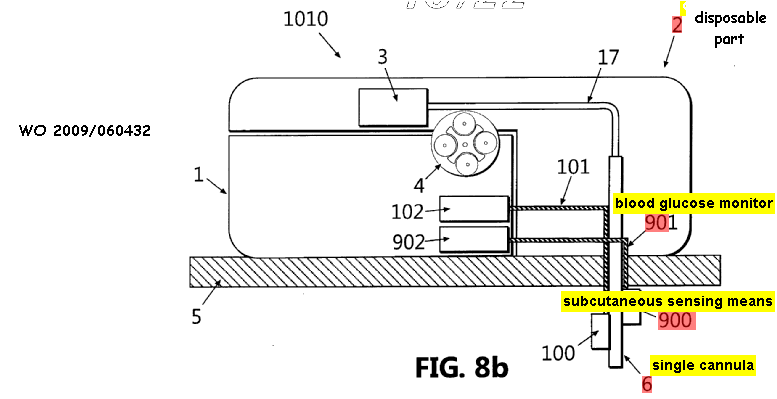
This place covers:
Sensor is mounted on body fluid circuit external to the body. Measurement is carried out during fluid exchange with the body
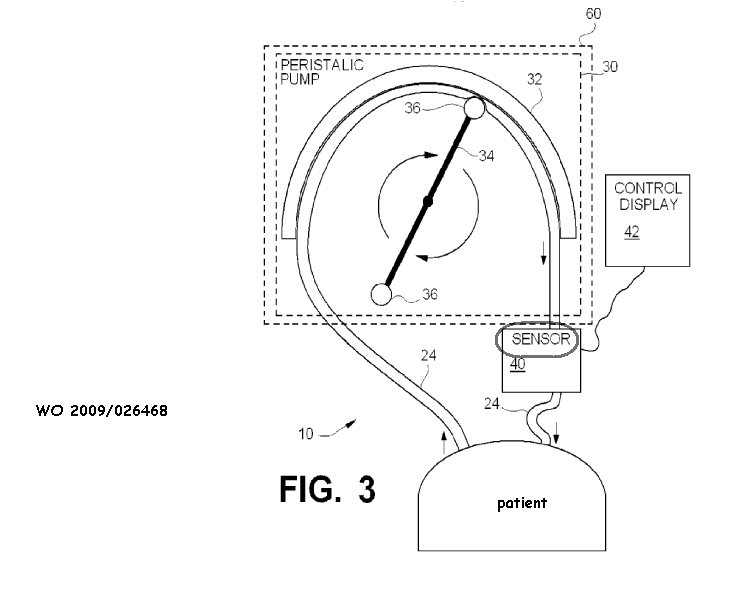
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for controlling media flow into the body |
This place covers:
Sensors suitable for contact with a specific internal body part, but no particular attachment means is foreseen.
This place does not cover:
Mounted on an invasive device |
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Assessing bladder function | |
Measuring pressure within urogenital tract |
This place covers:
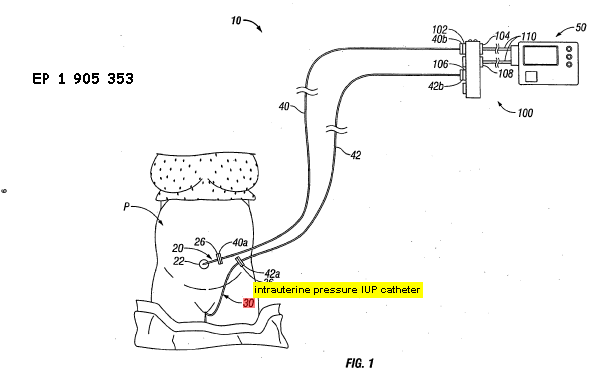
This place does not cover:
Intra-uterine pressure sensors | |
Pregnancy and labour monitoring |
This place covers:
Means specially adapted for maintaining contact between different surfaces, specially adapted to maintain contact between a sensor and internal parts of human or animal body.
This place does not cover:
Mounted on an invasive device |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sensors mounted on worn items |
This place covers:
Means for anchoring the sensor to body tissue i.e. with tissue penetration/piercing. Includes prongs, coils, barbs
This place covers:
Sensors attached to internal body tissue by sutures
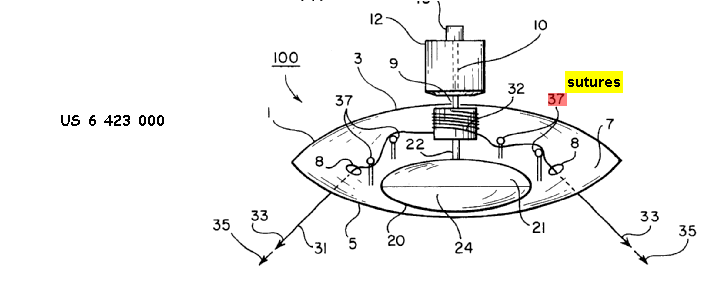
This place covers:
Sensor is used for measurement on the blood vessel. Adapted to be clamped/fitted to the blood vessel.
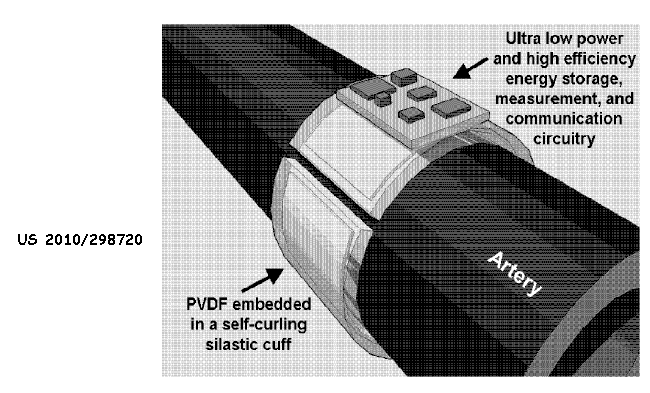 .
.
This place covers:
Monitoring contact between sensor and internal tissue by any means, e.g. spring bias, inflatable balloons, expanding baskets/arms, measuring impedance, measuring applied pressure etc. For all body cavities.
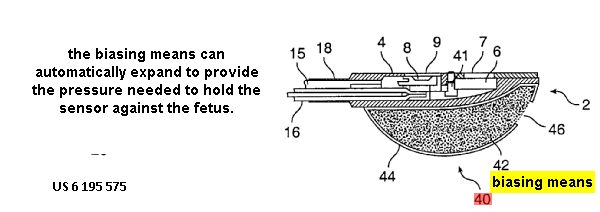
This place does not cover:
Apply compression while taking measurements |
This place covers:
Monitoring the spacing between a sensor/probe and internal tissue by any means, e.g. spacer, inflatable balloons. 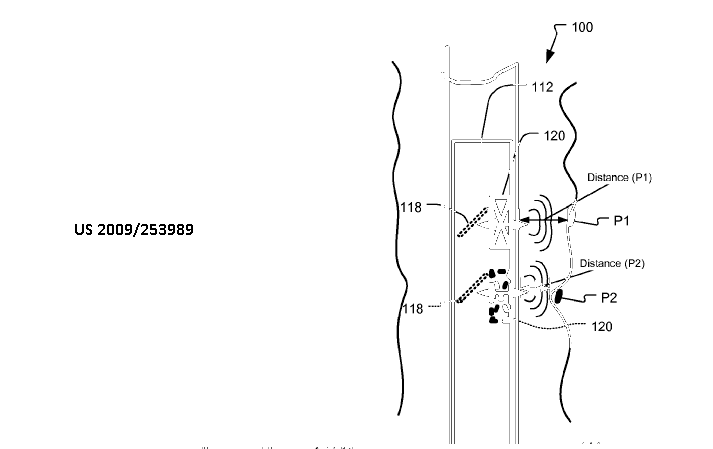 here.
here.
This place covers:
Sensors which are mounted in or on external devices or apparatus. The sensor is not held continuously in contact with the body, e.g. the body or body part is applied to the sensor for taking a measurement, the sensor is adapted to make a non-contact measurement.
This place covers:
Sensor mounted in a cabin or booth to provide isolated measurement environment or privacy
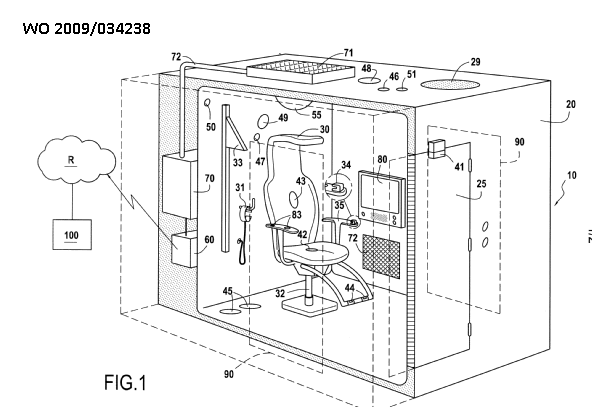
This place covers:
Sensors arranged on furniture, e.g. includes domestic and hospital furniture.
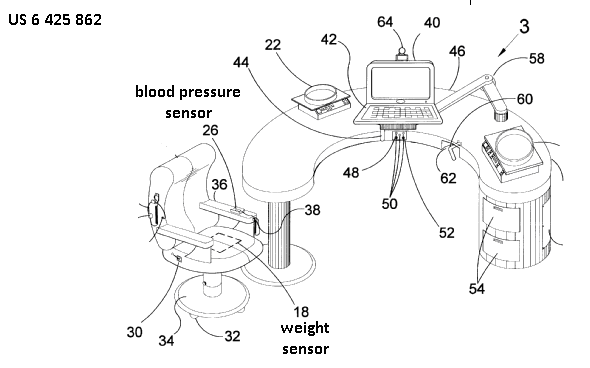
This place covers:
Mat/pad/mattress/cushion with built in sensor for measuring pressure applied by a body part, e.g. used in bed/chair/prosthesis.
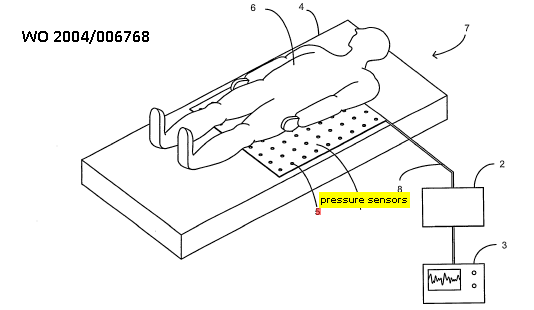
This place covers:
Sensors arranged in car to monitor the driver
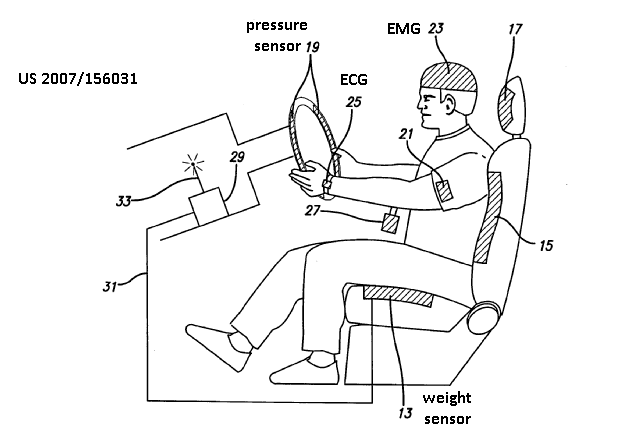
This place covers:
Sensors arranged in sports equipment
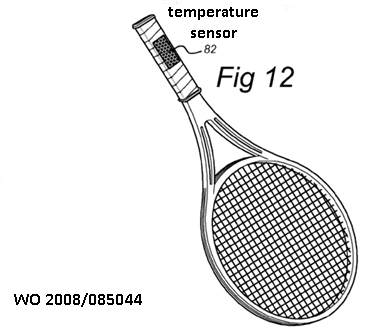
This place does not cover:
Determining movement (e.g. motion capture) | |
Sensors arranged on footwear, garments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluation of athletes | |
Exercising apparatus with means for tracking a movement path | |
Exercising apparatus sensing physical parameters related to user's performance | |
Exercising apparatus sensing physiological parameters of the user |
This place covers:
Sensors arranged on computer input devices
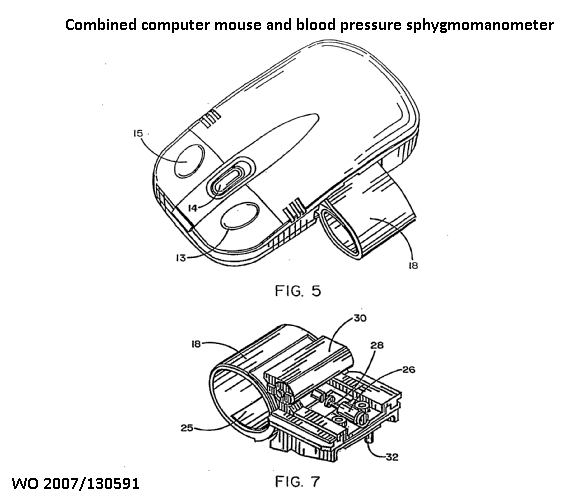
This place covers:
Sensors arranged on a portable electronic device, e.g. a telephone adapted to sense a physiological parameter.
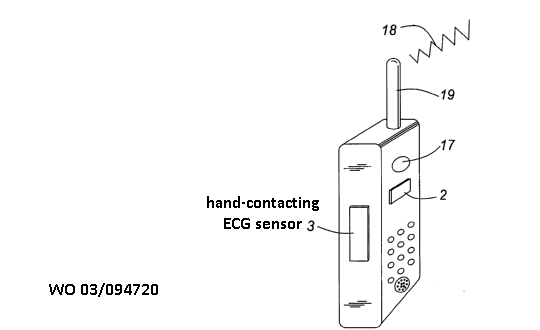
This place does not cover:
Monitoring a patient using a global network for transmitting the physiological signals, e.g. telephone network |
This place covers:
Means for ensuring that the patient, or of a part of her body, assumes the correct position during the measurement

This place does not cover:
Tables for x-ray examinations |
This place covers:
Means to restrain movement of the patient during the measurement, e.g. platforms, chairs, supports for limbs.
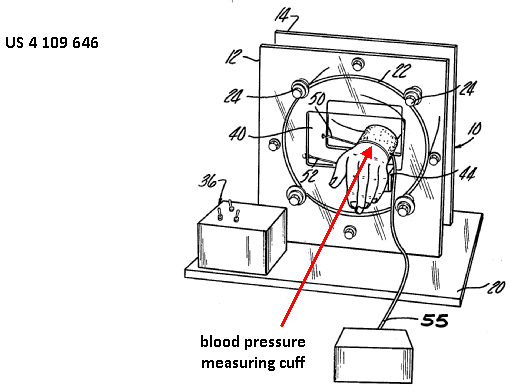
This place covers:
Measuring device comprising tables to aid patient positioning during examination. Special adaptations including windows, cut-outs, connections
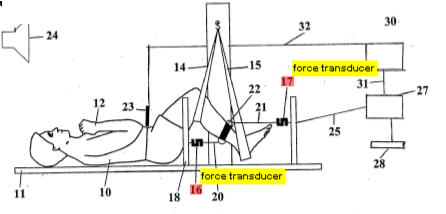
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for positioning patients (MRI, CT) |
This place covers:
Indicia/markings to aid positioning of patient during examination. It may be on apparatus, support, floor.
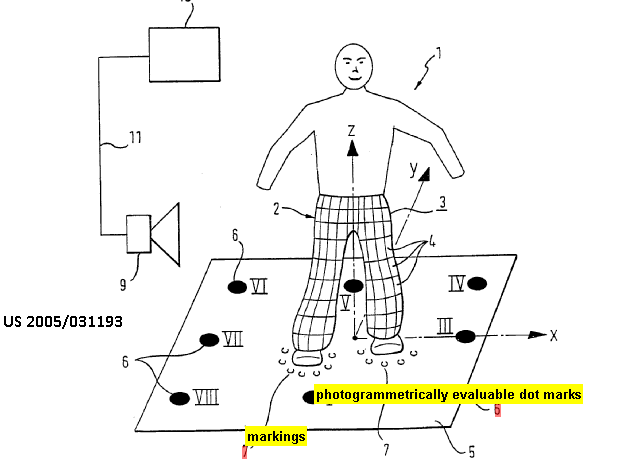
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
Breast positioning means for x-ray or ultrasound examination |
This place covers:
Diagnostic equipment and / or methods involving the use of ionising radiation, e.g. X-ray or gamma ray. Other devices for radiation diagnosis can be found in:
Electric currents or magnetic fields | |
Magnetic resonance | |
Optical imaging | |
Opto-acoustic imaging |
Devices for radiation diagnosis generally consist of complex electro-mechanical arrangements of radiation source and detection units, controlled following a particular acquisition technique to obtain medical diagnostic data relating to a patient's body part. A complete characterization of these devices therefore requires the identification of both constructional and operational aspects according to the following rules.
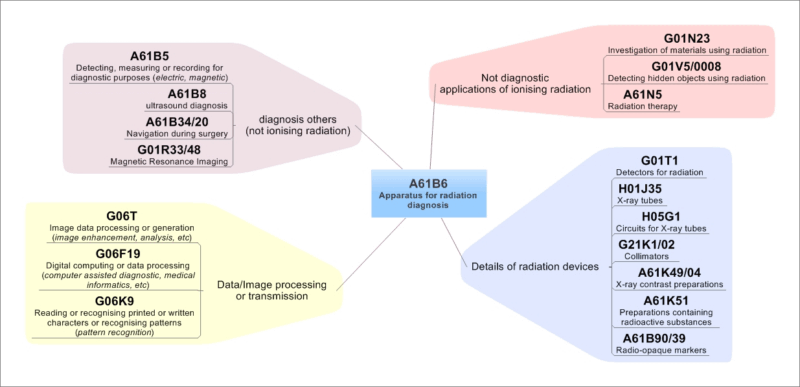
Several subclasses, groups and subgroups provide for the different components or functional aspects constituting the devices for radiation diagnosis. It should be emphasized that documents describing these components should be classified in A61B 6/00 only if they disclose a radiation diagnostic device and the link between said components or functional aspects and the radiation diagnostic device or clinical application is not trivial.
As an example, a document describing constructional details of a PET scanner should have the subgroup A61B 6/037 and the corresponding class for said constructional details (a subgroup of A61B 6/44). A document describing particular details of a radiation detector should be classified in the corresponding group of G01T 1/00, even if a clinical application of said detector is mentioned. However, if e.g. details of the arrangement of said detector in a scanner for said particular clinical application are disclosed, then it should also be classified in A61B 6/037 and in the corresponding subgroup of A61B 6/50.
The same principle applies to other neighbouring fields such as image processing G06T. A document disclosing an algorithm for image enhancement should be classified under the corresponding subclass of G06T, even if the document mentions that the images are X-ray images.
However, if the algorithm requires particular constructional or functional details of the radiation diagnostic device or if there is a non-obvious link to the particular clinical application, then the document should also be classified in the corresponding subgroup of A61B 6/00.
On the other hand, classify only in A61B 6/00, if there is only a mention of use of an algorithm for image enhancement, but the disclosure deals mainly with details of the radiation diagnostic device.
Devices for radiation diagnosis combined with radiation therapy equipment should be additionally classified in A61N 5/00.
This place does not cover:
Instruments measuring radiation intensity for application in the field of nuclear medicine, e.g. in vivo counting | |
Apparatus for taking X-ray photographs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis using light | |
Diagnosis using the opto-acoustic effect | |
Diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging | |
Diagnosis using sonic, infrasonic or ultrasonic waves | |
Navigation during surgery | |
Radio-opaque markers | |
X-ray contrast preparations | |
Preparations containing radioactive substances | |
Radiation therapy | |
Investigation of materials using radiation | |
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance imaging systems | |
Detectors for X-ray, gamma, etc radiation | |
Detecting prohibited goods, e.g. weapons, explosives, hazardous substances, contraband or smuggled objects | |
X-ray photographic processes | |
Image data processing | |
Medical informatics | |
Collimators and grids | |
X-ray tubes | |
X-ray apparatus involving X-ray tubes; Circuits therefor |
Some of the sub-groups are related to more constructional aspects and some to more functional aspects. This classification is however not strict, its purpose is only indicative, to simplify the overview of the scheme.
Construction-oriented aspects:
related to the generation of radiation | |
related to the detection of radiation | |
related to the device in general | |
related to the patient support |
Operation-oriented aspects:
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
(radiation) source | artificial or natural ionizing radiation emitting element per se, e.g. X-ray tube anode, tracer |
(radiation) source unit | constructional arrangement comprising a radiation source and housing, capable of emitting an oriented radiation beam, e.g. X-ray tube |
Raw data | data output from the sensor/detector requiring pre-processing to be used for diagnostic purposes |
diagnostic data | data readable or interpretable by medical personnel, obtained after pre-processing of raw data |
Image data | medical diagnostic data in the form of two- or three-dimensional data sets |
This place covers:
Devices and imaging techniques for obtaining images of different planes, i.e. slices of the patient's body, in a sequential way.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring radiation per se | |
Stereoscopic photography |
The term "sequential" is used here for historical reasons, meaning that the device can be configured to obtain an image of a plane and subsequently, only by changing the device configuration and without moving the patient, to obtain a different plane. This aspect is not relevant anymore in the current definition, since a cone-beam CT would obtain images of different planes simultaneously but would still be classified under A61B 6/032 (a subgroup of A61B 6/02).
Acquisition of projections for reconstructing an image is not considered to be a temporal series of images (A61B 6/486), since the reconstructed image will be associated to a single time.
This place covers:
Acquisition and/or display of two offset images.
This group covers both functional (e.g. stereoscopic imaging technique) and constructional aspects (stereoscopic imaging scanners) of radiation-based stereoscopic imaging.
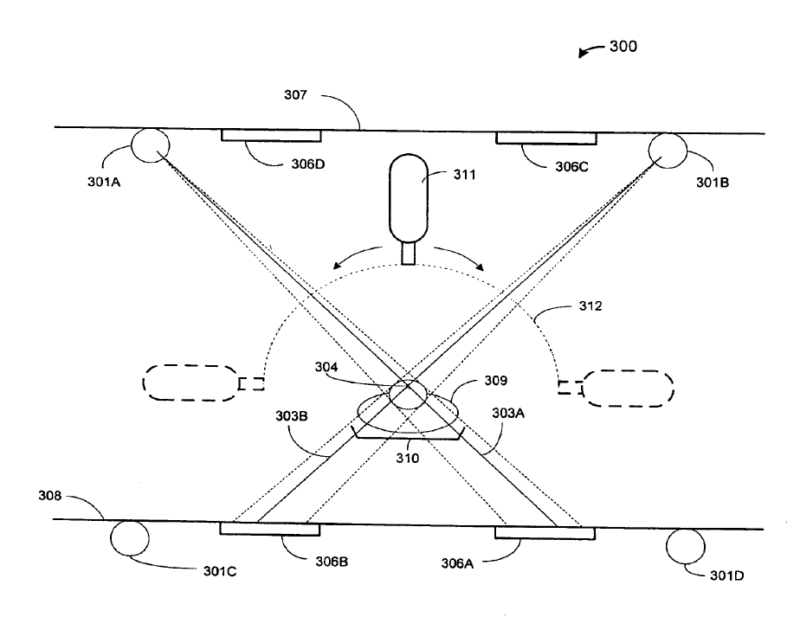
This place covers:
Classical geometric tomography is a method of producing an image of a three-dimensional object (human body) by moving an x-ray source in an opposing motion (x-ray tube and film housing) during exposure to sharpen the structure images in the focal plane and produce a single film integrated x-ray. The objects in the planes above and below the fulcrum are blurred in proportion to their distance from the plane of focus due to parallax.
Modern tomosynthesis is a technique of using a series of source positions from varying orientations to produce a group of images and with a computer program reconstruct the arbitrary planes into the final clear image.
This group covers both functional (e.g. tomosynthesis imaging technique) and constructional aspects (tomosynthesis scanners) of radiation-based tomosynthesis imaging.
Illustrative examples of the subject matter classified in this place:
1. Classical geometric tomography
2. Modern tomosynthesis
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission computed tomography | |
Application mammography | |
Reconstruction from projections |
In modern tomosynthesis the sequence of orientations defines an acquisition trajectory which, if relevant, should be classified under A61B 6/027.
In case of a circular trajectory of the source and the detector, said rotation is shorter than 180° + fan angle of the beam (acquisition of an incomplete dataset). If the rotation is longer, then a complete dataset is acquired and the technique is a computed tomography (see A61B 6/032).
This technique is often used for breast imaging; in such a case it should be classified also in A61B 6/502.
This place covers:
Relevant details concerning the sequence of positions of source and detector defining a trajectory along which X-ray images (projections of views) for a subsequent reconstruction are acquired. Diagnostic techniques requiring data acquisition along a particular trajectory are typically:
Computed tomography A61B 6/032
Tomosynthesis A61B 6/025
Helical acquisition trajectory for computed tomography (A61B 6/032):
Partial isocentric motion with stationary detector in tomosynthesis, A61B 6/025, in which the detector stays in one place or is stationary while the x-ray tube rotates around a point of rotation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tomosynthesis | |
Computed Tomography | |
Trajectory planning for programme-controlled manipulators (e.g. robotic arms) |
This class also covers devices where a movement of the source unit is superimposed to e.g. a circular trajectory.
This place covers:
Measuring radiation from different angles and reconstructing (computing) a 2D image (slice) or a 3D image (set of slices).
This group includes tomography (system or function) which does not fall into the subgroups of transmission tomography (A61B 6/032) or emission tomography (A61B 6/037), or wherein the kind of tomography is not specified.
This group covers both functional (e.g. tomography) and constructional aspects (tomographs) of both transmission and emission tomography imaging.
This place does not cover:
Echo-tomography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical tomography | |
Diagnosis using magnetic resonance tomography | |
Tomosynthesis | |
Reconstruction from projections | |
Healthcare informatics for handling or processing of medical images, e.g. DICOM, PACS |
Computed tomography in radiation diagnosis is basically either transmission tomography (A61B 6/032) or emission tomography (A61B 6/037). The subgroups of A61B 6/03 cover therefore all possible options so that A61B 6/03 is mainly to provide structure in the scheme. Documents disclosing transmission tomography (e.g. CT) or emission tomography (e.g. PET) should be classified in A61B 6/032 or A61B 6/037, respectively, but not in A61B 6/03.
This place covers:
The source emits a radiation beam from outside the body and the attenuation of the beam is measured by a detector after the beam has traversed the patient's body. This measurement is carried out from different angles and an image (representing the values of the attenuation coefficient of the radiation at every position in space) is reconstructed (computed) from the measurements.
A typical configuration consists of an X-ray source unit emitting a 2D dimensional beam in the form of a fan (fan-beam) and a curved detector (1 line) which rotate around the patient along a circular trajectory to reconstruct (compute) a 2D image (slice) of the patient on the plane of said circular trajectory.
To obtain a 3D image (set of slices) the patient table can be moved steadily during acquisition so that the acquisition trajectory of source and detector with respect to the patient becomes a spiral or helix (see A61B 6/027)
The group covers both functional (e.g. computerized tomography) and constructional aspects (computerized tomographs) of transmission tomography imaging.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical tomography | |
Diagnosis using magnetic resonance tomography | |
Tomosynthesis | |
Transmission ultrasound tomography | |
Reconstruction from projections |
Transmission tomography as a technique that can be carried out with any device capable of acquiring views (projections) from different angles and can rotate at least 180° + fan angle around the patient. Devices with a more constrained rotational trajectory are not capable of performing tomographic imaging and are restricted to perform tomosynthesis (A61B 6/025).
If the device is a CT scanner, it should be classified here (A61B 6/032), otherwise said devices are classified according to their constructional features A61B 6/44, e.g. C-arm (A61B 6/4441), robotic arms (A61B 6/4458).
To obtain a 3D image (set of slices) the patient table is moved during acquisition so that the acquisition trajectory of source and detector with respect to the patient becomes a spiral or helix (see A61B 6/027).
Alternatively, a device with a source emitting a cone-beam (A61B 6/4085) combined with a two-dimensional detector (A61B 6/4233) is used. Or both, a particular acquisition trajectory (A61B 6/027) and a cone-beam with a 2D detector (A61B 6/4085 and A61B 6/4233, respectively) are combined.
This place covers:
The source (typically a radioactive tracer) emits radiation from inside the body which is measured outside the body with one or more detectors from different orientations and an image (representing the distribution of the tracer inside the body) is reconstructed (computed) from the measurements.
PET or SPECT scanners are classified under A61B 6/037.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this place:
1.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical tomography | |
Diagnosis using magnetic resonance tomography | |
Echo-tomography | |
Measuring radiation | |
Radiation detection aspects of SPECT imaging | |
Radiation detection aspects of PET imaging |
This group covers devices for emission tomography, reconstruction of 2D images (slices) or 3D images (sets of slices). Other devices such as intraoperative gamma cameras should be classified under A61B 6/4258.
Documents concerning details of the detector should be classified under G01T 1/00, and only be classified under A61B 6/037 in the case where relevant details of the emission tomography scanner or the clinical application are disclosed.
This place covers:
Any means, e.g. tables, beds, chairs, suitable for positioning the patient in the diagnostic device.
This place does not cover:
Operating tables | |
Operating chairs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Involving electronic [EMR] or nuclear [NMR] magnetic resonance, e.g. magnetic resonance imaging | |
Positioning of patients in ultrasound diagnostic devices | |
Chairs, beds, mattresses | |
Radiation therapy |
This place covers:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Involving electronic [EMR] or nuclear [NMR] magnetic resonance, e.g. magnetic resonance imaging | |
Positioning of patients in ultrasound diagnostic devices | |
Hospital beds | |
Operating tables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Involving electronic [EMR] or nuclear [NMR] magnetic resonance, e.g. magnetic resonance imaging | |
Application mammography | |
Hospital beds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Application mammography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for cooling other parts of the device for radiation diagnosis |
This place covers:
[EP0490107]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Source unit or detector unit mounted to ceiling |
This place covers:
Conveyor bands or belts for transporting the patient.
[US2002112288]
[US20110092792]
This place covers:
Patient positioning chairs
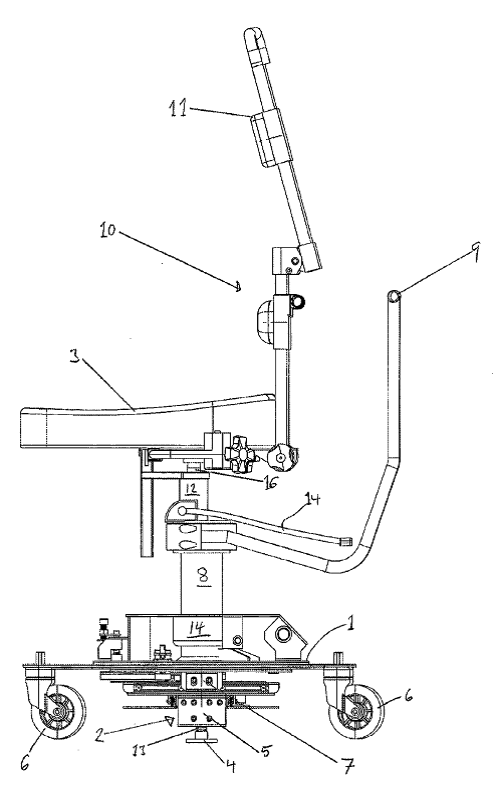
[EP2289370]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Operating chairs |
This place covers:
Motor controlled patient positioning
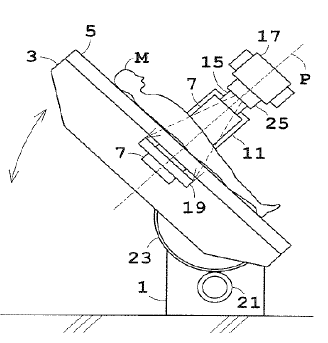
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tracking apparatus position |
This place covers:
Diaphragms specially adapted for particular diagnostic applications, e.g. tomography.
Devices adapted to modify the spatial confinement of the cross-section of the radiation beam, e.g. collimators, situated between the source unit and the patient.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Source combined with filter or grating | |
Detector combined with grid or grating | |
Multi-leaf collimators for intensity modulated radiation therapy | |
Diaphragms/collimators per se |
Rules for classifying other devices situated on the beam path, used to modify properties of the beam:
- Filters (A61B 6/4035): modify a property of the beam but not its spatial confinement, e.g. the spectrum, or the intensity distribution.
- Gratings: cause diffraction and are used mainly for phase measurements.
- Grids: arrangements of blades situated along the detector pixels and used to block scattered radiation.
Grids and gratings are classified depending on their position:
- A61B 6/4035 when situated between source unit and patient,
- A61B 6/4291 when situated between patient and detector.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising means for assessing direction and / or extent of the radiation beam before acquisition. The auxiliary means typically consist in a light source (e.g. laser) projecting light from a point near the radiation source towards an imaging region. The projected beam can be point-like or reflect the spatial extent of the radiation beam and is typically used for monitoring / setting the alignment of the source unit with the detector unit (A61B 6/587) and/or the distance between the source unit and the patient (A61B 6/589) and / or detector unit (A61B 6/588).
[WO2011141763]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation diagnosis devices with source and detector units movable relative to each other | |
Alignment of source unit to detector unit | |
Setting distance between source unit and detector unit | |
Setting distance between source unit and patient |
This place covers:
Any means for preventing collision between component parts of the device, or between the device and external objects, e.g. patient, other room equipments.
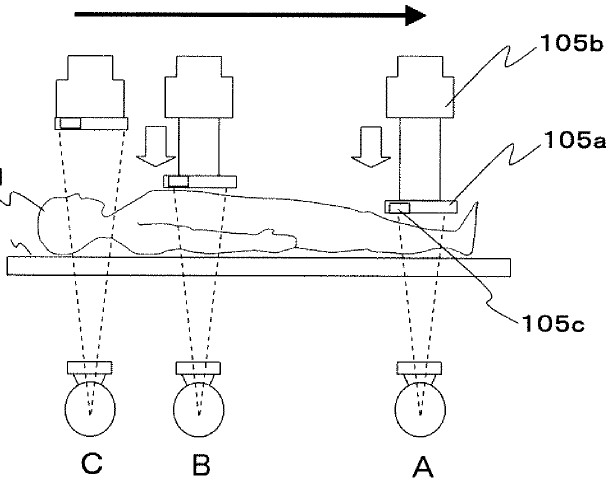
[WO2012050148]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mobile apparatus | |
Tracking apparatus position |
This place covers:
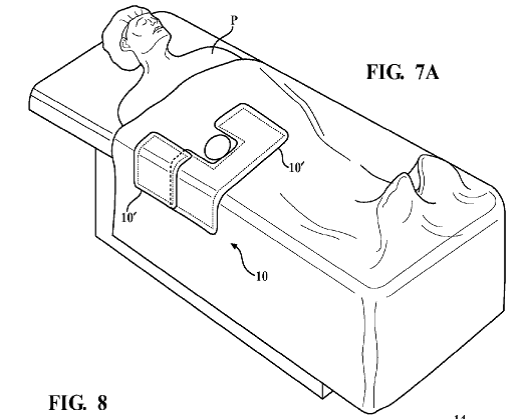
[US2012132217]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protection against effects of non-mechanical surgery | |
Radiation shielding per se | |
Techniques for handling radiation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other imaging methods for locating foreign bodies | |
Devices for diagnosis sequentially in different planes; Stereoscopic radiation diagnosis | |
Generating a temporal series of data | |
Extracting a diagnostic parameter from medical diagnostic data | |
Locating foreign bodies using ultrasound | |
Surgical navigation systems | |
Radio-opaque markers |
This group covers the use of radiation diagnostic devices to determine the position of a surgical instrument during an operation, e.g. using a C-arm classified in A61B 6/4441 for performing fluoroscopy classified in A61B 6/487. However, it does not cover path calculations and guiding of said instruments classified in A61B 34/20.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostic devices comprising a radiation source for generating radiation and arrangements for manipulating said radiation by shaping the radiation beam, displacing it or modifying its characteristics.
Radiation sources cover both radiation source units to generate a radiation beam outside the patient oriented towards the patient (e.g. X-ray tubes) and radioactive tracers emitting radiation from inside the body due to radioactive decay A61B 6/4057.
NOTE: radioactive tracers are not considered to be contrast agents but sources of radiation in the sense of A61B 6/40.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for focusing or moderating radiation | |
Irradiation devices | |
Details of X-ray tubes | |
Circuits for X-ray tubes |
Typically involves the generation of a radiation beam having a particular spatial configuration A61B 6/4007, A61B 6/4035, A61B 6/4064, movement A61B 6/4021, A61B 6/4057, intensity A61B 6/405 or spectrum A61B 6/4035.
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to radiation diagnosis devices AND
- they comprise constructional details of the source unit(s).
Devices for modifying the spatial confinement of the beam (collimators) should be classified under A61B 6/06.
This place covers:
A combination of a cathode and a dedicated anode is considered to be a single source unit. In cathode-anode based source units, multiple source units have therefore multiple cathode-anode pairs.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Circuit arrangements driving apparatuses comprising more than one X-ray tube |
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising a plurality of source unit and a plurality of detector units, each source unit being functionally associated with a detector unit.
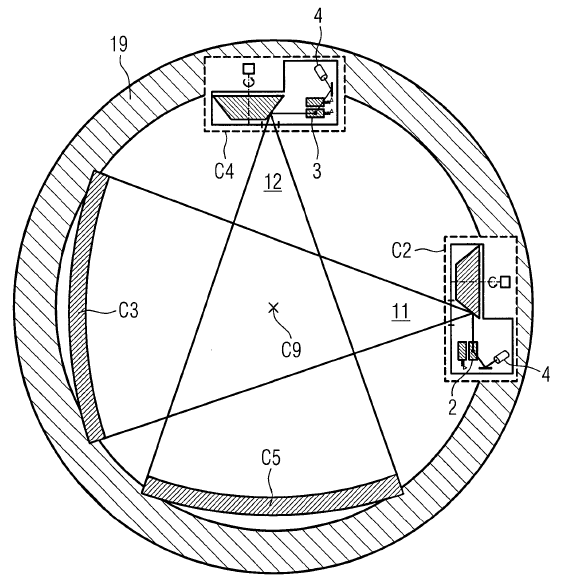
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for radiation diagnosis using a plurality of detector units | |
Multiple energy imaging | |
Circuit arrangements driving apparatuses comprising more than one X-ray tube |
Devices where each source unit emits a ray with a different energy should be also classified under A61B 6/482.
Although these devices also have a plurality of detectors they should not be classified under A61B 6/4266 since it is implicit that if the sources are arranged in source-detector units, the devices also have a plurality of detectors (i.e. A61B 6/4014 takes precedence).
This place covers:
Modification of focal spot position on the anode or between multiple anodes be it in static imaging or in imaging modalities where source unit and detector unit perform data acquisition while following a certain trajectory (swing focus, spring focus, alternating focus, flying focus).
This subgroup covers not only active control of the movement of the focal spot, but also analysis and correction of fluctuations of the position of the focal spot on the anode.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation devices characterised by the use of a certain acquisition trajectory | |
Multiple energy imaging | |
Tubes wherein the point of impact of the cathode ray on the anode or anti-cathode is movable relative to the surface thereof |
If modifying the position of the focal spot implies generating a beam of different energy, the device should be classified also under A61B 6/482.
See A61B 6/4007 for the definition of single/multiple sources.
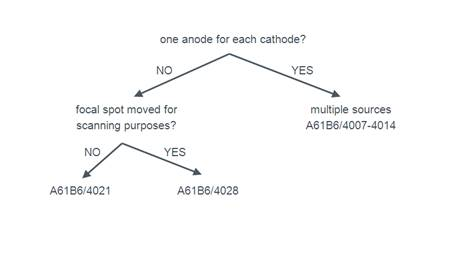
This place covers:
Devices where the displacement of the radiation beam during the data acquisition process (scan) to obtain images or projection data from different angles is carried out by translation of the focal spot, as is typically done in electron beam computed tomography (EBCT).
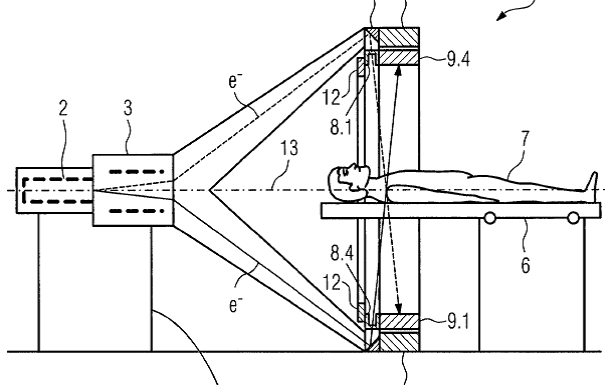
[DE102007036038]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tubes wherein the point of impact of the cathode ray on the anode or anti-cathode is movable relative to the surface thereof |
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices wherein the source unit is combined with a filtering means adapted to modify the spatial distribution of the intensity or the spectral characteristics of the radiation beam, e.g. bowtie filters.
Filters to modify a property of the beam but not its spatial confinement, e.g. the spectrum, or the intensity distribution, e.g. bowtie filters.
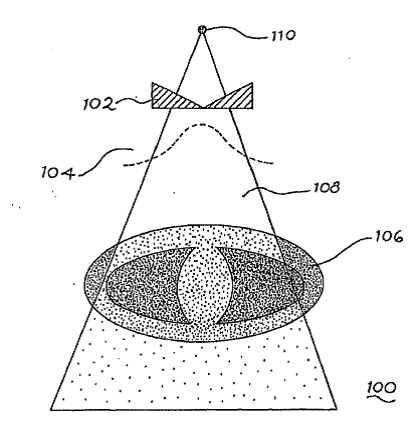
This class also includes gratings to cause diffraction and are used mainly for phase measurements, and grids, i.e. arrangements of blades situated along the detector pixels and used to block scattered radiation, when they are situated between source unit and patient.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Collimators for radiation diagnosis devices | |
Detector combined with grid or grating | |
Multiple energy imaging | |
X-ray phase contrast imaging | |
X-ray filters per se |
Rules for classifying other devices situated on the beam path, used to modify properties of the beam:
- collimators to modify the spatial confinement of the radiation beam should be classified under A61B 6/06,
- gratings or grids situated between the patient and the detector should be classified under A61B 6/4291.
Radiation devices using filters to modify the spectral characteristics of the beam (i.e. modify the energy of the radiation beam) should be also classified under A61B 6/482.
Grids for X-ray phase contrast imaging (A61B 6/484) should also be classified here, if they are positioned between the source and the patient.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices involving arrangements to modify characteristics such as voltage or tube current during the data acquisition process.
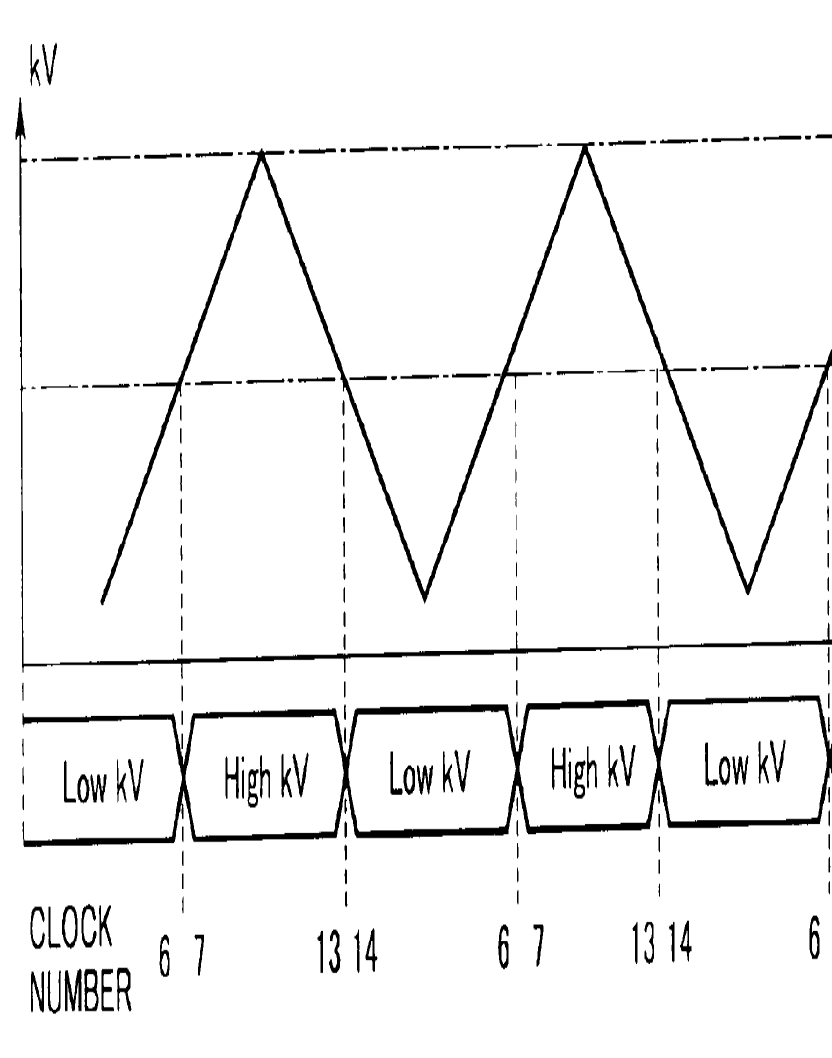
[US2012230466]
This place does not cover:
Movement of the focal spot | |
Source unit combined with a filter |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Multiple energy imaging | |
Control of exposure | |
Arrangements changing the time structure of an already generated radiation beam | |
Controlling X-ray tubes |
Modifying the characteristics of the beam by moving the focal spot or using filter should be classified under A61B 6/4021 and A61B 6/4035, respectively.
Typically changing the voltage during image acquisition is used to modify the energy spectrum of the beam, which is related to multiple energy imaging (A61B 6/4021).
Modifying the tube current during data acquisition is typically used to control exposure to radiation (dose), hence A61B 6/542 might be relevant too.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostic devices where the radiation source is introduced into the body, as part of a probe or capsule, or as a radioactive tracer.
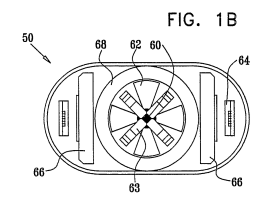
This place does not cover:
Emission tomography (PET/SPECT) |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capsule endoscopes | |
Diagnosis using light using a probe introduced into the body | |
Radiation diagnosis with detectors for detecting non X-ray radiation | |
Ultrasound diagnosis in body cavities | |
Detection of radiation | |
X-ray tubes with small cross-section |
A document disclosing a diagnostic application of PET or SPECT scanner A61B 6/037 does not need to be classified also under A61B 6/4057 to cover the radioactive tracer aspect since this is implicit in the A61B 6/037 code. Only in the case that the document discloses particular technical properties of said tracer that solve a technical problem (e.g. specific tracer injection protocol, combination of tracers, tracer carried to a specific organ by a capsule before release) should the document be classified here.
Applications of intraoperative gamma cameras to detect rests of tumours labelled with a radioactive tracer should get the codes A61B 6/4057 and A61B 6/4258.
This place covers:
Particular technical features of the radiation beam, e.g. geometrical properties or type of radiation.
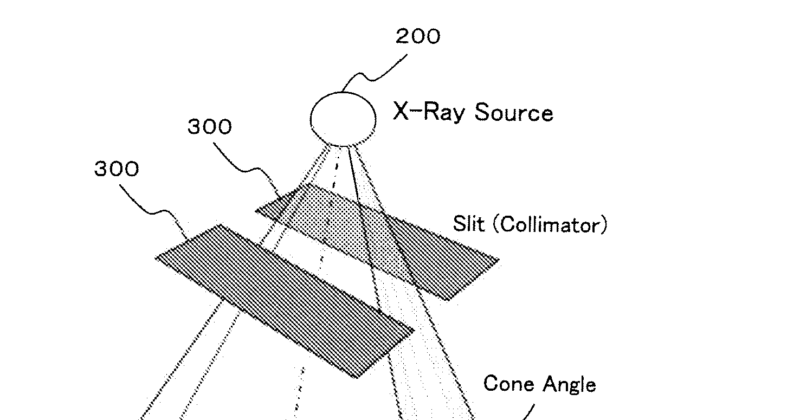
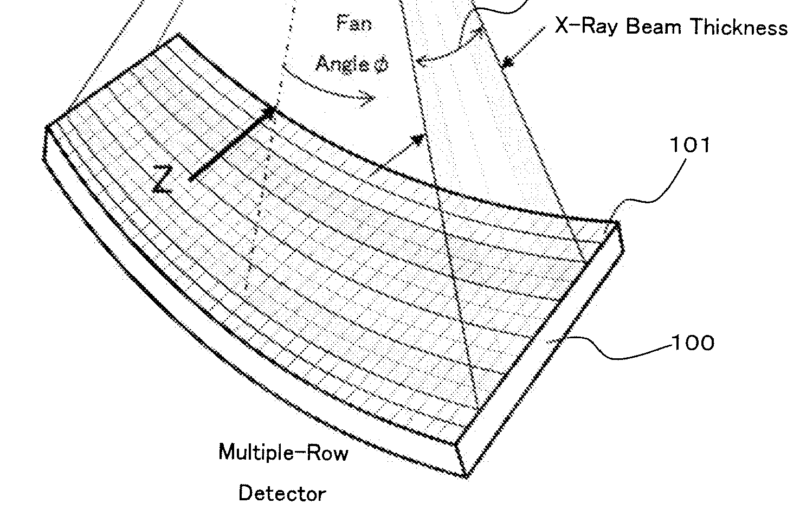
[EP2036498]
This class also covers the use for radiation diagnosis of a source generating any radiation which is not X-ray or synchrotron (A61B 6/4092) radiation, e.g. a radioisotope source.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising a detection unit arrangement specially adapted for a particular acquisition technique or diagnostic application, and arrangements for modifying the beam prior to detection, e.g. anti-scatter grids.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring radiation per se | |
X-ray films | |
Packages for X-ray films | |
Image intensifiers |
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to radiation diagnosis devices AND
- they comprise constructional details of the detector unit(s).
A document describing particular details of a radiation detector should be classified in the corresponding subclass of G01T 1/00, even if a clinical application of said detector is mentioned. However, if e.g. details of the arrangement of said detector in a PET scanner for said particular clinical application are disclosed, then it should also be classified in A61B 6/037 and in the corresponding subclass of A61B 6/50.
This place covers:
Radiation devices comprising a detector with special features not covered by any of the subgroups below.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of stimulable phosphor sheets |
This place covers:
Radiation devices using an image intensifier for radiation detection.
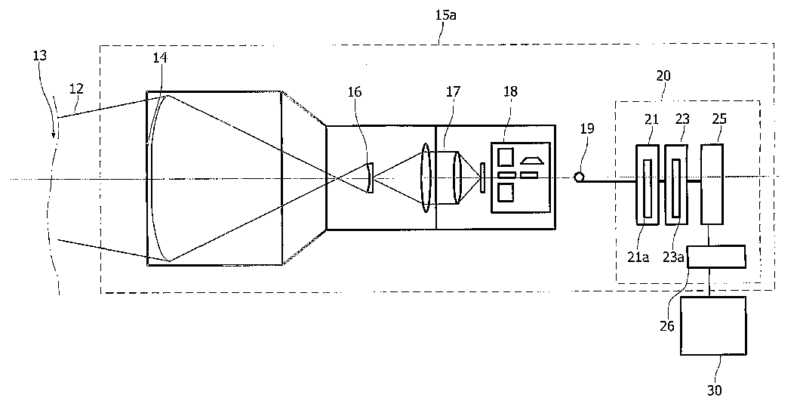
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Matrix detectors | |
Fluoroscopy | |
Image intensifiers per se |
Image intensifiers in radiation diagnostics are typically used for real-time intra-operative imaging using fluoroscopy (A61B 6/487). Currently (2012) they have been substituted by flat panel detectors which should be classified under A61B 6/4233.
This place covers:
Radiation devices using an array of pixel detectors which generates an output in digital format. The array might have different geometries, 1 dimensional like in a CT scanner with a line detector, 2 dimensional and flat like a flat panel detector for radiography, 2 dimensional and cylindrical like in some multi-slice CT scanners, etc.
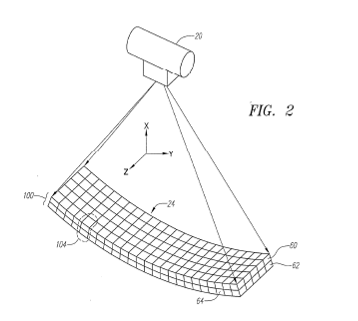
[WO2005037075]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Semiconductor radiation detectors |
This place covers:
Radiation devices using detectors capable of discerning several levels of energy of the detected beam.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Contrast agents in radiation diagnosis | |
Multiple energy imaging as an imaging technique | |
Radiation angiography | |
Radiation diagnosis of bone | |
Detectors for nuclear medicine |
Typically combined with the combination of radiation data acquired at different energies to extract a particular diagnostic information A61B 6/482.
Multiple energy in radiation diagnostics is typically used to produce enhanced angiographic images A61B 6/504 combined with a contrast agent A61B 6/481 or for the diagnosis of bone A61B 6/505.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostic devices where the radiation detector is introduced into the body, as part of a probe or capsule.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capsule endoscopes | |
Diagnosis using light using a probe introduced into the body | |
Radiation diagnosis with detectors for detecting non X-ray radiation | |
Ultrasound diagnosis in body cavities | |
Detector details for in vivo counting |
Applications of intraoperative gamma cameras to be introduced in to the body to detect rests of tumours labelled with a radioactive tracer should get the codes A61B 6/4057 (for the tracer), A61B 6/425 and A61B 6/4258.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostic devices comprising a detector to detect radiation other than X-ray radiation, e.g. gamma or beta radiation.
This place does not cover:
Emission tomography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation source for the interior of the body | |
Detecting radiation |
Applications of PET or SPECT A61B 6/037 do not require this class, since these techniques already imply the detection of non X-ray radiation. If the radiation is emitted by a radioactive tracer or in general a source inside the body (e.g. in a capsule) the class A61B 6/4057 should be given.
This place covers:
[US2011064193]
This place does not cover:
Devices for radiation diagnosis using a plurality of source - detector units |
An array of pixels is considered to be a single detector unit. If the device has more than one array, they are considered to be a single detector unit if there is no independent control of each of the arrays. Otherwise, if each array is controlled independently, each array is considered to be a single detector unit. Devices with multiple source-detector units should only be classified under A61B 6/4007.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising a detector unit forming a closed or almost closed structure around the patient, e.g. 4th generation CT scanners.
[US2004081277]
This place covers:
Both matrix and film detectors.
[US2012097860]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Film cassette holder construction |
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising a detector unit combined with a grid, such as an anti-scatter grid or with a grating, as used in X-ray phase contrast imaging (A61B 6/484).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Collimators for radiation diagnosis devices | |
Source combined with filter or grating | |
X-ray phase contrast imaging | |
Reduction of scatter by image processing in devices for radiation diagnosis | |
Anti-scatter grids | |
X-ray filters per se |
Rules for classifying other devices situated on the beam path, used to modify properties of the beam:
- collimators to modify the spatial confinement of the radiation beam should be classified under A61B 6/06,
- filters or gratings situated between the source and the patient should be classified under A61B 6/4035.
This place covers:
Diagnostic devices comprising structural or mechanical arrangements allowing a specific usage or property, e.g. movement, modularity.
This class covers all details concerning constructional aspects not covered by any of the subgroups below.
This place covers:
Mobile radiation diagnosis device, e.g. mounted on casters or rollers or small handheld devices, e.g. handheld intra-operative gamma cameras.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation diagnosis devices with anti-collision devices | |
Ultrasound diagnostic devices mounted on a trolley | |
Mobile robots |
This place covers:
Modular construction of radiation diagnosis device allowing part to be exchanged or replaced either for mounting different types of components or for simpler disassembling and reassembling.
This place does not cover:
Detector units housed in a cassette |
This place covers:
Constructional arrangements for facilitating the combined use of different imaging modalities including translation from one device to the other or integration of different modalities in one device. At least one modality using ionising radiation.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical diagnosis | |
Magnetic resonance imaging | |
Transmission tomography | |
Emission tomography | |
C-arms | |
Post-acquisition processing for combination of images from different modalities | |
Diagnosis with ultrasound |
This class covers all details concerning constructional aspects to combine different diagnostic modalities in one device.
(Ionising) radiation - (ionising) radiation: e.g. PET/CT
(Ionising) radiation - other type of diagnostics: e.g. CT/ultrasound A61B 8/00, X-ray/optical A61B 5/0059, CT/MRI A61B 5/055, G01R 33/48, etc.
This class does not cover the combination of images coming from the different modalities per se, said combination should be classified under A61B 6/5229 and its subgroups, which specify whether the diagnostic modalities are both B6 modalities or B6 and another modality.
This place covers:
[WO2004081867]
This place covers:
Details of the mounting arrangement of the source units and/or detector units.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for diagnosis sequentially in different planes; Stereoscopic radiation diagnosis |
Imaging devices under A61B 6/02 should only be classified here if the document describes particular details of the arrangement. E.g. a computed tomography scanner should be classified under A61B 6/032 but not under A61B 6/4435, since it is implicit in such a device that source and detector unit are coupled by a rigid structure. However, a radiation device where source and detector unit are coupled by a rigid structure and which is capable of performing tomographic imaging should be classified both under A61B 6/4435 and A61B 6/032 (in such a case A61B 6/032 code the functional aspect "computerised tomography" and not the constructional aspect "computerised tomograph").
This place covers:
Devices wherein the relative position and orientation of the source and detector units is fixed. Open structures such as C-frames and closed structures such as gantries.
Devices where the distance between source and detector or the orientation can be modified should be classified under A61B 6/4452.
This place covers:
Devices wherein the source and the detector are fixed on a c or u-shaped frame.
[WO2010128417]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Data acquisition trajectories in radiation diagnosis devices | |
Transmission tomography | |
Fluoroscopy |
C-arms are usually used for fluoroscopy (A61B 6/487) or for computerised tomography (A61B 6/032). Due to their flexibility they can acquire projection data (views) along different trajectories for tomographic reconstruction (A61B 6/027).
This place covers:
Devices wherein the source and the detector are fixed to a rigid frame forming a closed loop which can be tilted to image planes tilted with respect to the axial direction of the patient.
[US2003235266]
This place covers:
Devices wherein the relative position and orientation of the source and detector units can be changed, e.g. device for performing tomosynthesis (A61B 6/025) of the breast where source and detector units are shifted along a linear trajectory but the source always points to the detector unit.
[Dobbins and Godfrey, "Digital x-ray tomosynthesis: current state of the art and clinicalpotential", Phys. Med. Biol. 48 (2003) R65–R106]
This place covers:
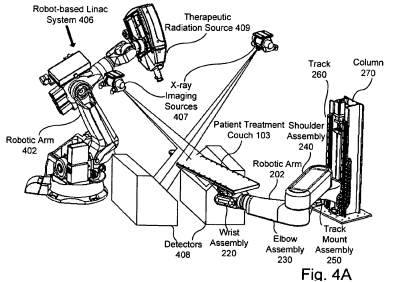
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details concerning robots |
A robotic arm is considered to be constituted by a base and a series of segments connected by joints (at least two links and two joints) and has at least 3 degrees of freedom. Typically each joint has a motor that allows the movement of the arm. An arm which is merely telescopic is not considered to be a robotic arm.
The robotic arm must be used to support at least part of the radiation diagnostic device, not e.g. only a radiotherapy source.
This place covers:
[US 2011/0182408]
This place covers:
Mechanical arrangements of the source and detector where their displacement is controlled by a counter balance or a spring.
This place covers:
Radiation devices where the movement of the source unit is controlled via a servomechanism, i.e. a feedback control to correct deviations in position (usually an electric or electronic motor).
This place covers:
Means for cooling in general, e.g. cooling of anode in the radiation source, cooling of the detector, etc.
This place does not cover:
Tables or beds provide with heating or cooling means |
This class covers all aspects related to cooling in a radiation diagnostic device except for tables or beds with heating or cooling means (A61B 6/045).
This place covers:
Any means for identifying X-ray apparatus or component parts thereof, e.g. removable filters, detectors. Includes bar codes, memory chips or RFIDs.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising input and/or output means structurally or functionally designed for allowing a specific interaction with the device user or the patient.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices |
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to radiation diagnosis devices AND
- they comprise details of the user interface.
This place covers:
Displays with special properties not covered elsewhere in A61B 6/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Displays for electrocardiography | |
Displays in magnetic or electric diagnosis | |
Displays for ultrasound diagnosis |
Touch screens should be classified here and as special input means under A61B 6/467.
This place covers:
Portable displays, supports for displays.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Viewing apparatus for X-ray images |
This place covers:
Display of images obtained by all types of X-ray imaging apparatus, combinations of images, e.g. side-by-side, superimposed, tiled. Also for combination of images and other data, e.g. graphs, ECG curves, pulse waveforms, alphanumeric data.
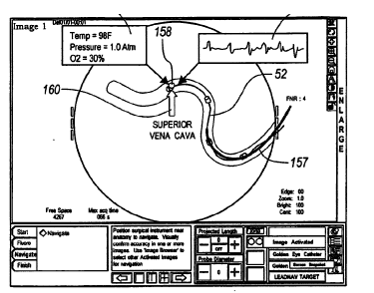
[EP1421913]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising processing means for combining image data of a patient |
This place covers:
[US2007064864]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
3D image rendering per se | |
manipulating 3D models for computer graphics |
This place covers:
Both constructional (e.g. touch-screen, trackball) and functional aspects (e.g. specific purpose) of input means.
[WO2011066486]
[US2012093298]
This place covers:
All types of message recording associated with radiation diagnosis imaging, e.g. annotation on image, sound recording.
This place covers:
Operator selection of region of interest or specific organs to be imaged, e.g. by touch screen, keyboard or switch. Also for definition of ROI after image analysis.
This class does not cover automatic selection of a region of interest using image processing which should be classified under A61B 6/5211.
This place covers:
Diagnostic devices involving a specific use of ionising radiation to perform a particular type of diagnosis. Imaging techniques are independent of the device used for implementing them.
This place does not cover:
Stereoscopic imaging | |
Tomosynthesis | |
Transmission computed tomography | |
Emission tomography |
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis imaging based on or improved using an agent with particular properties for the absorption of radiation..
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation diagnostic with radioactive tracers | |
Acquisition of a temporal series of data | |
Diagnosis of blood vessels | |
Diagnosis of hemodynamic parameters | |
Contrast agents in ultrasound diagnosis | |
X-ray contrast preparations | |
Contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging |
Mainly related to angiography (see also diagnosis of blood vessels A61B 6/504), but not exclusively.
The diagnostic of hemodynamic parameters (e.g. perfusion) by acquiring a temporal series of images should be classified under A61B 6/507 and A61B 6/486.
Radioactive tracers are not considered to be a contrast agent but a source to be introduced into the body (A61B 6/4057).
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostics using different radiation energy levels.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Source unit with multiple anodes | |
Source unit combined with a filter | |
Filters for multiple energy imaging | |
Energy resolving detectors for radiation diagnosis | |
Angiography | |
Diagnosis or bone | |
Measuring spectral distribution of X-rays |
Radiation diagnostic devices based on multiple energy imaging should be classified under A61B 6/482 and additionally according to the technique used to acquire the data at different energy levels, for example:
- A source with several anodes for producing beams with different energy A61B 6/4021.
- One beam with a certain energy spectrum which is filtered after leaving the source unit A61B 6/4035.
- One beam with a certain energy spectrum which is separated into several energy bands at the detector A61B 6/4241.
- A dual source-detector scanner with source units emitting radiation beams of different energies A61B 6/4014 and A61B 6/4266.
Multiple energy imaging is typically used for examining bone A61B 6/505 or with contrast agents A61B 6/481, where two energy bands, one above and one under the K-edge of the contrast material are used to enhance the effect of the contrast agent in angiography A61B 6/504.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostics using information from scattered radiation (non-ballistic photons).
This class does not cover reduction of artefacts caused by scatter from images (A61B 6/5282) or scatter correction performed in projection data before image reconstruction (A61B 6/5205).
[US2012157829]
This place covers:
Radiation diagnostics using characteristic "secondary" (or fluorescent) X-rays from an object that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Investigating material by X-ray fluorescence |
This place covers:
Dynamic imaging techniques, e.g. wherein a plurality of images of the same region are acquired during a predetermined amount of time.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ECG | |
Transmission tomography | |
Contrast agents in radiation diagnosis | |
Diagnosis of heart | |
Haemodynamic parameters | |
Extracting a diagnostic parameter from image data | |
Retrospective matching to a physiological signal |
Typically used for
- real-time imaging, e.g. fluoroscopy (A61B 6/487),
- acquisition of a series (A61B 6/486) of CT images (A61B 6/032) for the analysis (A61B 6/5217) of hemodynamic parameters, e.g. perfusion (A61B 6/507), with contrast agents (A61B 6/481),
- concurrent acquisition of data of the beating heart (A61B 6/503) with a CT (A61B 6/032) scanner and an ECG (A61B 5/318) for retrospectively matching the CT data to phases of the cardiac cycle (A61B 6/5288) and reconstruct a series of CT images of the heart in different cardiac phases (A61B 6/486).
This place covers:
Real-time X-ray imaging during an intervention.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Image intensifiers in radiation diagnosis | |
Flat panel detectors in radiation diagnosis | |
C-arms |
Initially fluoroscopy was carried out using a fluoroscope, i.e. using a fluorescent screen as a detector. Later image intensifiers (A61B 6/4225) were used, and nowadays (2012) typically flat panel detectors are used (A61B 6/4233).
Very often fluoroscopy is carried out using a C-arm (A61B 6/4441).
This place covers:
Diagnostic techniques in which a first acquisition is performed prior to the actual examination.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Exposure control based on patient thickness | |
Automatic setup of acquisition parameters | |
Calibration |
Typically used to identify the boundaries of the zone to be scanned and automatically adjust acquisition parameters (A61B 6/545) or to adjust the X-ray dose according to the size of the patient (A61B 6/544). The pre-scan acquisition might be carried out using a different device than the radiation diagnostic device, e.g. an optical camera.
This place covers:
Classification in this group depends on the body part or organ which is to be diagnosed. This group covers clinical applications not provided for in the subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electroencephalography | |
Ultrasonic brain imaging | |
Use of CT scans for customised prostheses |
This place covers:
[wikipedia.org]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mammography by transillumination | |
Patient immobilizing means for mammography | |
Ultrasonic mammography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrocardiography | |
Ultrasonic heart imaging |
This place covers:
[wikipedia]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locating blood vessels | |
Radiation imaging using contrast agents | |
Radiation diagnosis using multiple energy | |
Ultrasonic blood vessels imaging |
This place covers:
[radiologyinfo.org]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bone monitoring in general | |
Radiation diagnosis using multiple energy | |
Bone diagnosis using ultrasound |
This class covers bone analysis such as quantitative analysis of bone structure or imaging of bone, e.g. for the diagnostic of fractures.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nerves diagnosis | |
Locating nerves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting heart rate, blood pressure or blood blow | |
Radiation diagnosis imaging techniques involving the generation of a temporal sequence of image data | |
Extracting physiological parameters from image data |
This place covers:
Animal imaging and pre-clinical research. Also for veterinary imaging.
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices specially adapted for dental examination, e.g. devices for panoramic imaging of the teeth.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Analysis of teeth using light | |
Tomosynthesis | |
Computed tomography | |
Multiple detectors | |
Radiation diagnosis of bone | |
Dentistry per se |
Due to their rotation capabilities needed to acquire panoramic images of the teeth, devices for panoramic radiography are often adapted to acquire projection data and generate computed tomographic images or tomosynthesis. In that case, they should be also classified under A61B 6/032 or A61B 6/025, respectively.
If the device combines panoramic radiography and other imaging techniques, then it might have different detectors for each imaging technique and it should be classified under A61B 6/4266.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
X-ray tubes having a small cross-section to facilitate introduction into small cavities |
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices involving any kind of processing of data (raw data or diagnostic data) or image processing for enhancement purposes, e.g. artefacts reduction or resolution improvement.
This class covers data or image processing in radiation diagnostics not provided for in the subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Signal processing of physiological signals | |
Data/image processing in ultrasound diagnostics | |
Image processing per se | |
Image analysis per se | |
Image reconstruction from projection |
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to radiation diagnosis devices AND
- they comprise details of data or image processing.
Image processing alone should not be classified in A61B 6/52, except when the processing is clearly adapted to a particular diagnostic device (e.g. removal of patient table from a CT image) or a specific diagnostic application (e.g. assessment of breast tumour size evolution from subsequent mammography acquisitions).
The subgroups are separated into processing of raw data (data output from the sensor requiring pre-processing to be used for diagnostic purposes) and diagnostic data (data readable or interpretable by medical personnel, obtained after pre-processing raw data).
This place covers:
Pre-processing of data output from the sensor requiring pre-processing to be used for diagnostic purposes, e.g. sinogram filtering, combination of detector rows, columns or reconstruction of CT images from X-ray projections.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detectors calibration | |
Processing of raw ultrasound data | |
Image reconstruction from projection |
This place covers:
Processing of data readable or interpretable by medical personnel, obtained after pre-processing raw data.
This place covers:
Acquired data is used to derive a particular diagnostic index, e.g. tumour size or perfusion rate.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Extracting a diagnostic/physiological parameter from ultrasound diagnostic data | |
Algorithms for biomedical image analysis | |
Segmentation algorithms | |
ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining |
This class includes also extracting a region of an image representing a certain organ or body part by segmentation.
This place covers:
Generation of user selected planar views not coincident with CT slice images from CT data, e.g. sagittal or coronal slice images. Usually combined with 3D imaging.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation diagnosis devices adapted to display 3D data | |
3D image rendering |
This class also covers specific medical imaging processing such as:
- generating a planar view from a 3D data set, e.g. DRR (digitally reconstructed radiographs),
- generating a planar view from a temporal series of 2D data, e.g. MIP (maximum intensity projection).
This place covers:
Means for combining images of one or several imaging modalities, e.g. merging of contiguous sub-images to obtain a larger image or multi-modality image registration.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details concerning the combination of different modalities in a device | |
Algorithms for image registration |
This place covers:
Combining images of the patient obtained by a diagnostic technique classified under A61B 6/00 (ionising radiation).
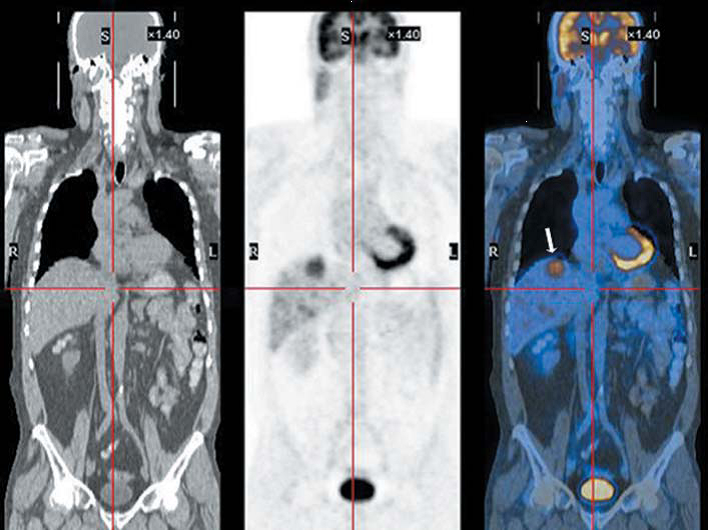
[Finger et al., "Whole body PET/CT for initial staging of choroidal melanoma", Br JOphthalmol 2005;89:1270-1274, doi:10.1136/bjo.2005.069823]
This place covers:
[US2004081271]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Angiography in radiation diagnosis | |
Spatial compounding in ultrasound diagnosis |
Typically used in angiography A61B 6/504.
This place covers:
Combining images of the patient obtained by a A61B 6/00 diagnostic technique (ionising radiation) and a non A61B 6/00 diagnostic technique.
[Wein et al., " Automatic CT-ultrasound registration for diagnostic imaging and image-guided intervention", Medical Image Analysis, Volume 12, Issue 5, October 2008, Pages 577-585]
This place covers:
Objects such as patient table, headrest, markers are eliminated from the diagnostic data. Does not apply to artefacts i.e. unpredictable features determined by heat, dust, light.
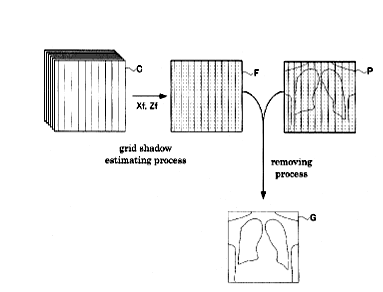
This subgroup concerns removing objects of known origin from the diagnostic images, it does not concern removing artifacts per se (i.e. unpredictable features determined by heat, dust, light), which should be classified under A61B 6/5258. Typical examples are removing the patient bed from a CT image or the anti-scatter grid from a radiograph (the artifact caused is of known geometry and has the shape of the grid, so it is considered as removing the grid and not an artifact), nor does it concern removal of body tissues such as bones or anatomic parts such as blood vessels.
This place covers:
Data or image processing for noise or artefact reduction in radiation diagnostic images.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Algorithms for image enhancement |
Applies to reduction of artifacts inherent to the imaging technique (e.g. beam hardening in CT) or reduction of noise, but not to the removal of objects from the image (A61B 6/5252).
This place covers:
Data or image processing for artefact reduction wherein the artefacts are caused by motion.
This place covers:
A motion sensor is used to detect motion and information from said sensor is used in the processing to remove motion artefacts.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Patient motion evaluation per se | |
Motion derived by measuring table sag | |
Retrospective matching to a physiological signal | |
Acquisition triggered by a physiological signal |
This class does not cover triggering data acquisition based on a physiological signal (A61B 6/541) or retrospectively associating acquired data to a physiological signal which has been acquired simultaneously with the data (A61B 6/5288).
This place covers:
Correction of misalignment errors caused by lack of rigidity of the patient table, where measurements of table sag are used.
[US2007003020]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Patient positioning supports |
This place covers:
Post-acquisition synchronization of image and physiological data (e.g. heart rate, breathing rate), the latter being either acquired in parallel with the image acquisition, or extracted from the acquired data.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heart rate measurement per se | |
Evaluating respiratory organs | |
Monitoring thoracic expansion occurring during breathing | |
Electrocardiograms | |
Diagnostic technique involving the generation of a temporal series of image data | |
Extraction of physiological parameters from medical diagnostic data | |
Radiation diagnosis devices where acquisition is triggered by a physiological signal |
The physiological signal is typically an electrocardiogram (ECG) A61B 5/318 or a device to measure the cardiac cycle A61B 5/0803.
As an example, a radiation diagnostic device with synchronous acquisition of projection data with a C-arm (A61B 6/4441) and an ECG (A61B 5/318) wherein the projection data is retrospectively associated to a certain cardiac phase (A61B 6/5288) to reconstruct a temporal series of images (A61B 6/486) of the heart (A61B 6/503) in different cardiac phases.
This place covers:
Processing of data using non measured data, such as patient name or age, or image identification. Typically data can be found in the header of a digital image file (e.g. a DICOM header).
[US2006257040]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data |
This place covers:
Aspects of radiation diagnostic devices concerning control of the device or parts of the device. All control aspects not covered by the subgroups should be classified in A61B 6/54.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices |
This place covers:
Acquisition control wherein a signal of physiological origin (heart rate, breathing rate) is used to initiate data acquisition.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Heart rate measurement per se | |
Monitoring thoracic expansion occurring during breathing | |
Retrospective matching to a physiological signal | |
Circuit arrangements for obtaining X-ray photography at predetermined instants in the movement of an object, e.g. part of a human body |
This place covers:
Control of exposure parameters, e.g. to optimize exposure of different body thicknesses, to reduce patient dose, to avoid oversaturation of detector.
[US2006018425]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Source units adapted to modify characteristics of the beam during the data acquisition process | |
Automatic setup of acquisition parameters | |
Controlling X-ray tubes |
In X-ray imaging, exposure is typically controlled by modifying characteristics of the source unit such as intensity or voltage (A61B 6/405). This class covers control of exposure during data acquisition. Automatic setup of the exposure parameters based on information about the patient or the diagnostic application should be classified under A61B 6/545.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Based on pre-scan |
Exposure control dependent on patient size is often carried out by performing a pre-scan (A61B 6/488) to estimate the dimensions of the patient.
This place covers:
Automatic setup of apparatus parameters using patient specific information, e.g. weight, height and/or diagnostic specific information, e.g. perfusion CT acquisition protocol.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Control of exposure during data acquisition in radiation diagnostic devices |
This class does not cover dynamic control of acquisition parameters to minimise patient exposure to radiation A61B 6/542.
This place covers:
Means for tracking position of any part of the radiation diagnosis device (e.g. table, C-arm). Includes optical markers, ultrasound sensors, visual linear scales.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locating a surgical device in the body with a radiation diagnostic device | |
phantoms for determining position of parts of the device | |
Surgical navigation systems |
This class does not cover tracking the position of a surgical device A61B 6/12 or guiding a surgical device A61B 34/20.
This place covers:
Remote control of any operational aspect (data acquisition, configuration, etc) of radiation diagnosis devices.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission of radiation diagnosis data via a network | |
Transmission of radiation diagnosis images via a network |
Remote control is often carried out through a data network and involves transmission of data A61B 6/56 or image data A61B 6/563.
This class covers any kind of remote control, either of the diagnostic device itself or of devices, which are directly related to acquisition of diagnostic data. Typically remote control is carried out through a data network and involves transmission of data A61B 6/56 or image data A61B 6/563, but the concept is to be interpreted broadly, covering e.g. also a cable with a controller to be used in the same room. It is important however that there is a technical effect associated with the distance to the device.
- If there is a link between the remote controlled device and the data acquisition, then the subgroup A61B 6/548 should be given, even if what is remote controlled is e.g. an injector.
- This class also covers voice control.
Relationship between A61B 6/548 and A61B 6/581: A61B 6/548 relates to control of data acquisition for diagnostic purposes (e.g. remote configuration) while A61B 6/581 relates to checking malfunctioning or adjusting the device itself (e.g. remote calibration or fault detection).
This place covers:
Radiation diagnosis devices comprising :
- means for transmitting / receiving data to / from an external device or between components of the device, e.g. image transmission to a remote physician workstation for diagnosis; or
- means for supplying power to any component of the device, e.g. between stationary and moving parts.
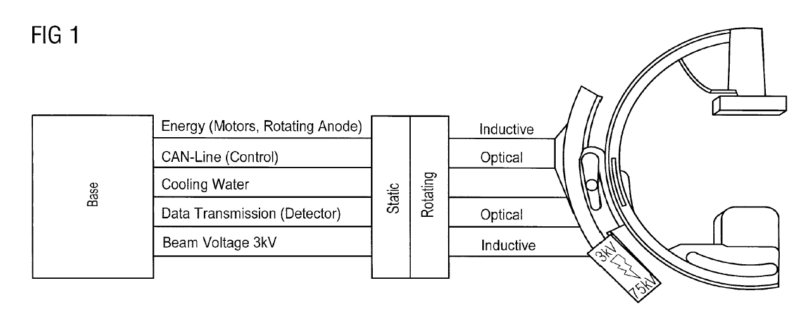
[US2011066022]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flexible or turnable line connectors | |
Details of X-ray tube power supply arrangements |
This class covers aspects of data transmission or aspects of power supply. Sometimes these are combined like in slip rings (H01R 39/08), where power and data are transmitted from a stationary to a rotating structure.
This place covers:
Transmission of diagnostic image data via a network, e.g. transmission of image data from a radiation diagnosis device to a server for archiving.
[US2012018641]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of medical images |
This class cover transmission of images via a PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) or a HIS (Hospital Information System).
This place covers:
Details of radiation diagnosis devices related to the transfer of data between two imaging systems.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional details related to combined acquisition of different diagnostic modalities |
Transfer of data between parts of diagnostic system are classified under A61B 6/56.
This place covers:
Means for assessing and adjusting the parameters of the device as a function of the system geometry.
This place covers:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Communication between imaging systems | |
ICT specially adapted for the remote operation of medical equipment or devices |
Typically involves data transmission over a network (A61B 6/56). However, the class A61B 6/56 should only be given if said data transmission is not merely mentioned but technical details therefore are disclosed.
Relationship between A61B 6/548 and A61B 6/581: A61B 6/548 relates to control of data acquisition for diagnostic purposes (e.g. remote configuration) while A61B 6/581 relates to checking malfunctioning or adjusting the device itself (e.g. remote calibration or fault detection).
This place covers:
Includes methods or devices for determining particular properties (geometrical or other type) of radiation diagnosis device.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Algorithms for calibration |
This place covers:
Methods or devices for calibration where a reference object (phantom) is used to determine particular properties of the radiation diagnosis device.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Models for medical purposes |
This class covers e.g. determining the distortion caused by the acquisition geometry of a C-arm A61B 6/4441 or using a reference object to calculate quantitative values from an image.
This place covers:
Methods or devices where a reference object is used to determine the absolute or relative position of components of the device.
[DE102008012857]
This class covers e.g. the determination of the position of the source unit and detector unit of a C-arm (A61B 6/4441) at every angular position during rotation to be used in the reconstruction algorithm (G06T 11/003) to generate CT images (A61B 6/032).
This place covers:
All types of calibration, correction or compensation, e.g. compensation for non-linear response of X-ray detectors, electric noise, saturation, charge leakage offset, temperature, crosstalk, defective pixels.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Processing of raw data | |
Calibration techniques for radiation measuring devices |
This place covers:
Any means for determining or identifying a fault or failure in X-ray apparatus or component parts thereof.
[US2011129067]
This place covers:
Any means for aligning the source and detector unit or any use of a radiation diagnostic device involving the alignment of source and detector units.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for directing the radiation beam to a particular spot | |
Radiation diagnostic devices comprising source and detector units movable relative to each other | |
Calibration in radiation diagnostic devices | |
Calibration using phantoms to determine position of parts of a device |
A calibration method for aligning the source and detector units should also be classified under A61B 6/582 or A61B 6/584 (if a phantom is used).
This place covers:
Any means for setting the distance between source and detector unit or any use of a radiation diagnostic device involving the modifying said distance.
[US2010215152]
This place covers:
Any means for setting the distance between source and patient or any use of a radiation diagnostic device involving the modifying said distance, e.g. to modify the magnification of an X-ray image.
This place covers:
Any instrument allowing to detect a sound generated within the body :
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or devices for transmitting, conducting or directing sound in general |
- Stethoscopes, i.e. devices allowing to listen to the sound, classified in sub-groups A61B 7/02 - A61B 7/045;
- Devices were sound patterns are only displayed and no listening takes place, classified in sub-groups A61B 7/001-A61B 7/00-A61B 7/006
This place covers:
Instruments comprising patient's head-mounted sensors which detect acoustic signals generated from pulsing blood flow through the patient's brain.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting intracranial pressure |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting, measuring or recording devices for evaluating the respiratory organs | |
Monitoring sleep apnoea | |
Devices for preventing snoring |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Prostheses implantable into the body |
This place does not cover:
Detecting lung or respiration noise | |
Detecting noise of gastric tract |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosing the musculoskeletal system or teeth |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosing the gastrointestinal system |
This place covers:
Any instrument allowing to listen to sound/noise emitted by the body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods or devices for transmitting, conducting or directing sound in general |
This place does not cover:
Endotracheal, oesophageal or gastric probes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopes |
This place does not cover:
Deriving pressure in blood vessels from Korotkoff sounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood pressure |
This place covers:
Diagnostic equipment and/or methods which involve the use of ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves.
A complete characterisation of the equipment or method requires the identification of both constructional and operational aspects according to the following rules.
Several subclasses, groups and subgroups provide for the different components or functional aspects constituting the devices for diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves. It should be emphasized that documents describing these components should be classified in A61B 8/00 only if they disclose a device for diagnosis using ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves and the link between said components or functional aspects and the clinical application is not trivial.
Techniques for short-range imaging with ultrasound per se (both devices and methods) are classified under G01S 15/8906 and G01S 7/52017. These techniques should only be classified under A61B 8/00 when the link between the use of a particular technique and a clinical application is not obvious. The fact that the device is a medical diagnostic device is not a sufficient criterion for classifying in A61B 8/00 and not in G01S. As an example, a document disclosing an ultrasonic device adapted to calculate cardiac output using Doppler would be classified under A61B 8/00. If on the other hand the document discloses the sequence of pulses and their processing to obtain the Doppler measurements, then it should be classified under G01S 15/8906 or G01S 7/52017, even if the document mentions that the device is a diagnostic device. However, if there is a link between the particular implementation of the Doppler measurements and the clinical application, it should be classified in both A61B 8/00 and G01S 15/8906. Similarly, a modular medical diagnostic device wherein the probe can be exchanged to choose among a set of probes according to several clinical applications would be classified under A61B 8/00. However, a modular medical diagnostic device with exchangeable circuit boards to provide for easier upgrade would be classified under G01S. Only if the choice of a particular board was related to a clinical application should it be classified under A61B 8/00.
The same principle applies to other neighbouring fields such as, e.g. image processing (G06T). A document disclosing an algorithm for image enhancement should be classified under the corresponding subclass of G06T, even if the document mentions that the images are x-ray images. However, if there is a link between details of the algorithm and a particular clinical application, then the document should also be classified in the corresponding subclass of A61B 8/00. On the other hand, if is only mentioned that an algorithm for image enhancement is used but the disclosure deals mainly with details of the radiation diagnostic device, then it should only be classified in A61B 8/00.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis using photo-acoustic measurements | |
Diagnosis using acousto-optic measurements | |
Diagnosis using electronic [EMR] or nuclear [NMR] magnetic resonance | |
Apparatus and techniques of diagnosis using ionizing radiation | |
Ultrasound therapy | |
Ultrasound transducers per se | |
Investigating or analysing materials by the use of ultrasonic, sonic or infrasonic waves; Visualisation of the interior of objects by transmitting ultrasonic or sonic waves through the object | |
Details of systems according to G01S 15/00 | |
Systems using the reflexion or re-radiation of acoustic waves, e.g. acoustic imaging | |
Short-range imaging using acoustic waves | |
Pattern recognition techniques in general | |
Image data processing or generation, in general | |
Image enhancement or restoration | |
Image analysis | |
Image or video recognition or understanding, e.g. pattern recognition | |
Methods or devices for transmitting, conducting or directing sound, in general | |
Healthcare informatics | |
Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Ultrasound transducer | sound generating and / or receiving element |
Probe | combination of at least one ultrasound transducer and its housing |
Raw data | data output from the sensor/detector/transducer requiring pre-processing to be used for diagnostic purposes |
Diagnostic data | data readable or interpretable by medical personnel, obtained after pre-processing of raw data |
Image data | medical diagnostic data in the form of two- or three-dimensional data sets |
In patent documents, the following abbreviations are often used:
US | ultrasound |
This place covers:
Apparatus for detecting, measuring or recording pulse rate or heart rate, e.g. given in beats per minute.
[US2011152688]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring pulse or heart rate in general | |
Measuring pulse or heart rate for foetuses | |
Ultrasonic heart imaging | |
US blood vessel imaging | |
Diagnosis using US Doppler signals | |
Pulse or heart rate derived from US image |
Typically done by analysis of Doppler signals (A61B 8/488) or derived from ultrasonic images (A61B 8/5223). For foetus heart rate, classify here and in A61B 8/0866.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood pressure in general | |
Ultrasonic blood vessels imaging | |
Blood pressure derived from US image |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring blood flow in general | |
Ultrasonic blood vessels imaging | |
Ultrasonic Doppler imaging | |
Measuring volume flow | |
Measuring speed of fluids |
Typically done by analysis of Doppler signals (A61B 8/488) or derived from ultrasonic images (A61B 8/5223).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determination of blood output from the heart in general | |
Heart imaging using ultrasound |
This place covers:
Clinical application of the diagnosis device or method. Classification in the subgroups depends on the body part or organ which is to be diagnosed. Group A61B 8/08 covers clinical applications not otherwise provided.
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis by electrical, magnetic, pressure, light,...sensing means, of particular parts of the body | |
Diagnosis by radiation devices of particular parts of the body | |
Extraction of a diagnostic parameter from ultrasound images |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Head diagnosis using radiation |
This place covers:
Use of ultrasound to study the intracranial structures of the brain, wherein pulse of ultrasonic waves are beamed through the head and echoes reflected by midline structures are recorded and analysed.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis using electro-encephalography |
A typical application is Trans-Cranial Doppler (TCD) imaging wherein a Doppler acquisition (A61B 8/488) allows evaluation of blood flow in a variety of intracranial arteries by applying ultrasound to areas or windows of the skull where the bone is relatively thin. The Doppler acquisition may be combined (A61B 8/5246) with a B-mode acquisition for locating the arteries (A61B 8/085).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mammography by transillumination | |
X-ray mammography | |
Patient support for imaging suspended breast | |
Detection of breast cancer using biopsy |
May involve the use of specific positioning means (A61B 8/40), e.g. compression means (A61B 8/403) or means for positioning the patient in prone position (A61B 8/406). May also be used in combination with biopsy needles (A61B 10/0041), wherein the needle is attached to an ultrasound probe (A61B 8/4455) and / or tracked by the probe (A61B 8/0841).
This place covers:
Ultrasound diagnosis devices for localisation or tracking of organic structures (e.g. blood vessels) or foreign bodies, i.e. any kind of instrument or tissue which does not belong to the patient body by nature, e.g. tumour, implant, surgical instrument.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other imaging methods for locating foreign bodies | |
Locating foreign bodies using radiation | |
Surgical navigation systems | |
Echogenic markers |
This place covers:
Instruments like biopsy needles, catheters.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Biopsy needles | |
Surgical navigation systems |
For example, a biopsy needle (A61B 10/0041) attached to an ultrasound probe (A61B 8/4455), wherein movement of the needle is tracked by the probe, would be classified here.
This place covers:
Detection of tumours, calculi, blood vessels, nodules for anatomical localization (e.g. detection of arteries as a support to Trans-cranial Doppler ultrasound) or diagnosis (evaluation of tumour size) purposes.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locating particular structures in or on the body in general | |
Processing for extracting a physiological parameter |
This place covers:
Pregnancy detection, foetal ultrasound monitoring in general (e.g. foetal imaging or foetal heart rate determination).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Foetal pulse or heart rate determination in general | |
Pregnancy and labour monitoring | |
Foetal pulse or heart rate determination using (ultra/infra) sonic waves |
This place covers:
Includes both quantitative analysis of bone material and visualization of bone structure.
This place does not cover:
Detecting, measuring or recording devices for testing the shape, pattern, colour, size or movement of the body or parts thereof, for diagnostic purposes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bone monitoring in general | |
Bone diagnosis using radiation | |
Measuring interfaces by ultrasound |
This place covers:
Includes both functional (e.g. heart-related physiological parameters) and anatomical (e.g. visualization of heart structure) analysis of the heart.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrocardiography | |
X-ray heart imaging | |
Retrospective matching to a physiological signal | |
Acquisition triggered by a physiological signal |
Documents relating to heart rate (A61B 8/02) and / or blood output monitoring (A61B 8/065) should be classified here only if they describe other features pertaining to heart diagnosis. The same applies to documents relating to blood vessels analysis (A61B 8/0891).
As the heart is a permanently moving organ, diagnostic devices or methods are often adapted to take into account the dynamic aspects. In particular, retrospective (A61B 8/5284) or prospective (A61B 8/543) synchronization to a physiological signal may be used to obtain motion-free images. M-mode (A61B 8/486) or Doppler signals (A61B 8/488) may be used to visualize motion.
This place covers:
Mainly related to the structural diagnosis of blood vessels (since blood flow assessment is dealt with in A61B 8/06).
This place does not cover:
Measuring blood flow |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locating blood vessels | |
Radiation imaging using contrast agents | |
X-ray blood vessels imaging | |
Use of ultrasound contrast agents, e.g. microbubbles |
Documents relating to heart, brain or blood flow analysis should be classified here only if they describe other features pertaining to blood vessels diagnosis.
Blood vessels diagnosis is often performed using Doppler signals (A61B 8/488), due to the high accuracy of this technique to visualize blood moving inside the vessels.
A typical example of blood vessel diagnosis is compression ultrasonography, wherein venous compression (A61B 8/403) is applied and B-mode images are acquired to detect and locate (A61B 8/085) deep vein thrombosis.
This place covers:
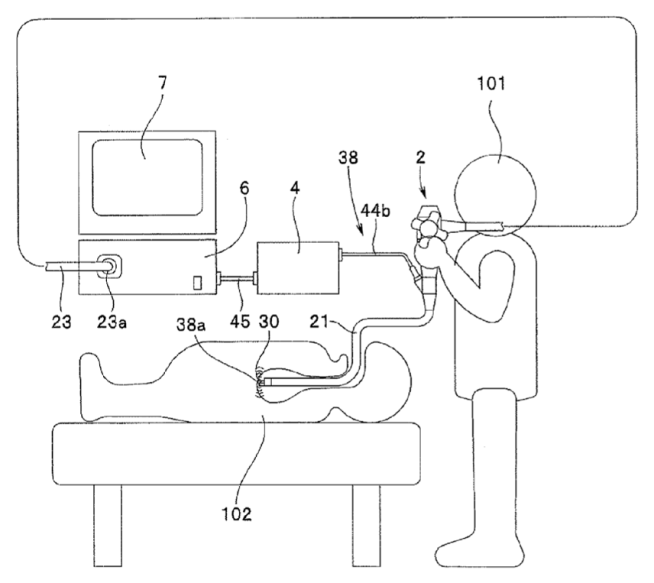
[US2010063401]
This place does not cover:
Details of catheter construction | |
Catheters per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Medical endoscopes | |
Wireless probes |
Details of catheter construction (e.g. use of balloons, pigtails or splines) can be found in A61B 8/445. Scanning mechanisms for moving the transducers are classified in A61B 8/4461.
This place covers:
Acquisition of a plurality of slices or planes (e.g. B-modes or C-mode images) for reconstruction of 2D or 3D images.
This place does not cover:
For eye inspection | |
Using catheters | |
Acquisition of a 3D volume of data |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tomography for radiation diagnosis |
This place covers:
Tomography based on the measurement of waves reflected from the inspected structures, e.g. B-mode or C-mode images.
This place covers:
Simultaneous acquisition of a plurality of planes.
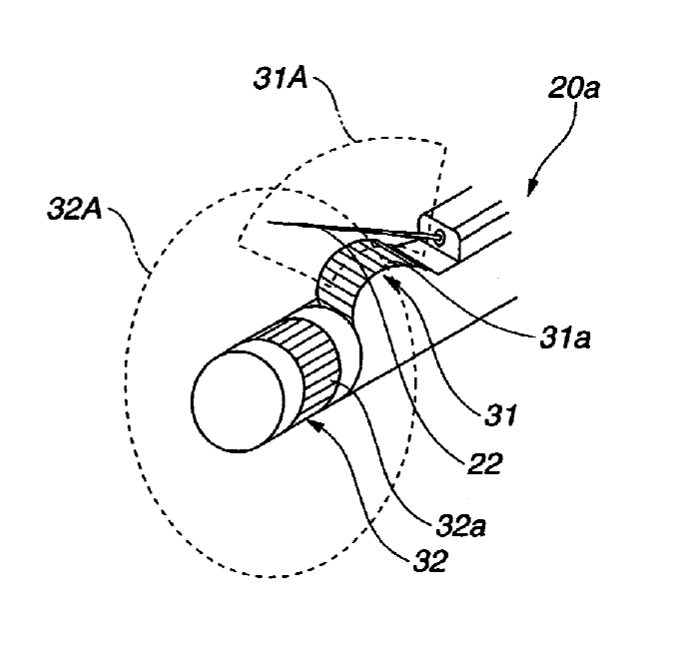
[US2009082674]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using several separate transducers or probes | |
Using a specific transducer arrangement |
This place covers:
Tomography based on the measurement of attenuation of waves transmitted or diffracted through the inspected structures.
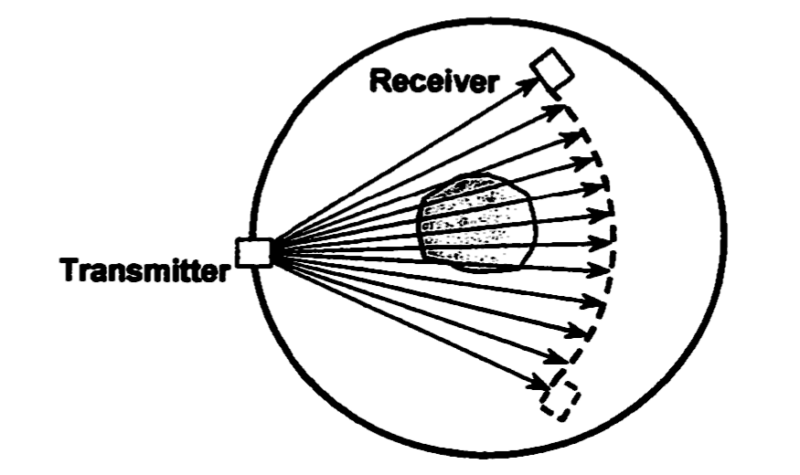
[Jin and Wang, "Correction of the effects of acoustic heterogeneity on thermoacoustic tomography using transmission tomography", Proceedings of SPIE Vol.6086 (2006) 60860W-1 - 60860W-5, XP002447465]
This place covers:
Any means for supporting (e.g. tables, beds) or positioning (e.g. support position control, movement restraining devices) the patient, including immobilising part of the patient body.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Positioning of patients in radiation diagnosis devices |
This place covers:
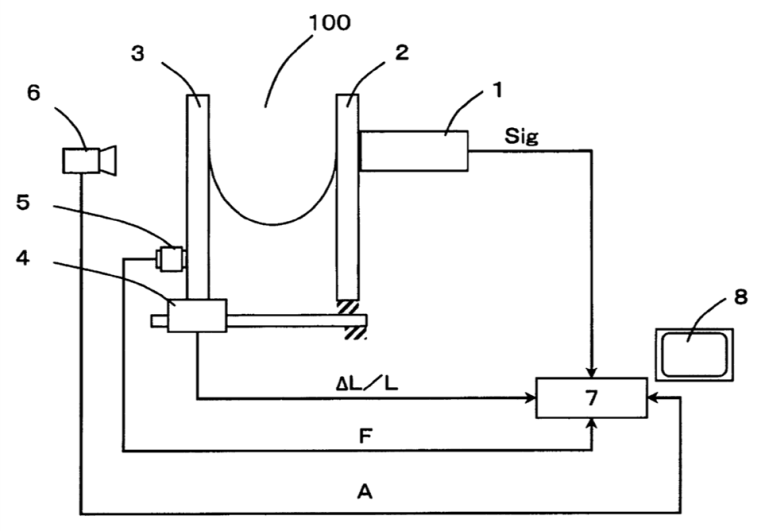
[WO2012036106]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Patient supports using compression means in radiation diagnosis devices | |
Diagnosis of breasts | |
Diagnosis of blood vessels |
This place covers:
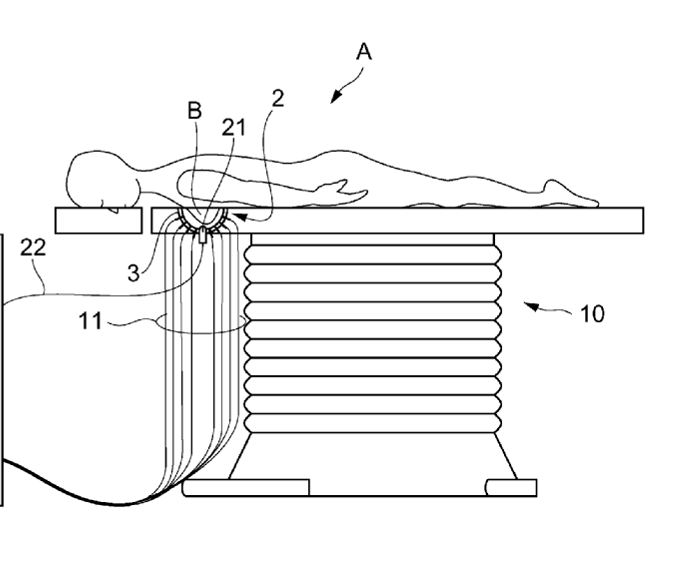
[WO2012053518]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Patient supports for imaging suspended breasts using radiation | |
Ultrasonic mammography |
This place covers:
Any means for positioning and / or determining the position of the probe with respect to the patient.
This place does not cover:
Particular shape of the probe for better grip | |
Details of transducer steering |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Supports, positioning and alignment in fixed situation for ultrasound inspection of materials | |
Supports, positioning and alignment in moving situation for ultrasound inspection of materials |
This place covers:
Any means for positioning the probe on the patient
[US2004087851]
This place covers:
Articulated arm (including sliding, pivoting) for holding the probe. May be provided with position encoders.
This place does not cover:
Catheter with a probe at the tip |
This place covers:
Attachment of the probe with a strap, belt, cuff, brace. Probes mounted in a fitting attached to a strap.
This place covers:
Adhesive patch for attaching the probe to the skin surface. May be combined with a swivelling/pivoting mount to allow change in probe position.
This place covers:
Any means for determining the position of the probe with respect to the patient or to an external reference, e.g. imaging or therapy system. Typically involves the use of a position and/or movement sensing unit provided either on/in the probe (A61B 8/4254) or outside the probe (A61B 8/4263).
[WO2012018851]
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Determination of probe position or applied pressure used to compress the tissue in sonoelastography |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radiation devices for locating probes | |
Locating instruments by ultrasound | |
Determining the quality of coupling between the probe and the tissue | |
Surgical navigation systems |
This place covers:
Any kind of sensor within or attached to the ultrasound probe, providing information on the current position of the probe (e.g. accelerometer, coils sensing external magnetic fields, GPS-type position sensor).
This place does not cover:
Position encoders part of an articulated arm | |
Sensing the position of the probe from an external sensor |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Intracavitary probe positioning |
This place covers:
Any kind of probe position tracking means not attached to or part of the probe, e.g. tracking LED markers on the probe, tracking the probe position with a camera, probe emitting ultrasound signal for localisation purpose.
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Intracavitary probe positioning |
This place covers:
Any means for facilitating, regulating or monitoring the quality of coupling between the transducer and the tissue.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Methods and devices for transmitting, directing or conducting sound in general |
This place covers:
Any means used as interface between the transducer and the tissue, e.g. coupling pad, special conformable shape of the probe, fluid filled reservoir. The mere application of a layer of conducting gel between the probe and the skin does not require a classification in A61B 8/4281, unless specific details of this application are described, e.g. gel containment structure on surface of the probe or particular gel mixture having specific viscosity.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Probe holders |
This place covers:
Any means for monitoring the quality of coupling between the transducer and the tissue. Also for the purpose of triggering/initiating image acquisition or for monitoring applied pressure in elastic imaging (A61B 8/485).
This place does not cover:
Measuring the position of the probe per se |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sonoelastography |
This place covers:
Structural and mechanical features of the ultrasound device specially adapted for diagnostic use.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Constructional features of devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Apparatus mounted on casters or rollers, often resembling a cart / trolley and comprising a sonic probe. May include battery supply, telemetry means and display.
[US2012/0108965]
This place covers:
Modular construction of the device allowing parts to be exchanged or replaced either for mounting different types of components of for simpler disassembling and reassembling.
[EP1935343]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Modular devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Constructional arrangements for facilitating the combined use of different imaging modalities including translation from one device to the other or integration of different modalities in one device. At least one modality relates to ultrasound imaging.
[US2011/0295115: Combination of gamma-ray detector (112) and ultrasound probe (103)]
This place does not cover:
Using several separate ultrasound transducers or probes |
This place covers:
Any means for protecting the probe from outside environment, e.g. hygienic cover.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Sanitary sheaths for endoscopes |
This place covers:
[US2012083693]
This place covers:
Docking unit or station for power or data transfer, either for connecting the probe or the monitoring unit
This place covers:
Any means for identifying the diagnostic apparatus or component parts thereof, e.g. replaceable components. Includes barcodes, memory chips or RFIDs.
This place covers:
Constructional details of sonic diagnostic devices relating to the probe itself.
This place covers:
Particular construction of catheter devices, e.g. balloons, pigtails, basket.
[US2003208119]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Use of catheters for ultrasound diagnosis | |
Catheters per se |
This place covers:
Any constructional related to the specific design of the external probe shape for a particular purpose, e.g. special grip, attachment for auxiliary devices, connectors.
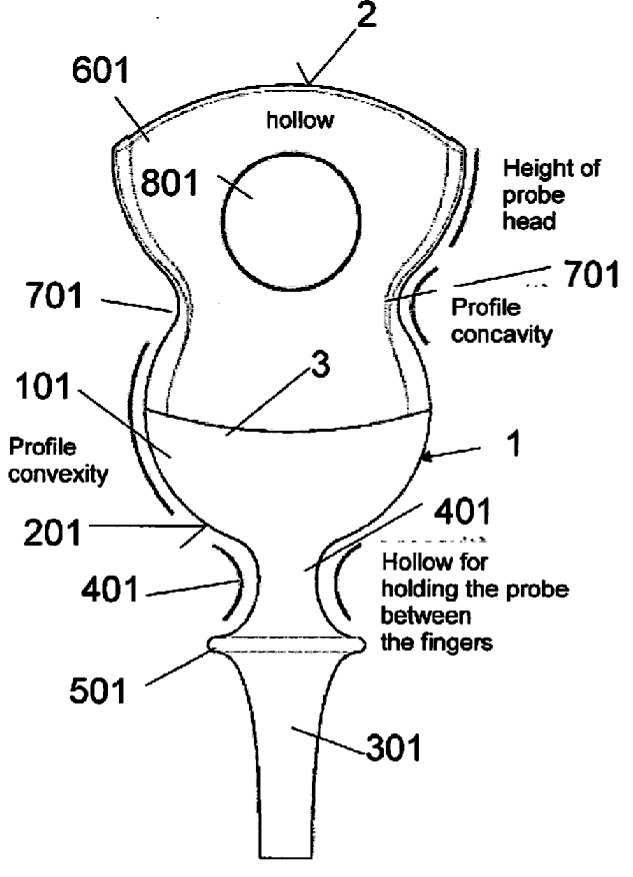
[EP1935343]
This place covers:
Probes or catheters provided with a mechanical scanning mechanism allowing to move the transducer with respect to the probe housing, e.g. for beam steering.
[WO2010013175]
This place does not cover:
Electrical steering mechanisms |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Intra-cavitary probes with motor driven transducer elements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dynamic transducer configuration in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Probes comprising a scanning mechanism involving a deflection of the probe or part of the probe. Typically used by intracavitary probes (A61B 8/12).
[US2009264759]
This place covers:
Probes comprising wireless data and/or power transmission means. Includes pill-like cameras
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of data transmission | |
Wireless probes for inspecting or analysing materials |
This place covers:
Simultaneous use of multiple probes or transducers in similar or different modes for scanning of one or a plurality of patient body parts.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Using separate transducers for transmission and reception in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Specific details or configuration of the transducer adapted for medical imaging application, e.g. particular transducer shape
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Static transducer configuration in short-range imaging systems |
This place covers:
Use of phased array transducers for electrical steering of the sound beam.
This place covers:
Particular arrangement of the transducer elements for facilitating the diagnostic technique, e.g. annular array on intracavitary probes (A61B 8/12) or T-shaped arrangement allowing to scan perpendicular planes simultaneously (A61B 8/145).
[WO2012127737]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements of transducers in generation of mechanical vibrations of infrasonic, sonic or ultrasonic frequency | |
Devices for short-range imaging using particular transducer elements arrangements |
This place covers:
Ultrasound diagnostic devices comprising input and / or output means structurally or functionally designed for allowing a specific interaction with the device user.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices |
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to ultrasound diagnosis devices AND
- they relate to details of the user interface.
This place covers:
Displays with special properties not covered by any of the subgroups.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Displays for electrocardiography | |
Displays in magnetic or electric diagnostics | |
Displays for radiation diagnostic |
Touch screens should be classified here and as special input means (A61B 8/467).
This place covers:
Construction or arrangement of display. Also for goggle-like or head up displays. Supports for display.
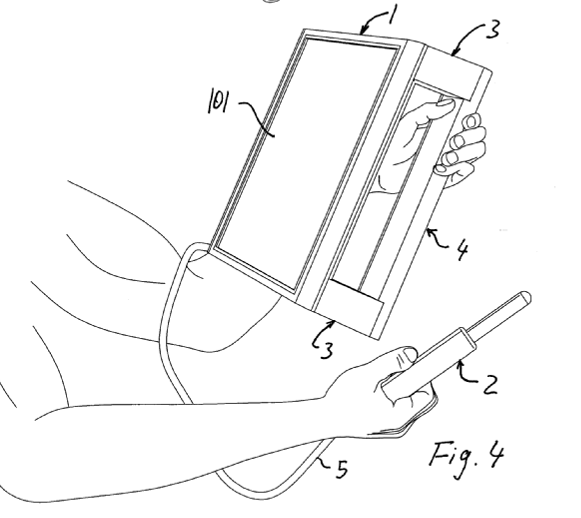
[WO2010012314]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Display arrangements for sonar systems |
This place covers:
Combination of images, e.g. side-by-side, superimposed.
Combination of images and other data type, e.g. ECG waveforms or alphanumeric information.
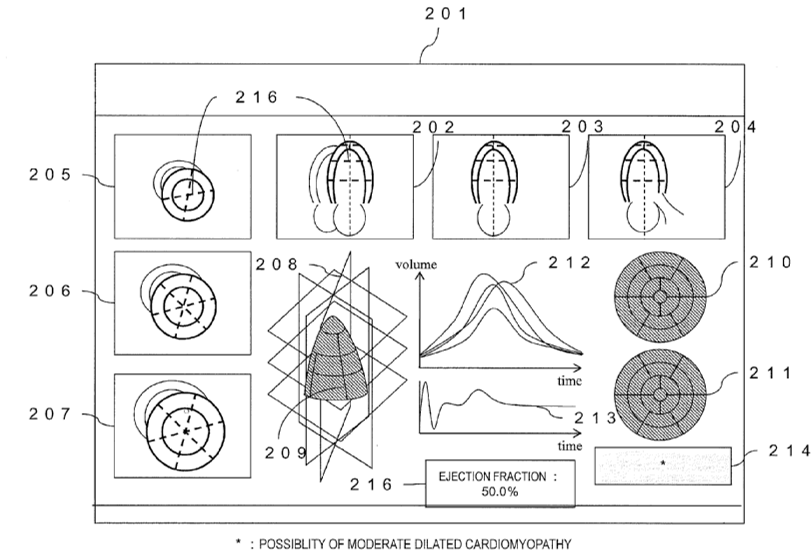
[EP2415401]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Processing means adapted for combining images | |
Composite display in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
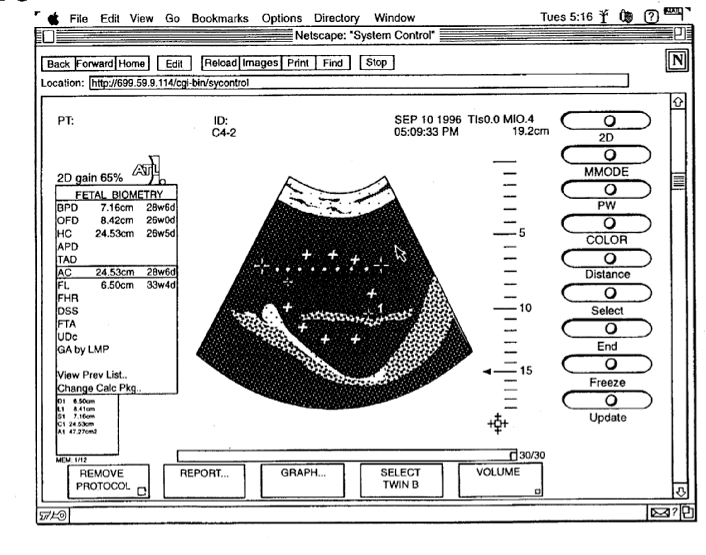
[EP0833266]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
3D imaging and stereoscopic displays in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves | |
3D image rendering per se |
This place covers:
Both constructional (e.g. touch screen, trackball) and functional aspects (e.g. specific purpose) of input means.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Particular user interfaces in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
All types of message recording associated with ultrasound imaging, e.g. annotation on image, sound recording.
This place covers:
Operator selection of region of interest or specific organs to be imaged, e.g. by touch screen, keyboard or switch. Also for definition of ROI after image analysis.
This place covers:
Use of substance, typically introduced into the body, which presents echogenic properties and can therefore be identified and / or tracked by the diagnostic device. Also for surgical instruments coated with echogenic materials to allow them to be tracked (A61B 8/0841).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis of blood vessels | |
Echographic preparations; ultrasound imaging preparation | |
Analysis of echo signal exploiting properties of a contrast enhancer in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Direct acquisition of a 3 dimensional image, e.g. a combination of B-mode and C-mode images.
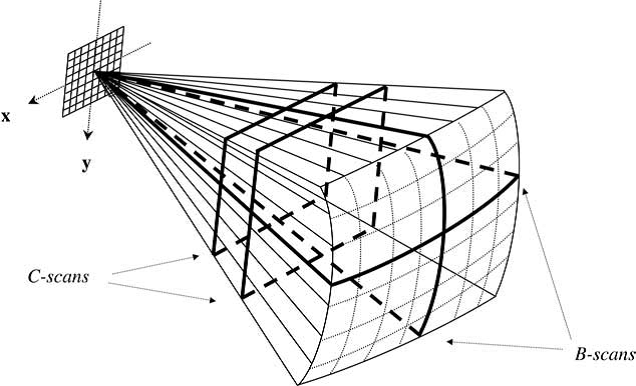
[Smith et al., "Feasibility study: Real-time 3-D ultrasound imaging of the brain", Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology 30(10) (2004)1365-1371, XP004872070]
This place covers:
Imaging elastic properties (e.g. strain, elastic modulus, stiffness) of tissue by exciting the tissue (by direct mechanical means or ultrasonic radiation force) and detecting the resulting displacement, motion or deformation.
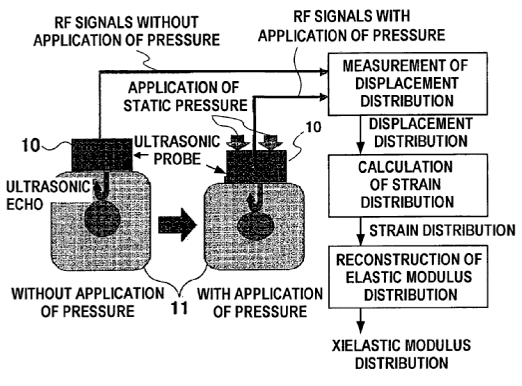
[EP1541090]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determining or monitoring contact between transducer and tissue | |
Extracting elastic properties in devices for short-range imaging with acoustic waves |
Detection of the effects of tissue excitation can be performed by Doppler measurement (A61B 8/488) or pulse-echo methods. Resultant information is usually displayed as images (called elastograms), representing the spatial distribution of strains, shear waves, elastic moduli or tissue stiffness. Elastograms are often fused with B-mode images (A61B 8/5246) to facilitate identification of the anatomical structures to which they relate.
This place covers:
Motion-mode ultrasound wherein pulses are emitted in quick succession along the same path to visualize the spatial variation (e.g. movement) of a reflecting structure as a function of time. May be directly acquired or reconstructed from arbitrary line (straight, curved or polygonal) defined by a user on a B-mode image.
[EP1679038]
This place covers:
Ultrasound imaging technique using the wavelength (or frequency) shift of ultrasound waves reflected from moving structures. Typically used for the diagnosis of dynamic structures function, e.g. heart movement or blood flow.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For measuring pulse or heart rate | |
For measuring blood flow | |
For heart diagnosis | |
For blood vessels diagnosis |
Often fused with B-mode images (A61B 8/5246) to facilitate identification of the anatomical structures to which Doppler signals relate.
This place covers:
Ultrasound diagnosis devices involving any kind of data or image processing for enhancement purposes, e.g. artefacts reduction of resolution improvement.
This place does not cover:
Image processing per se |
Documents should be classified in these subgroups only if:
- they explicitly relate to ultrasound diagnosis devices AND
- they relate to details of data or image processing.
Image processing alone should not be classified in A61B 8/00, except when it consists in straightforward steps (e.g. thresholding, filtering) directed to an explicit diagnostic application.
This place covers:
Pre-processing of data output from sensor to derive data usable for diagnostic purpose, e.g. filtering, phase modification.
This place covers:
Any kind of post-acquisition image processing
This place covers:
Acquired data is used to derive a particular diagnostic index, e.g. tumour size.
This place does not cover:
Algorithms for biomedical image analysis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for computer-aided diagnosis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ultrasound diagnosis devices adapted to display 3D data |
This place covers:
Means for combining images of one or several imaging modalities, e.g. merging of contiguous sub-images to obtain a larger image or multi-modality image registration.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Determination of transform parameters for the alignment of images, i.e. image registration |
This place covers:
Combining images of the patient obtained by a diagnostic technique classified under A61B 8/00.
This place covers:
Compilation of multiple views acquired at different angles.
[Rohling, PhD Thesis : 3D Freehand Ultrasound: Reconstruction and spatial compounding]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Spatial compounding for short range imaging systems |
This place covers:

[Wein et al., "Automatic CT-ultrasound registration for diagnostic imaging and image-guided intervention", Medical Image Analysis, Volume 12, Issue 5, October 2008, Pages 577-585,]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Elimination of unwanted signals in devices for short-range imaging using acoustic waves | |
Determining parameters from multiple pictures |
This place covers:
Data or image processing for artefact reduction wherein the artefacts are caused by motion.
This place covers:
Arranging or processing an image or a plurality of images after acquisition for synchronization purpose. Includes synchronization based on an independently acquired signal (e.g. ECG) or on a feature derived from the image(s).
This place does not cover:
Synchronizing the ultrasound measurement to a physiological event | |
Retrospective scan-line arrangements in devices for short-range imaging using acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Processing of data using non measured data, such as patient name and age, or image identification. Non measured data can be typically found in the header of a digital image file (e.g. a DICOM header).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data |
This place covers:
Ultrasound diagnosis devices comprising means for adapting the operation of the device during acquisition.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the operation of medical equipment or devices |
This place covers:
Acquisition control wherein a signal of physiological origin (heart rate, breathing rate) is used to initiate acquisition.
This place does not cover:
Retrospective matching to a physiological signal |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Synchronization techniques in devices for short-range imaging using acoustic waves |
This place covers:
Any means for controlling or assessing the temperature of the diagnosis device, e.g. cooling means for preventing skin burn
This place covers:
Ultrasound diagnosis devices comprising:
- means for transmitting or receiving data to or from an external device or between components of the device, e.g. image transmission to a remote physician workstation for diagnosis; or
- means for supplying power to any component of the device, e.g. between stationary and moving parts.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Docking units for ultrasound devices | |
Wireless diagnostic ultrasound probes |
This place covers:
Transmission of diagnostic image data via a network, e.g. from a diagnostic device to a server for archiving.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data |
This place covers:
Any calibration related features or methods, including phantoms.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for monitoring or calibrating in devices for short-range imaging using acoustic waves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
ICT specially adapted for the remote operation of medical equipment or devices |
This place covers:
Automatic setup of data acquisition parameters (diagnostic protocol) using patient specific information, e.g. weight, height and/or diagnostic specific information.
This place covers:
Methods or devices for calibration where a reference object (phantom) is used to determine particular properties of the diagnosis device.
[US2008139933]
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Calibration phantoms for radiation diagnosis devices | |
Models for medical purposes |
This place covers:
Any device used for tapping on a surface of a body area in order to determine the underlying structure condition, e.g. reflex hammer.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Percussion or vibration massage |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Pleximeter | Plate to be struck in mediate percussion, generally by a reflex hammer |
This place does not cover:
Determining the level of anaesthesia by measuring a physiological parameter, e.g. EEG, EMG |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detection of movement |
This place covers:
instruments for taking a sample from a body:
- devices for taking fluid samples or cell samples;
- biopsy devices;
- devices for taking faeces samples;
- containers for storing such samples;
- devices for determining ovulation;
- devices for detection of breast cancer;
- vaccination diagnosis (allergy test patches);
- devices for sex determination
This place does not cover:
Vaccination instruments | |
Menstruation tables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical instruments in general | |
Surgical cutting instruments |
The breakdown symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" or non "mirror" symbols) and "orthogonal" symbols are to be used for classifying the invention information (in addition to the invention symbols) in case the invention is insufficiently classified by an invention information symbol. They are also to be used for classifying the additional information. They are stored in the additional information field.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ovulation determination for animals | |
Menstruation tables |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Anal receptacles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mammography by transillumination | |
Mammography by X-rays | |
Mammography by c ultrasonic means |
This place does not cover:
Devices for taking blood samples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for receiving spittle |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Artificial insemination | |
For animals | |
Genital receptacles for the male member | |
Massage of the genitals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring sweat production |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring urological functions | |
Genital receptacles | |
Urinals for bed-ridden persons |
This place does not cover:
Devices for taking faeces samples | |
Devices for taking samples of body liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Preservation of living parts of the human or animal body | |
Containers for retaining a material to be analysed | |
Containers in general | |
Apparatus for microbiology | |
Containers for enzymology or microbiology | |
Swab-sampler being part of enzymology or microbiology container |
This place does not cover:
Devices for taking faeces samples | |
Devices for taking samples of body liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical Instruments | |
Surgical cutting instruments with sample retaining means | |
Needle location or guiding means | |
Accessories for Surgery and Diagnosis | |
Samplers for enzymology or microbiology | |
Sampling or preparing biological specimens |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Minimally invasive operation on prostate: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Trocars for bone | |
Filters for solid matter |
This place covers:
devices with a sample notch, which may be, e.g. on an inner stylet or on an outer cannula
This place does not cover:
Instruments for taking bone, bone marrow or cartilage samples | |
Instruments with means for severing sample |
This place covers:
devices used in or near the uterus, includes devices for cervix
This place does not cover:
Devices for taking samples of body liquids |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Gynecological or obstetrical instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
General surgery devices to be introduced in the working channel of an endoscope |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
General surgical forceps |
This place does not cover:
Stomatoscopes when combined with illuminating and viewing instruments: |
This place covers:
Instruments or appliances used in connection with autopsy
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
similar devices for medical purposes, see the relevant groups for such devices, e.g.
General Surgical Instruments | |
Autopsy tables |
This place does not cover:
Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body | |
Eye surgery | |
Ear surgery |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Contraceptive devices, pessaries, or applicators therefor |
T The use of the CPC indexing codes (2000-series symbols which include both breakdown and orthogonal symbols) for classifying the additional information is mandatory in this field.
The breakdown and the orthogonal symbols of A61B 17/00 are also used for documents classified in the main trunk of A61B 18/00 to index relevant aspects for which no suitable symbol is available under A61B 18/00, A61B 2018/00005 or A61B 2218/00.
This place does not cover:
Specula | |
Drainage appliances for wounds |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
With illuminating arrangements | |
Devices for opening or enlarging the visual field, e.g. of a tube of the body | |
Device for performing tracheotomy | |
Dilators |
This place does not cover:
For abdominal wall lifters | |
Suturing instruments for use in minimally invasive surgery, e.g. endoscopic surgery | |
For ligaturing or otherwise compressing tubular parts of the body | |
For applying or removing clamps or clips | |
Forceps for minimally invasive surgery | |
Endoscopic cutting instruments in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For minimally invasive surgery in general |
This place does not cover:
Endoscopic heart surgery | |
Endoscopic access devices, i.e. trocars |
This place does not cover:
Trocars attached to inner organs or inner body tissue |
This place does not cover:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For intervertebral joint distraction by acting on anchors embedded in vertebrae | |
For restoring the shape of collapsed bones by injecting cement into them | |
For restoring the shape of collapsed bones by expanding devices inside them |
This place does not cover:
Suture materials |
This place covers:
See patent # US2004138707
This place does not cover:
Surgical staples for bones | |
Fixation devices for tendons or ligaments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Purse-string suturing |
This place does not cover:
Other bone dowels | |
Dowels for connecting prosthetic parts |
This place does not cover:
Other bone rivets | |
Rivets for connecting prosthetic parts |
This place does not cover:
For applying suture clamps, clips or locks |
This place does not cover:
For removing suture clamps, clips or locks |
This place covers:
Intended to encompass "large" barbs, e.g. ribs going around at least 1/2 of the diameter on the anchor
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For "thin" barbs (seen in a transversal cross section) |
This place does not cover:
Lateral eyelet for attaching suture to needle |
This place covers:
Rigid barbs
This place covers:
Slotted shaft, i.e. distal part
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Threaded staples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coil staples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Coil staples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For passage of suture |
This place covers:
Includes caps or covers pressed inside or outside the body anchor. It does also includes snap fit (e.g. connection by tab and recess)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Increasing friction between anchor and suture; hence if ribs are present to increase snug fit between an additional element and the anchor only this class is given |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Barbed sutures |
This place covers:
Triangular barbs on the suture which lock in a hole of the anchor or biased locking means in the hole of the anchor locking on protrusions of the suture
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for tensioning the suture as such |
This place does not cover:
Surgical cutting instruments |
This place does not cover:
Shuttle needle with sharp tips at both ends | |
MIS ligaturing |
This place does not cover:
J-shaped suture needles |
This place does not cover:
Reshaping the heart with bags, strips, bands |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cushions encircling the heart | |
Blood pumps |
This place does not cover:
Guides for drills, pins or wire (bone) | |
For puncturing needles |
This place does not cover:
Suturing instruments for use in minimally invasive surgery, e.g. endoscopic surgery | |
Other holders for needles or sutures | |
Surgical forceps | |
Forceps | |
Surgical pincettes |
This place does not cover:
Suture anchors | |
Wound clamps or clips | |
Ligaturing clamps or clips | |
Clamps comprising opposed elements which grasp one vertebra between them |
This place does not cover:
For applying suture anchors | |
For applying wound clamps | |
For applying ligaturing clamps or clips |
This place does not cover:
For removing suture anchors | |
For removing wound clamps | |
For removing ligaturing clamps or clips |
This place covers:
See patent # US3878848
This place does not cover:
Blunt suture needles | |
Other devices for protecting against accidental cutting or pricking |
This place does not cover:
Reinforcement for staple lines |
This place covers:
Essentially flexible elements
This place does not cover:
Puncturing needles | |
Hypodermic needles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Essentially rigid suture like elements are "staples" | |
Nerve needles for teeth | |
Sewing needles |
This place does not cover:
Tipping |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connecting wire to other metallic objects) |
This place does not cover:
Lateral opening for attaching suture to suture anchor |
This place does not cover:
Glue applicators | |
For connecting prosthetic parts |
This place does not cover:
For connecting prosthetic parts |
This place does not cover:
Hollow suture needles |
This place covers:
See patent # GB2011259
This place does not cover:
Hand-held holding instruments | |
Holders for articles | |
Racks for syringes or for hypodermic or infusion needles |
This place does not cover:
Proximally pointing needle at distal end of MIS suturing instrument | |
Multiple-needled MIS suturing instruments | |
Attaching suture to needle | |
Suture placed inside a tubular needle | |
Double-armed sutures | |
Puncturing needles | |
Hypodermic needles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Making needles used for surgical purposes; needle tips |
This place does not cover:
For sutures |
This place does not cover:
Bunt dissectors |
This place does not cover:
MIS suturing instruments | |
Jaws of MIS forceps |
This place does not cover:
Suture extending inside a hollow needle | |
Hollow sutures |
This place covers:
This place does not cover:
For suture anchors | |
For MIS suturing instruments | |
Packages for sharps | |
For dental floss |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Packaging in general | B65D 83/00, B65B85/00 |
Packages for needles in general |
This place covers:
See patent # BE693850
This place does not cover:
Instruments for cutting sutures | |
For sharps |
This place does not cover:
With a slip knot | |
Pre-tied sutures | |
Attaching suture to needle | |
Suture placed inside a tubular needle | |
Double-armed sutures | |
Purse-string sutures | |
Suture materials |
This place does not cover:
Means for attaching suture to needle |
This place does not cover:
Big needles, either gripped by hand or connectable to a handle |
This place does not cover:
Completely embedded in the heart wall for tensioning it |
This place does not cover:
Staplers containing only one staple | |
Magazines or containers for staples | |
For performing anastomosis | |
Forceps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Staplers in general |
This place covers:
Curved in longitudinal direction or curved in the transversal direction
This place does not cover:
Circular staplers |
This place covers:
Devices for bringing together the edges of a wound
This place does not cover:
Suture bridges |
This place does not cover:
Approximator for anastomosis |
This place does not cover:
Containing multiple wound clamps | |
For removing surgical staples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Containers, packaging elements or packages specially adapted for particular articles or with special means for dispensing contents |
This place does not cover:
For packaging sharps |
This place does not cover:
Tubular implants | |
Obesity treatment |
Prostheses implantable into the body to facilitate anastomotic coupling |
This place does not cover:
Y-shaped blood vessel prostheses |
This place does not cover:
Closure means for urethra or rectum or for artificial body openings therefor | |
Closure means, constricting the lumen | |
Filters | |
Specially adapted for vas deferens or fallopian tubes | |
Transcervical canal | |
Materials for ligaturing blood vessels |
This place does not cover:
MIS suturing |
This place does not cover:
Plugging an opening in the wall of an organ | |
Occluders for the cervical canal | |
Vas deferens occluders |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
When only reducing the blood flow; combine with stents modifying blood flow | |
Stent graft or graft for the treatment of aneurysms | |
For occluding the hole of a cardiac valve cyclically | |
Stents, different from stent-grafts, adapted to cover an aneurysm |
This place does not cover:
Introducer for blood filters | |
Introducer for stents |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Multiple balloon catheters | |
Balloon catheters or temporarily occluding a vessel for isolating a sector |
This place does not cover:
For the vas deferens |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pressure applied to the urethra by an element placed around the penis, e.g. penis clamp |
This place does not cover:
Clip magazines incorporated in a clip-applying instrument | |
For surgical articles |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
This place does not cover:
Sphygometers |
This place does not cover:
Inflatable | |
Pressure pads |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Occluders to close blood vessels, e.g. against the skin for measuring blood pressure | |
Occluders to close blood vessels, e.g. against the skin for measuring blood pressure of small dimensions | |
Hemostatic bandage with means for applying local pressure |
This place does not cover:
Pressure pads |
This place does not cover:
For measuring blood pressure | |
Gastric bands, remotely adjustable, using inflatable ports | |
Inflatable pressure pads |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/14
Typical example (DE20303018U):
This place does not cover:
Hollow drills or saws creating a curved cut, e.g. cylindrical | |
Tooth saws |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implanting tools or instruments for the jaw bone | |
Cast-cutting saws | |
Saws in general |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/15
Typical example (EP1224912):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arrangements for guiding straight saw blades in general |
This place covers:
This group covers equipment for guiding resection of more than one of the bones at the knee) (femur, tibia, patella), for example (US6478799):
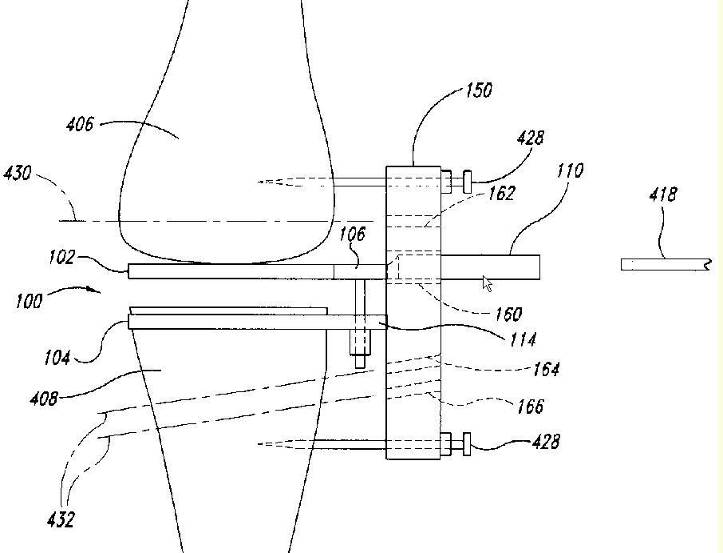
This place does not cover:
Cutting femur only | |
Cutting tibia only | |
Cutting patella only |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/155
Typical example (FR2838626):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/157
Typical example (WO03013371):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/158
Typical example (US5542947):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Arthroscopic bone cutters | |
Abutting on tissue or skin | |
Dental implant drills potentially for other surgical use | |
Bone grinders |
A61B 17/1662 takes precedence over all other subgroups of A61B 17/16 except A61B 17/17
This place covers:
This group covers impacting or shearing devices for removing or indenting bone, for example chisels such as (EP1308132):
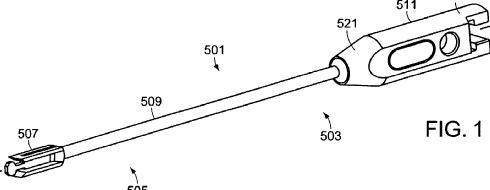
This place covers:
Typical bits :
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand-held or like portable drilling machines |
This place covers:
Examples:
US6358251
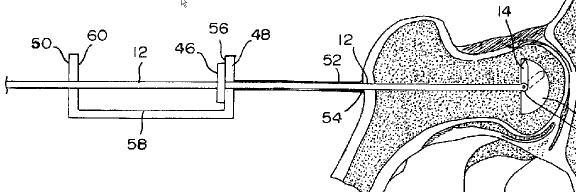
US2001006593
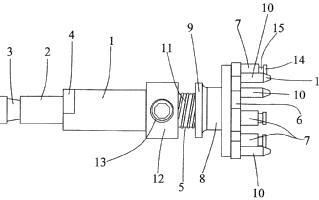
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/162
Typical chuck (DE20304155U):
Typical tool part to be held in a chuck (US5634933):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1622
Typical handpiece (WO0167970):
This place does not cover:
Control means and display units | |
Motors and power supplies |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1624
Examples:
WO2004047664 (uses planetary gears)
US2003219184 (uses particular ball-bearing layout)
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1626
"An advantage of the foregoing system is that it allows a single control console to be used to supply the energization signals that are applied to the handpiece that have different power consuming units, such as motors. Thus, a single control console can be used to operate a first handpiece with a motor that rotates at speeds under 3,000 RPM and requires 350 Watts or more of power, a second handpiece that has a motor that operates at speeds over 70,000 RPM and that requires approximately 150 Watts of power and a third handpiece that operates at speeds between 10,000 to 40,000 RPM and that requires only 40 Watts of power."
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Checking screw impingement on nerves |
This place covers:
Examples:
US5796188
"A medical instrument comprising a handpiece including a body, an electrical device disposed within said body and having an operating characteristic responsive to DC voltage, and a first battery disposed within said body for applying a first DC voltage to said electrical device to cause said electrical device to operate in a first mode; and
a booster disposed externally of said body, said booster including a DC power source and means for detachably connecting said DC power source with said first battery to apply a second DC voltage greater than said first DC voltage to said electrical device to cause said electrical device to operate in a second mode;
wherein said connecting means includes a power cord extending between said booster and said handpiece to permit said booster to be located remotely from said handpiece when said electrical device is operated in said second mode."
DE20105480U
"Antriebsmotor für chirurgische Geräte mit einer stromdurchflossenen, eine Motorwicklung bildenden Leiterbahn, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Leiterbahn (7) in der Motorwicklung aufgeteilt ist in eine Anzahl von elektrisch voneinander isolierten, nebenein- ander verlaufenden Leitungsdrähten (8)."
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1631
Example (WO0045713):
"Der Schaft ist mindestens auf einem Teil seiner Länge bezüglich Torsion und/oder Biegung um die Längsachse (2) elastisch."
NB device provides graft material so is also classified in A61B 17/1635.
This place does not cover:
Intramedullary reamers | |
For producing a curved bore |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1633
Typical examples:
The group also includes so-called "shavers" i.e. instruments with sleeve having a lateral opening exposing the cutter.
This place does not cover:
Using fluid other than turbine drive fluid |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1635
Example (WO03030766):
"The present invention facilitates harvesting a small amount of autologous bone necessary for supplementing insufficient alveolar bone when treating artificial teeth, which has a grip part formed in an insert injection molding to have an anticorrosive blade at the front end thereof, a bone-passing opening formed between the blade and the grip part, a cross wall forming a storage space for bone harvested by the blade and past through the bone-passing opening to be collected, and a cover detachably coupled to the grip part to slide along a guide groove formed in the upper portion of the cross wall and forming a storage space to be used as a surgical treatment container storing the harvested bone."
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1637
Examples:
US6120511
FR2749154 (20 is a cut bone ejection rod of this instrument) -
This place does not cover:
For taking bone, bone marrow or cartilage samples | |
Trepans or craniotomes, i.e. specially adapted for drilling thin bones such as the skull |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/164
Example (US6283970):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1642
Example (US4941466):
This place covers:
Examples:
WO03025102
LUBRICATING OIL FOR ROLLING BEARING UNIT OF HIGH-SPEED CUTTER
WO02085223
CUTTING DEVICE FOR BONE TISSUE
"The invention relates to a cutting device (1), which is provided for cutting bone tissue (3), is intended for correcting malpositions, and which enables a segment of the bone tissue (3) to be cut along a predetermined cut surface (5). To this end, a high-pressure fluid jet (2) is produced by the cutting device (1), and the jet produces, in accordance with a control program stored in a control unit (4), a cut surface (5), for example, in the shape of a circular arc."
US3076904 - Acoustically vibrated material cutting and removing devices. Ultrasonic, with cooling fluid
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1646
Examples:
US4975056
"TI - Medical, especially dental handpiece
AB - A medical handpiece, and especially a dental handpiece, including a drivable worktool or implement which is rotatably supported with its shaft at one end of the handpiece and which projects from this handpiece end with its operating end. The implement possesses an elongate blind bore-like passageway which communicates with the outside at the work end of the implement through the intermediary of a discharge opening, and with which there is associated a supply line arranged within the handpiece for the infeed of cooling media to at least one radial through-opening of the implement which stands in communication with the elongate passageway; whereby the at least one radial through-opening is sealed with respect to the interior of the handpiece through the intermediary of a seal which encompassing the shaft of the implement and contacts against a wall portion of the handpiece."
DE20202724U:
"A surgical tool (10) has a fluid connection into the motor housing (18) with thermally operated sintered, ceramic or porous plastic sealing membrane such as Goretex or mechanical valve to close the link to liquids and open it to the hot steam used for sterilization."
PN - US5823774 A 19981020
AB - "A device is disclosed that dynamically seals the collet of a high-speed surgical or dental drill from the ingress of contaminating substances with which the tool or collet of the drill comes into contact, such as blood, saliva, saline, tissue, bone chips, and tooth particles. The dynamic seal comprises an impeller and a bearing that rotatably supports both the impeller and a surgical tool; furthermore, the seal may be disposed within a burguard that is mounted on the distal end of a surgical drill. The spinning impeller has a disc portion that imparts a centrifugal force to the flow of contaminating substances and thereby pumps the flow entering through the tool opening radially outward through discharge holes in the burguard housing. The dynamic seal further includes an O-ring for sealing against the tool shaft and blocking the contaminating substances from continuing up the tool bore and into the collet of the surgical drill. A backring retains the O-ring in place."
US-A-5823774 Dynamically sealed surgical drill
" A device is disclosed that dynamically seals the collet of a high-speed surgical or dental drill from the ingress of contaminating substances with which the tool or collet of the drill comes into contact, such as blood, saliva, saline, tissue, bone chips, and tooth particles."
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1655
Examples:
US2002143343
US2003018337 (bone drill and tap combination)
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1657
Examples:
US6547796
Simultanously pulling the lever anteriorly and pushing the forehead posteriorly breaks the midface bones free from the skull.
DE98961 (osteoclast):
JP7136187 Bone cruser from outside of human body by impact wave in liquid.
"To enable the crushing of a human bone in a non-invasion manner from outside by arranging a plurality of fine pieces of powder on an axis vertical to a straight line connecting first and second focuses passing through a first focus of a rotary ellipse body to increase energy of an impact wave. Constitution :This apparatus is provided with an impact wave generation chamber 1 with the internal surface thereof so formed as to follow a part of a rotary ellipse body. a plurality of fine pieces 2 of powder for generating an impact wave and an igniter 3 for detonate these fine powder pieces 2 simultaneously. The fine powder pieces 2 are arranged in one row on the axis vertical to a straight line linking between focuses of the rotary ellipse body passing through a first focus, and the impact wave generated is propagated to a liquid 6 in a water tank 7 with the bottom thereof being formed by a flexible film 8. Then, the plurality of fine powder pieces 2 are detonated simultaneously to apply energy of an impact wave in a wide range centering the second focus on the axis vertical to a straight line linking the first and second focuses passing through the second focus, thereby crushing a human bone."
This place does not cover:
Dental osteotomes i.e. tools producing a groove, channel or trench in the jaw |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1659
Examples:
DE10108757 (rasp with passageway)

JP2000210316 (for vertebrae):
US5733288 (when the fibers of the bone brush are placed into contact with the soft tissue covering bone, the rotary action of the brush head removes the soft tissue from the bone): 
FR2742038 (rasp handle):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1662
Example (US5782924, for bone joints):
This place does not cover:
Means other than saws for removing bone from the acetabulum only | |
Means other than saws for removing bone from the upper femur only |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1666
Example (WO03059178):
"CONTOURED REAMER TEETH- An acetabular reamer (10') for cutting a required cut shape"
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1668
Examples:
WO0062718
FR2802080
This place does not cover:
Intramedullary reamers |
This place covers:
Devices for making holes in vertebral bodies (e.g. for pedicle screws, or along the axis of the spine),or, as in the example below (US6224604), for preparing an intervertebral space by machining the vertebral end faces:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guides for spinal drills |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1675
Examples:
US6015411
US6482289
"An apparatus for sculpting the articular surface of a first bone that normally articulates in a predetermined manner with a second bone, the apparatus comprising:a bone-sculpting tool; a mount attachable to the second bone for mounting the tool in position to sculpt the articular surface as the second bone is articulated in the predetermined manner with respect to the first bone."
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1677
Examples:
US6277121
US2003163137
This place covers:
Illustrative examples of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1695
Examples:
EP1245194 (dura guard for craniotome)
US5876405 "The perforator of this invention includes safety mechanism that prevents penetration of the perforator when the drill bit has completed the cutting operation and the resistive load is removed. The perforator cuts the hole by an annular slot leaving a plug of the bone structure that is removed and returned to the original hole for re-filling the hole which aids in the healing process. A clutch may be provided that decouples the drill bit from the drive motor upon sensing a void in the drill passage during the drilling operation:"
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/1697
Example (GB353706):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Abutting means, stops, e.g. abutting on tissue or skin | |
Stops attached to drilling tools, tool holders or drilling machines per se, e.g. drill depth limiters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Implements for applying tendons or ligaments |
This place does not cover:
Drill guides using imaging means | |
Drill guides using electromagnetic effects |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Drill guides using imaging means |
This place covers:
The cutting may be into the vertebral body, e.g. guiding pedicle screw bores as in this example:
or to prepare vertebral end faces as in this example:
or longitudinally along the spine:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Joint distraction for the spine | |
Spinal drills |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guiding dental drills |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Diagnosis by vaccination other than by injuring the skin | |
Cleaning the skin previous to the vaccination | |
Apparatus for injections |
This place covers:
Mainly arrays of needles also for use other than vaccination.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Intradermal administration through microneedles | |
Introducing media into the body by using microneedles |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
For biopsy | |
Gynaecological or obstetrical instruments or methods |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dilators | |
Ultrasound therapy |
Atherectomy devices for cutting or abrading and similar devices performing similar functions should be classified in A61B 17/3207.
This place does not cover:
Or extracorporeal lithotripsy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
(Handheld) ultrasonic cutting devices | |
Sound producing devices | G10K/00 |
This place covers:
Generally catheter like devices for breaking obstructions in vessels or organs.
This place does not cover:
Removing obstructions in blood vessels by laser |
This place does not cover:
Gripping devices in the form of loops or baskets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopic forceps, |
This place does not cover:
Surgical snare instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Intracorporeal lithotripsy | |
Mechanical waves not for extracorporeal lithotripsy | |
Ultrasonic waves for treatment of bones or cancer, e.g. with pneumatic drives |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
positioning of patients for radiation diagnosis | |
Positioning of locating means inside shock wave apparatus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inspections of cavities in the body |
Maxillary sinus lift is classified in A61C 8/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
for holding suture needles or materials | |
for removing or smashing calculi | |
Surgical scissors | |
Obstetrical forceps | |
for inserting intraocular lenses | |
Hand-held gripping tools in general |
This place does not cover:
Forceps for minimally invasive surgery |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for protection against accident injuries by used needles | |
Tools enabling the (needle) cap placement; Some of the devices under these codes are pincette or forceps like |
This place covers:
Details or special features of pivot points.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For biopsy |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For biopsy | |
Mechanical endoscopic instruments performing multiple functions | |
Ultrasonic cutting devices with additional clamping means |
This place does not cover:
Wound clamps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For holding suture needles of materials | |
Electrosurgical pincettes | |
Means for protection against accident injuries by used needles | |
Tools enabling the (needle) cap placement; Some of the devices under these codes are pincette or forceps | |
Hand held gripping tools without pivotal connections in general |
This place does not cover:
Suture cutters | |
Surgical instruments, devices or methods for transferring non-mechanical forms of energy to or from the body | |
Specially adapted knives for eye surgery |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instruments for ligaturing or cutting | |
Instruments for rupturing the amniotic membrane |
This place covers:
Mainly shavers for cutting away unwanted tissue from for instance a knee or an intervertebral disk.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rotating cutters for atherectomy | |
Similar devices for eye surgery |
This place does not cover:
Removing obstructions, in direct contact or very close to the obstruction | |
Dental tooth drilling devices operated by vibration | |
Removing intra-ocular material using mechanical vibrations |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/320068
This place covers:
In general catheters for cutting or abrading obstructions from blood vessels or similar organs.
This place does not cover:
Fluid jet cutters: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopic cutting instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cutting balloons |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lancets |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Packages or dispensers for sharps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for removing or collecting used sharps |
This place covers:
Sharp or blunt tools for making an entry site in the body for inserting a surgical tool or implant device. Tube like devices forming an entry port into the body.
This place does not cover:
Piercing needles for placement of a catheter or tool in a blood vessel: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pointed biopsy instruments | |
Skull plugs for access to the brain | |
Devices for piercing the ear lobe | |
Catheters | |
Access sites | |
Seals or hemostasis valves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Local anaesthesia | |
Epidural catheters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guides for suture needles | |
Stereotactic needle or instrument guides | |
Guiding or tracking by nuclear magnetic resonance |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Details of tips or shafts | |
Gastrostomy feeding tubes | |
Body piercing guide needles for introducing catheters |
This place covers:
Generally more flexible shorter cannulas closely fitting in the created tissue tract such that the distal end does not substantially enters the body beyond the tract.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Retractors | |
Access sites for liquids: |
This place covers:
Made of floppy material such that the shaft collapses under pressure in the absence of an inner instrument.
This place does not cover:
Access ports |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flexible shafts |
This place covers:
This group deals mainly with sealing arrangements at the proximal side (nr. 122 in the drawing).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Expandable cannulas | |
Valves such as flapper valves: | |
Haemostasis valves |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for introducing media in the form of pellets: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bone biopsy | |
For injecting reinforcing material into bone |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Insufflators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrosurgical trocars |
This place covers:
In general flexible endsocopic tools or endoscopes having a distal needle for performing a puncture at the remote distal site.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Biopsy needles | |
Catheters with injection needles | |
Catheters with needle tips |
This place covers:
This group deals mainly with Open/close type valves such as flap valves without any sealing effect around the shaft of an inserted tool.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Haemostasis valves | |
Check valves |
Open/close type valves that form part of a sealing arrangement that can change diameter to seal around an instrument should be classified in A61B 17/3462 unless they have special features, then they should also be classified in A61B 17/3498.
This place does not cover:
Ligaturing clamps or clips for the umbilical cord | |
Curettage | |
Dilators |
This place does not cover:
Forceps, specially adapted for performing or assisting anastomosis |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Contraceptive devices, pessaries; applicators therefor | |
Vas deferens occluders, fallopian occluders | |
Means specially adapted for ligaturing, compressing or clamping of oviduct or vas deferens |
This place does not cover:
Specially adapted for use with animals |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Use with animals – embryo transplant |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/46
See patent # FR987704
This place does not cover:
For animals |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/48
See Patent # GB494596
This place does not cover:
Locating otherwise | |
Locating by radiation | |
Removing calculi | |
From the eyes |
This place does not cover:
Manicuring or pedicuring implements | |
Nail files, e.g. manually operated | |
Bathing sponges, brushes, gloves, or similar cleaning or rubbing implements for cleaning the feet or toes | |
Chiropractic devices | |
Files in general |
This place covers:
When the only subject matter of a document is a method, this class is given.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Orthopaedic methods or devices for non-surgical treatment of bones or joints |
Documents concerning exclusively surgical methods are classified only in this group.
Surgical instruments or devices are classified only in the relevant subgroups of A61B 17/56.
This place covers:
These are implants which do not restrict the relative movement of the bones and are therefore not in any way fixators.
This place does not cover:
Surgical saws | |
Drills and other bone removal means other than saws |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Splints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Non-surgical i.e. non-invasive devices for reduction or distraction | |
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads |
This place does not cover:
External osteosynthesis devices for body parts other than limbs | |
External osteosynthesis alignment, compression or distraction mechanisms |
This place covers:
External osteosynthesis equipment comprising, or attached to, heavy or bulky objects, such as floor- or furniture-mounted fracture-setting means.
This place does not cover:
Devices used without surgery |
This place covers:
Equipment in which the pin-clamp connecting element comprises distinct parts joined to each other.
This place does not cover:
Devices specially adapted to be fitted across a bone joint | |
Bilateral fixators i.e. with both ends of pins or wires clamped |
This place does not cover:
Ring frames | |
Devices not permitting mobility | |
Devices specially adapted to be fitted across a bone joint | |
Devices for body parts other than limbs | |
Devices allowing small scale motion of bone ends |
This place covers:
Equipment in which pin-clamp connecting elements are either multiple in parallel or not essentially linear.
This place does not cover:
Devices specially adapted to be fitted across a bone joint | |
Bilateral fixators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
External osteosynthesis pin clamps movable along a rod |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Clamp elements used in wound retractors |
This place does not cover:
Orthodontic, i.e. tooth-mounted, positioning devices | |
Periodontal regeneration |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Maxillary sinus lift |
This place does not cover:
Bone staples |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dental regeneration membranes | |
Prostheses implanted into the body – bones, bone grafts | |
Prostheses implanted into the body – joints, e.g. shoulder, spine | |
Devices for fastening or securing constructional elements or machine parts together, e.g. nails, bolts, clamps, clips |
This place covers:
- Devices embedded in the vertebrae, e.g. US2009005816
- Devices placed at least partially in the disc space e.g.FR2799638, US2006224241
- Staple-like devices, e.g. US2009270917
- Vertebra or disc reinforcements other than annulus repair patches, e.g. US2008125778
- Longitudinal elements with bone anchors other than screws, hooks or wires, e.g. WO2009004625
- Nerve or anti-scarring shields, e.g. DE102008020111
- Extra-vertebral devices combined with fusion cages or disc prostheses, e.g. W00010473
- Vertebra or disc filler material, e.g. US6251139, US2008172058
Because spinal fusion cages generally cannot be removed without causing failure of the spinal column they are considered equivalent to prostheses and are hence classified in A61F, specifically A61F 2/4455.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Means for repairing the disc annulus | |
Orthopaedic corsets |
This place covers:
"longitudinal" means designed to be placed approximately along the axis of the spine from one vertebra to another. Typical examples:
A61B 17/7001 also includes devices where the orientation of the longitudinal element relative to the anchors can be modified before use, but is fixed in the implanted state, e.g.
The last example above is also in A61B 17/7014 because the length of the longitudinal element can be adjusted.
This place does not cover:
Plates mounted on top of bone anchor heads or shoulders |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7002
Example:
this document is classified here (as well as in A61B 17/7001 because of rod-to-hook fixation arrangement) because of the surface (in this case knurled) of the longitudinal rod:
A further example:
" Tige de liaison pour redresser les deformations du rachis, caracterisee en ce qu'elle est realisee en un materiau a memoire de forme et en ce qu'elle est pourvue d' au moins un canal de circulation (2) pour un fluide calorifique ou frigorifique afin de modifier sa temperature et par suite, sa rigidite."
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7004
Examples:
The example below shows a typical Harrington rod, classified here because of its ratcheting annular projections:
This place does not cover:
Longitudinal elements which have flexible parts, or are connected together such that in use they can move relative to each other |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7005 :
Examples:
WO2007097905
DE202007009970U
EP0516567
US2006149252
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7007
Examples: US2001037111
WO2006023514 :
WO2007124249
FR2827499
This place does not cover:
Plate-like head-mounted longitudinal elements with multiple screw hole rows or a non-aligned single row |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7008
Example DE3722590 :
Note that the group includes devices where a part on the longitudinal element bears against an outside of an anchor-to-longitudinal element connector, as the second of the above examples.
This place does not cover:
Longitudinal elements with parts specially adapted to fit around the screw or hook heads |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/701
Example:
WO2007045895
This place does not cover:
Longitudinal elements with parts specially adapted to fit in the screw or hook heads | |
Longitudinal elements with parts specially adapted to fit around the screw or hook heads |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7011
Examples:
US2005033295
This place does not cover:
Longitudinal elements connected together such that in use they can move relative to each other |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Adjustable length longitudinal elements |
This place covers:
The means for adjusting the distance either adjust the length of the longitudinal element (first two examples), or displace the screws or hooks along it (third example):
This place does not cover:
Bone anchors incorporating an articulation |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Sleeve | Anything surrounding a core or insert, e.g. a coil spring |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7032
A typical example:
The device below is classified in A61B 17/7032 as well as A61B 17/7035, because the feature of having both inner (32) and outer (31) locking screws is unrelated to the device as a whole being polyaxial, and is hence "invention-type" information for any U-shaped head screw:
Classified in A61B 17/7032 for left-hand embodiment and in A61B 17/7035 for right-hand:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7034
Examples (the second of which is polyaxial):
This place covers:
Rotation of the bone-anchoring part about its own axis is not considered to be pivoting.
Note that the longitudinal member must be a rod (i.e. without openings, at least in the vicinity of the bone anchors) for a document to get this class.
This group includes so-called polyaxial screws/hooks, where in at least some embodiments the connection between the rod-clamping part and the rod can be locked separately from the connection between the rod-clamping part and the bone-anchoring part (otherwise classification would be in A61B 17/7037), such as this example:
The group also includes devices in which the rod cannot lie on the axis of the bone-anchoring part (and which are therefore also classified in A61B 17/7041), i.e. ones not referred to as polyaxial, such as this:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7038
Examples (in the first, the bone-anchoring part 16 pivots about pin 26, and hence only in one plane):
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7043
Examples (note that, as in the second example, there may be more than one longitudinal element):
This place covers:
The group contains devices with bone plates, staples or washers mounted to the vertebrae by screws, wherein the rod is mounted to the plates, staples or washers, not to the screws, as in this example: 
Also it contains devices where the rod is mounted to the screws as in this example:
This place covers:
Typically the devices look like this - 
or (an example where connection takes place at the screw heads)
Also classified here are devices where the connectors and longitudinal elements are integral parts of a frame:
And this is an example of a document classified here wherein the longitudinal elements have a crossing at which they are connected (300 is an embodiment of 100):
This place does not cover:
Longitudinal elements connected together such that in use they can move relative to each other | |
Positioners or stabilisers attached by wires, straps, sutures or cables | |
Positioners or stabilisers attached to sacrum, pelvis or skull |
This place covers:
The ends may be aligned (the lower connector in this example) or side-by-side (the upper connector in this example):
Also classified here are arrangements such as the example below, in which bone anchors which can accommodate two rods are shown being used to link two rods near their ends, even though the bone anchors themselves are no different from those which are used with multiple rods extending in parallel the entire length of the device and which are classified in A61B 17/7001 and subgroups:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7052
Examples:
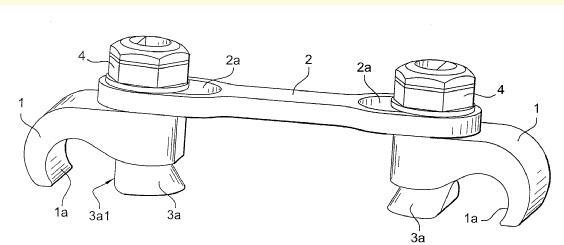
(variable length is provided in the above example by screws 4 being able to translate in elongated holes 2a)
This place covers:
Examples:
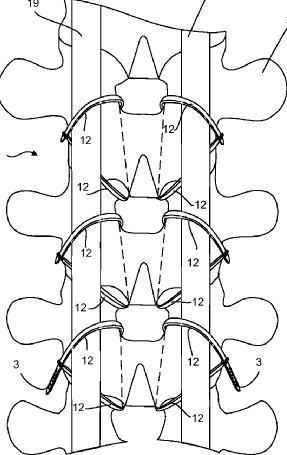
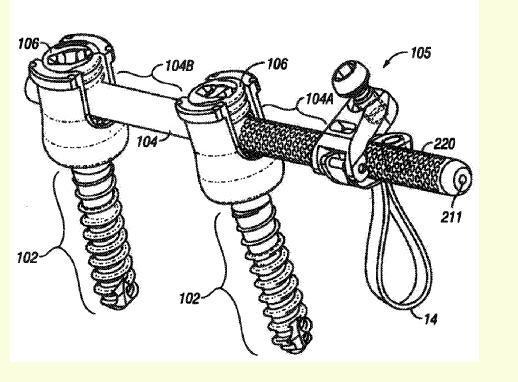
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7055
Examples:
- connected to sacrum/pelvis:
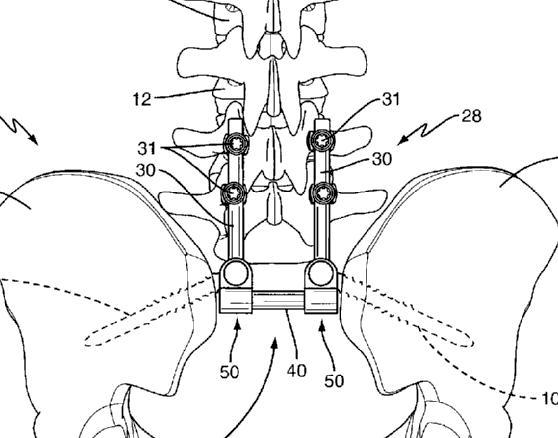
- connected to skull:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7056
Example (notch 3c is the novel feature of the bone-contacting part, which is the claw-like portion):
Note that "bone-contacting part" is interpreted to mean any part of the hook other than features for clamping it to a longitudinal element.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7058
Examples:
WO2007143709
US2002143328
This place does not cover:
Plate-like longitudinal elements with a single row of aligned holes, mounted on bone anchor heads or shoulders | |
Cortical plates i.e. plates bearing directly on bone |
This place covers:
"cortical" means applied to the surface of the bone (the cortex is the dense face layer of bones).
Example (one which is also classified in A61B 17/8042, because of its screw anti-backout means):
This place does not cover:
Screw or hooks combined with longitudinal elements specially adapted to fit around their heads | |
Plates mounted on top of bone anchor heads or shoulders |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Construction aspects of cortical plates | |
Plates specially adapted for the ribs or sternum |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7061
For example:
- a fluid conduit is provided (101):
- medication pellets 42 are implanted:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Intraosseous injection devices | |
Prostheses with pharmaceutical reservoir |
This place covers:
Spinous processes as in this example:
An example where the device is not a simple wedge but two brackets and a hinge:
This shows an example of a tool classified here (it applies suture loop 316 to the spinous processes):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Rib fixation plates |
This place covers:
This group comprises two sorts of devices: devices which immobilise the facet joint (also known as the apophyseal or zygapophyseal joint), e.g. simple clamps or screws as in this example -
and devices which attempt to maintain the natural effect of the facet joint on the relative motion of the vertebrae. The documents concerned (examples are shown below) usually call these devices "prostheses", even when they do not have the form of the natural facet joint and are not mounted near it.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Facet joint prostheses, i.e. implants attached in the location of the natural facet joint surfaces after at least partial removal thereof |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7065
Example:
Inflatable example (WO2009149079):
"The present invention is directed to an inflated interspinous spacer. The interspinous spacer is inserted into the interspinous space between adjacent spinous process in a deflated or unexpanded state, and is inflated or expanded with an injectable filler material. Upon inflation, the spacer preferably distracts the spinous processes and assumes a shape that retains the spacer in position and preferably mechanically locks with the spinous processes. The spacer includes two separate balloons configured to have different compressive modulus so that one balloon is softer and more deformable than the other balloon."
Example of tool for varying the configuration of an implant (10) with movable arms (14), (16), classified here:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flexible or articulated longitudinal spinal elements with screws or hooks |
This place covers:
A part of the device intended to bear only on the left side of the processes must be separate from a part intended to bear only on the right side, until they are in position against the processes.
An example where one component includes an inter-process projection (802):
Example comprising plates either side of vertebrae:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/707
Example of device on ribs:
Example of device on transverse processes:
This place covers:
Typically these devices are inserted between the cut ends of a lamina following laminectomy to increase the space available to the spinal cord.
The group covers reconstructing the vertebral arch as well as expanding it.
Example:
The group also covers expansion of the space available to the spinal cord by distracting adjacent vertebrae (V1, V2 in this example showing a vertical section) apart using a wedge between their laminae or pedicles:
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Both reconstructing the vertebral arch and expanding it are known as laminoplasty.
This place covers:
Examples:
"Methods and apparatus for vascular protection in spinal surgery" (US2007055111)
"Methods for determining pedicle base circumference" (WO2007087381)
"Procedure for visualising and checking the equilibrium of a vertebral column of which a segment is corrected using known instrumentation, comprising determining the positions of the uppermost and lowermost instrumented vertebrae by means of anatomical points or contours identified by radiography, determining as a function of said positions the positions of the vertebrae adjacent to said uppermost and lowermost vertebrae, and visualising the equilibrium or inequilibrium of the vertebral column in a vertical position viewed from the front and from the side" (WO03073946)
An example for which A61B 17/70 was given for the implant (10) as well as A61B 17/7074 for the tool (22) for implanting it:
This place does not cover:
Tools for vertebral process or facet devices | |
Instruments for holding or positioning bone plates, including vertebral plates | |
Tools for expanding or compacting vertebrae or discs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for shaping or cutting osteosynthetic equipment | |
Image producing devices, including spinal | |
Markers, including spinal |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7076
Examples:
- for positioning a hook:
- for positioning (the receptacle of) a polyaxial screw:
- for assembling a polyaxial screw:
- for inserting a fusion-cage-like threaded anchor (not tapered or pointed and hence not considered as a screw):
- for inserting a vertebral clamp:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7077
Typical example:
Example of so-called "derotation" devices, usually complex tools, that are classified here:
Tool attached to spinous processes classified here (but not adapted for use with an interspinous implant otherwise it would be classified in A61B 17/7062):
e.g. of distractor combined with soft tissue retractor which is classified here : 
Example, classified here, where the anchors are plates: 
Example of document classified here where the device comprises a large frame on the patient's back:
This place covers:
Examples where the tool merely pushes at least one anchor (the left-hand one in the second example) rather than being connected to it, so the longitudinal element is required to guide the motion:
Example acting on a hook and on the rod it is slid along:
Example where anchor movement is perpendicular to the longitudinal element :
Example where the longitudinal element is a plate and hence the document is also classified in A61B 17/8019:
Example where the tool uses the longitudinal element to displace the anchors (the implant itself is classified in A61B 17/7014):
Example where the tool acts on longitudinal anchor-connecting elements: 
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Vertebral displacement perpendicular to the spinal axis is known as spondylolisthesis.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/708
Examples:
Note the tubular nature of the extensions in the example above (without which it would be classified in A61B 17/7077). These allow tools to be inserted through them, which permits a minimally invasive procedure.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7082
Example (screwdriver for pedicular, spinal-rod-holding screws):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Driving non-spinal bone screws |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7083
Example rod inserter:
An example where the rod is inserted along a guide wire (NB the wire appears arcuate but this is purely schematic, hence the document is classified here instead of in A61B 17/7089): 
Example where the longitudinal element to be inserted is not a rod:
Examples for inserting rod-to-anchor connectors:
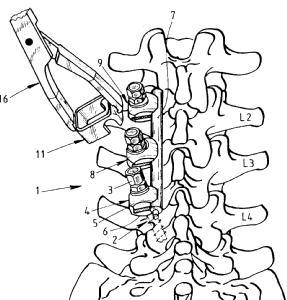
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7091
Typically these devices look like this:
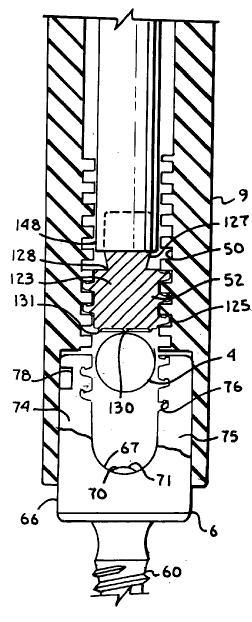
This is an example for a nut (52):
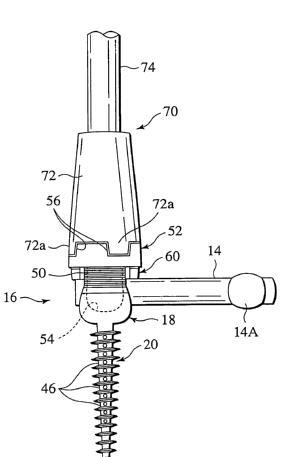
An example for a cap:
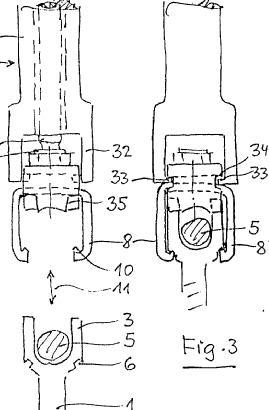
An example for a wedge:
An example where the longitudinal element (44, only part shown) is not a rod. (The bone anchors are 50; tool 100 tightens nut 84 and screw 72 and thus locks the assembly.)
This place does not cover:
Pedicle drill depth limiters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electromyography for checking screw impingement on nerves | |
Means for controlling the depth to which a pedicle is drilled |
This place does not cover:
Bone-expanding elements which form a mechanism rather than merely being particles joined together |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Filler | a material without a fixed shape, although the individual elements which form it may have a fixed shape, e.g. spherical beads |
This place covers:
Vertebral fillers comprising particles, whether or not embedded in a matrix as in the following example; and devices for insertion thereof:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Inserting bone graft implants, e.g. particles thereof |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7097
Example (fig. 15 shows filling of container 22, fig.14 shows it left in the vertebra as an implant):
This place does not cover:
Filler introducer tips comprising containers which are removed from bone after filler has been introduced into them, leaving the filler in place |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Disc prostheses made of inflatable chambers or pockets filled with fluid | |
Replacing the nucleus pulposus |
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7098
Porous example:
Example where the implant is an annulus surrounding the filler:
Example of injection through cannulated screw
(US2009264895:):
This place does not cover:
Devices for the head, neck or trochanter of the femur, including IM pins or the like | A61B17/78 |
This place does not cover:
IM nails with laterally expanding parts |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/7053
Includes, for example, nails with special means comprising a plate-like end, or a connector like (50) shown here:
This place covers:
Nails with locking pins or screws which are adapted, or particularly suited, for use with nails.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for the head, neck or trochanter of the femur |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Trochanteric devices connected to the proximal part of an endoprosthetic femoral shaft | |
Endoprosthetic devices for the head or neck of the femur |
This place covers:
Cortical plates classified in this group as opposed to its subgroups include for example those with a particular form unrelated to a particular bone such as:
or having a particular material; a particular manufacturing processes; or with functions in addition to fixing bone, for instance this one with a strain gauge:
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Cortical plates used as spinal positioners or stabilisers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plates to support bone grafts | |
Plate-like wound dressings |
Cortical plates including a ratchet are classified in A61B 17/8009 even when the cortical plate is not explicitly used for compression or distraction of the bones.
This place covers:
Bones or fragments of bone must be compressed against each other in this group. The definition does not refer to plates that simply press against the surface of the bone when their screws are tightened, something ordinary cortical bone plates do and as a result of which such plates are occasionally called "compression plates".
Example of a compression mechanism classified here:
Example of a plate classified here because it has a property that can be used to achieve compression/distraction, e.g. made of shape memory or, as in this case, plastically deformable to clamp bone fragments together (the deformed outline is shown dashed)
It would be difficult to draw a dividing line between distraction/compression plates and other subcutaneous distraction/compression devices mounted on the bone surface, so "plate" has been generously interpreted, e.g. this is classified in A61B 17/8004:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Alignment, compression or distraction mechanisms with parts external to the body, including those which are mainly implanted but have percutaneous means of operation |
Plates which allow compression or distraction due to relative movement of parts of these plates, e.g. dynamic plates or static compression plates, and which are not "locked in" by a device such as a ratchet, should be classified also in A61B 17/8023.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8009
Example:
Thanks to the ratchet the plate halves can only move relative to each other in one direction, so due to movement in the implanted state either compression or distraction of the bone will develop.
This place covers:
Most commonly, as here, the ramped form of the bone screw holes forces the screw heads laterally, and hence displaces the bone fragments to which the screws are attached:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8019
e.g. (tool 13 is removed once the plate is fixed): 
This place covers:
Plates whose length can be changed in both directions, i.e. it must be possible both to lengthen and to shorten any plate classified in this group.
Either the length may be adjusted and then fixed (here using screw 21):
or the parts may be left free to move in the implanted state:
As with A61B 17/8004, the term "plate" is generously interpreted, e.g. the device below comprising two blocks which can slide relative to each other guided by mating projections in bores is classified in A61B 17/8023:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plates having a ratchet |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8028
For example, here the cushions are 3, 11-13 and 21-24:
Here the cushion is 5:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Washers, i.e. pads placed around screws or bolts |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8033
Another example is
where the additional component is cam 42 which deforms the plate so as to clamp the screw head.
This place covers:
Typically the inserted component expands the screw head so that it cannot escape from the plate hole, although occasionally, as indicated here dashed in the lower figure, the expansion is not so great that the screw can no longer pivot in the screw hole:
This place covers:
There may be one cover (here, sliding cover 98) for many screws:
Or one cover per screw as in this example:
Also, the "cover" may be a small element that only lies over a part of the screw head, such as 40 in this example:
This place covers:
Most commonly in this group the screw head expands the additional element, either so that the head is merely trapped in the plate hole but can still rotate (upper figure in this example), or so that plate, screw and additional element are locked relative to each other by friction (lower figure):
This place does not cover:
Plates with fixed inserts or inlays |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Washers, i.e. pads placed around screws or bolts |
This place covers:
Possibilities include for example threading, a Morse-tapered head and hole, deformation of the material of the head or hole material as the former is screwed into the latter, high friction (sometimes referred to as "textured") surfaces (lower figure in this example), and snap-fitting (upper figure in this example):
This place covers:
Plates wherein the thread is either in the body of the plate or, as in this example (DE19629011), in a fixed insert:
This place does not cover:
Spinal cortical plates | |
Devices for the head, neck or trochanter of the femur |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Partial acetabular cups |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mandibular prostheses |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/808
Example plate positioning tool: 
Example plate holding tool:
Example screw locking mechanism adjuster: 
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tools for use with a plate to extend or compress bone |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8085
Examples:
Plates that can be easily bent due to their material, without or (as in this case, using heater 4,4') with, application of heat:
- due to their structure (on the left a wire mesh, on the right a textile):
Due to thinness (on the left) or folds (on the right):
- due to areas of reduced cross-section (upper below) or hinges (lower below):
Because the craniofacial (head) bones have such complicated shapes, plates for them usually comprise small strips so that they can be bent to fit by the surgeon. Hence almost all plates for the head are also classified here e.g.
This place does not cover:
Plates specially adapted for the jaw | |
Plates specially adapted for the ribs or sternum |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connecting prostheses with the body |
This place covers:
Example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/809 (the projections are bent into perpendicular spikes by the surgeon):
Also, very plate-like devices like this with an integral nail for the femoral head are classified here as well as in A61B 17/74:
This place does not cover:
Bone staples i.e. spiked plate-like devices so small they do not have screw holes | |
Intramedullary nails with a plate at an end |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Spiked plate | plaque-agrafe in French |
IM nails with an end plate | clou-plaque in French and Nagelplatte in German. |
This place covers:
All devices for fixing an opening-wedge osteotomy (as in the first four figures) or a closing-wedge osteotomy (as in the last figure):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wires, bands or straps other than for cerclage | |
Apparatus for manipulating flexible wires or straps |
This place covers:
All devices for osteosynthesis of the sternum.
This place does not cover:
Intramedullary devices | |
Cerclage devices | |
Threaded wires, pins or screws |
This place does not cover:
Intramedullary devices | |
Threaded wires, pins or screws |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nails, staples |
This place covers:
Threaded wires, threaded pins and screws, for fastening internal fixators to bone, cartilage or intervertebral disc; and nuts, washers and packaging therefor.
This place does not cover:
Intramedullary nails |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Pins for external fixators | |
Devices for the head, neck or trochanter of the femur | |
Fasteners using screw-thread |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Spinal positioners or stabilisers with screws or hooks combined with longitudinal elements which do not contact vertebrae |
Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system:
Screw-in dental implants |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Racks for surgical articles | |
Packaging for dental implants | |
Packaging for prostheses | |
Kinds or types of packages |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Nuts for connecting prosthetic parts | |
Nuts or like thread-engaging members |
This place does not cover:
Cushions between bone plate and bone | |
Annuli surrounding screw heads in plate holes |
This place does not cover:
Tools specially adapted for spinal fixation operations |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Special tools or methods for implanting or extracting artificial joints, accessories, bone grafts or substitutes, or particular adaptations therefor |
This place covers:
An example of a device in this group - in this example the cement is applied on, rather than in, the bone:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Cement for adhering prosthetic parts | |
Plugs or restrictors for bone cement | |
Tools for filling disc chambers with fluid | |
Tools for introducing bone graft | |
Tools for insertion of spinal prostheses | |
Prostheses with coating of bone cement | |
Bone graft materials | |
Syringes |
This place covers:
Contains miscellaneous documents concerning introducing or removing fillers into or from bone, e.g:
which concerns guiding apparatus for the filler injector (230)
This place does not cover:
Stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant, e.g. balloon; devices for inserting or filling such implants | |
Preparing or supplying cement or other fluid fillers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Glue applicators | |
Trochars for intraosseous injections | |
Injecting graft material |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Injection of cement into the vertebra without prior creation of a cavity in it is called "vertebroplasty". If there is prior preparation of a cavity the procedure is "kyphoplasty".
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8811
e.g. US2010121336:
US2010145277:
US2009163872:
In this example the tip is a container into which fluid is injected; the container can be opened or ruptured and then removed (which is why the document is not in A61B 17/7097) leaving the filler in place:
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8816
e.g. WO2007036815:
e.g (of connectors) CN201150561Y : TI - Bone cement injection syringe AB - The utility model relates to a bone cement injector, which relates to an injector, and particularly relates to a bone cement injector for vertebral injection. The utility model provides a bone cement injector which has the advantages of convenient and swift operation, simple structure, low production cost and pollution prevention, which comprises an injection tube, a spiral push rod, an injection tube connector, a connecting flexible pipe, a connecting flexible pipe joint and an injection needle, wherein the rear end of the injection tube is provided with a handle with an internal screw hole, the handle is connected with the spiral push rod through screw threads, the front end of the injection tube is connected with the injection tube connector through screw threads, the front portion of the spiral push rod is arranged in the injection tube, which forms relative rotation and piston-type sliding engagement with the inner cavity of the injection tube, the rear end of the spiral push rod is provided with a handle, one end of the connecting flexible pipe is connected with the injection tube connector, and the other end of the connecting flexible tube is connected with the connecting flexible pipe joint, and the connecting flexible pipe joint is connected with the injection needle.
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8819
e.g. (WO2008140519):
e.g. of nesting (WO2008011262):
An outer cannula (1) has a wall, an open end, an open distal end suitable for insertion into intraosseous cavity (27) of a spinal vertebra (26). A lumen extends between the proximal and distal ends. Wall has a side-port (5) situated near the distal end such that a lumen is fluidly coupled with the cavity. An inner cannula is received inside the outer cannula. Inner cannula has a second wall, an open proximal end, a closed distal end and a second lumen. Second wall has a side-port that aligns to outer cannula side-port for discharged of bone cement from within the second lumen into the cavity.
This place does not cover:
Equipment for introducing fluid filler characterised by syringe details |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8822
EP2269541: 
US2006122625:
WO0200143:
This place does not cover:
Fluid filler introducers with means facilitating fluid expulsion | |
Fluid filler introducers with filtering, degassing, venting or pressure relief means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tools for preparing fluid fillers e.g. bone cement | |
Equipment for mixing cement or other fluid fillers for bones |
This place covers:
e.g. EP0470393 (air vent), US2007255287 (pressure relief)
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mixing devices |
This place covers:
Curing: EP16880979 The invention is based on the use of polyisobutylmethacrylate instead of PMMA as an adhesive or spinal fill material for treating diseases of the spine. Polyisobutylmethacrylate has several advantages over PMMA, mainly less heat is developed during the in situ polymerization process. When using any spinal adhesive of fill material that is light activated, a tube can be used to transmit activating light to the light-activated adhesive or spinal polymerizable fill material at the surgical site. In addition, a mesh bag comprising optical fibers or similar light transmitting material can be employed to receive the injected light-activated fill, with the mesh bag, irradiated externally, for directing the light via the bag to the polymerizable fill.
Heater (WO2010008814):
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hardening surgical adhesives |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/885
Example documents in this group:
- for the jaw: movement of wedges 32 causes the device to expand, thus enlarging the cavity for a dental prosthesis:
- blunt broaches for enlarging the intramedullary canal for hip prosthesis insertion:
- compacting bone graft to form implants
This place does not cover:
Stabilisers comprising fluid filler in an implant, e.g. balloon; devices for inserting or filling such implants | |
Equipment for introducing fluid filler into bone or extracting it |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Compacting bone graft or substitute in the body | |
Preparation of bone graft, bone plugs or bone dowels, e.g. grinding or milling bone material |
This place covers:
A device using shape memory effect:
Winding a coil to expand a vertebra:
A non-spinal example: a device for expanding a crushed long bone
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Kyphoplasty | Creating a vertebral cavity to be filled with reinforcing cement, typically by expanding a balloon |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8855
In this example fig.25 shows the balloon creating a second cavity after the first has been filled with material 55:
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Balloon catheters |
This place covers:
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in A61B 17/8858
Illustrative examples:
Sometimes a mechanically expandible device is left in place; there is no special class for this (unlike A61B 17/7097 for containers left in place), so even though in this case the device is as much an implant as an instrument, nonetheless it is classified in A61B 17/8858 (besides, unlike with containers, there is little or no difference between the structure and materials of mechanical expansion devices which are removed after use, and those which are left in place). Here is an example:
This place does not cover:
Inflatable bone expanders/compacters |
This place covers:
As well as devices explicitly for wires or straps, this group covers devices intended to manipulate cables or plastically deformable sutures.
This place does not cover:
Devices for inserting Kirschner wires |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bone cerclage | |
Wire working |
This place covers:
Apparatus for shaping or cutting by medical personnel.
Tools for breaking or fracturing osteosynthetic equipment.
Tools for adjusting the length of orthopaedic equipment.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Apparatus for manufacturing osteosynthetic equipment | |
Hand tools |
This place does not cover:
Distractors which pull bones apart other than via elements embedded in the bones |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Expanding bones to restore their shape using devices inserted in the bone |
This place does not cover:
Tools specially adapted for spinal fixation operations | |
Instruments for holding or positioning bone plates |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Guide wires for catheters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Insertion or extraction of artificial joints |
This place covers:
Surgery, i.e. destruction, modification or removal of tissue, by non-mechanical forms of energy, mainly by heating or cooling the tissue beyond the temperature for irreversible tissue damage.
This place does not cover:
Mechanical surgery in general | |
Ultrasonic mechanical disintegration of calculi etc. | |
Cutting with an ultrasonic vibrating blade | |
Lasers for dentistry | |
Therapy by heating or cooling | |
Eye surgery (including lasers therefor) | A61F 9/007, A61F 9/008, A61F9/01 |
Ear surgery | |
Radiation therapy | |
Ultrasound therapy (including ultrasonic thermal destruction of tissue) |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instruments for medical examination in the interior of the body, e.g. endoscopes | |
Instruments for examination of the eyes | |
Detecting, measuring or recording for diagnostic purposes | |
Apparatus for radiation diagnosis | |
Apparatus for ultrasound diagnosis | |
Accessories for surgery or diagnosis | |
Lasers for dentistry | |
Lasers in eye surgery | |
Electrically conductive preparations for use in therapy or testing in vivo, e.g. conductive adhesives or gels to be used with electrodes | A61K50/00 |
Suction or pumping for medical purposes | |
Mechanical or structural details of catheters | |
Details of catheter tip steering | |
Electrotherapy | |
Magnetotherapy | |
Working by laser beam | |
Materials for the production of heat or cold by chemical reaction | |
Light guides | |
Lasers in general | |
Generation of oscillations, AC generators |
Control aspects for surgery not covered by A61B 2018/00636 should be indexed using CPC codes A61B 2017/00017 - A61B 2017/00225. Additional features or accessories for surgery not covered by A61B 18/00 should be classified in A61B 90/00 or A61B 34/00.
The use of the CPC indexing codes (2000-series symbols which include both breakdown and orthogonal symbols) is mandatory in this field. The breakdown and the orthogonal symbols of A61B 17/00 are also used for documents classified in the main trunk of A61B 18/00 to index relevant aspects for which no suitable symbol is available under A61B 18/00, A61B 2018/00005 or A61B 2218/00.
The area relating to the body part being treated is classified in A61B 2018/00315 - A61B 2018/00565.
This place covers:
Cooling or heating an instrument or tissue NOT to be treated. The cooling or heating has no therapeutic or surgical effect, it just serves to maintain a normal thermal status which would be changed by the thermal therapeutic energy.
This place covers:
The subgroups define various surgical applications or body areas which are treated.
Groups not used for invention information. Headgroup A61B 2018/00315 not to be used for classification.
This place covers:
The subgroups define various surgical effects achieved by the thermal energy.
Headgroup A61B 2018/00571 not used for classification.
This place covers:
The subgroups define various control aspects during thermal surgery.
Headgroup A61B 2018/00636 not to be used for classification.
This place covers:
Cooling, i.e. cryogenic surgery.
Tissue destroyed by freezing.
This place does not cover:
Cooling of probe heat treatment probe, reheating of cryoprobe and cooling or heating of non target tissue surrounding thermally treated target tissue | |
Cooling for non-destructive therapy to be classified in | |
Devices for cooling specific reflex points of the body within cell-life limits |
This place covers:
Heating for tissue destruction in general. Specific energies used therefor in classes below.
This place does not cover:
by applying electromagnetic radiation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hyperthermia using electric or magnetic fields, radiation or ultrasound |
This place covers:
The subgroups define various mechanical features of the treatment devices.
Headgroup A61B 18/042 not to be used for classification.
This place covers:
Using heat caused by chemical reaction, e.g. moxibustion.
This place covers:
Using electrically heated probes. No current is guided through the tissue. Part of the probe itself is heated by current passing through it, e.g. due to its resistivity.
This place covers:
Power sources for the electrically heated probes defined above.
This place covers:
Heating by passing electrical current through tissue to be heated, e.g. with RF frequencies. Electrodes themselves to not (substantially) heat up. Generators therefore in A61B 18/1206.
This place covers:
(Active) Electrodes and probes carrying those for passing current through tissue to be heated.
Indexing codes A61B 2017/2901 – A61B 2017/2948 are used to index specific structural features of forceps-type probes or electrodes.
This place covers:
Passive (indifferent, return, ground) electrodes for grounding the patient. Usually large surface electrodes to be attached to the patient to collect current emitted by the active electrode(s). No surgical effect intended under these passive electrodes.
This place covers:
using electromagnetic radiation, e.g. light other than laser or microwaves (A61B 18/1815).
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for therapy with light or microwaves |
This place covers:
Using laser. Lasers for eye surgery to be classified in A61F 9/008 and subgroups.
This place covers:
The laser beam being guided through a flexible conduit, e.g. optical fiber.
This place covers:
The laser beam being guided through a catheter or needle like introducer.
This place does not cover:
for producing a shock wave, e.g. laser lithotripsy | |
for heating a thermal probe or absorber |
This place covers:
The laser light producing a mechanical shock wave in a liquid or part of the device.
This place covers:
The laser heating a thermal probe or an absorber which transfers the heat to the tissue to be treated.
This place covers:
Determination of a treatment plan for surgery.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
(non virtual) simulation | |
CAD computer aided design with virtual models | |
Image analysis | |
Healthcare informatics | |
ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data |
This place covers:
also if model representation of body part is adapted / specifically registered;
software data model, e.g. after segmentation or mapping, pointing, surface reconstruction after scanning;
also determination of anatomic character lines (e.g. femoral axis determination, special planes), ligament tension.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Movement of an organ (i.e. brain shift) | |
Optical scanners, Terahertz scanners |
In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated:
Cleaning of dental devices | |
Cleaning of fluid or tube connectors | |
Endoscopes with cleaning features | |
Cleaning by methods involving presence of liquid or steam |
Typical soft tissue models: mass spring model, FEM, mass tensor model
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For selection of endoprosthetic joints or for pre-operative planning |
This place covers:
A system which measures just a relative position of, e.g. a tip of a certain instrument relative to, e.g. a wall of a blood vessel is not to be understood as a tracking system.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Optical coordinate determination |
For tracking based on tissue impedance combine with A61B 2017/00026.
This place covers:
Includes MR-tracking if the electromagnetic signal of the apparatus is used, i.e. by an antenna on the tool, receiving an induced signal
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscope positioning internal sensor | |
Systems using NMR or MRI | |
Coordinate measuring machines |
If only the image is used with the tool visible on the image, classify in A61B 90/37 and A61B 2090/374
This place covers:
Not by marker but by relative movement of mechanical parts, i.e. rotation of potentiometer, registering of a moving strip patter change of capacity.
Also position decoder in robotic arms.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Forward kinematics to calculate/estimate position of robot arm: |
This place covers:
Tracking by image analysis (automatic)
If tracking is by image analysis only, classify in A61B 34/20 instead of in A61B 34/20 together, e.g. with A61B 2090/376, e.g. in case of a fluoroscopic image being analyzed.
A61B 34/20 alone means the surgeon looks at the screen and acts accordingly.
A61B 34/20 together with A61B 2034/2065 means the system analyses the image, detects the location of the tool (e.g. in a video image) and than displays the tool, e.g. in a previously taken MRI image
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Calibration |
This place covers:
External field generators for triggering the position trackers having special features.
Reference units (to detect the emitted position signals) on moveable arms to be put close to the patient.
Not restricted to electromagnetic transducers
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
User/computer interaction |
This place covers:
The computer system indicating the surgeon what to do next (i.e. by prompting on the screen for a specific action to be taken).
This place covers:
Including communication to hospital server/ other unit via network, e.g. patient information, preferences of a surgeon etc.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical encoders for the position of the robot arm | |
Steering catheters | |
Robots in general | |
Robotic wrist joints |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Self propelled catheter | |
Control is internal to a catheter |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Connected to the body wall |
This place covers:
proximal of the actual instrument held by the arm
This place covers:
Robots with a separate console
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Steerable by drive cable or rod |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capsule endoscopes | |
Magnets on catheters for steering |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand gesture control. | |
Details of input devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Input arrangements with force or tactile feedback |
This place does not cover:
Glove-boxes for manipulating, gloves therefor |
This place does not cover:
Gloves in general |
This place does not cover:
Bandages, dressings or absorbent pads |
This place does not cover:
For part of endoscope entering the body | |
For dental instruments |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For part of an endoscope entering the body |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tubular drapes, e.g. for arm or legs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Holders for articles |
This place does not cover:
Surgery through the lower body openings, e.g. urology, gynaecology |
This place does not cover:
Instrument-protective drapes | |
Cleaning devices for surgical instruments | |
For preservation of living parts of the human or animal body | |
For sterilising articles | |
For cleaning for sterilising hypodermic or infusion needles or syringes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Having adhesives means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toggle latches or clamps |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ties |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Draw-strings |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Locking clamps | |
Swingable wire bails |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Toggle latches or clamps | |
Carrying handles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Permanent closure means |
This place does not cover:
Supports for surgeons | |
Medicine cabinets | |
Accommodation for nursing |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Other holding stands |
This place does not cover:
Holders for suture needles or materials | |
Drapes with means to hold surgical instruments | |
Supports as part of surgical instruments | |
Hangers for particular articles | |
For tooth drills | |
For receptacles and tubing attached to beds | |
For pharmaceutical containers | |
For irrigation devices | |
Racks for syringes or for hypodermic or infusion needles | |
For infusion devices | |
For catheters | |
Holding devices for laboratory apparatus | |
Racks for work tools |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mayo stands |
This place does not cover:
For endoscopes | |
For test samples | |
For surgical needles or sutures | |
For ligaturing clips | |
For gloves or finger-stalls | |
For dental floss | |
For dental instruments | |
For prostheses | |
For contraceptive devices | |
For bandages or the like | |
For pharmaceutical products | |
Kits for diabetics | |
For catheters | |
In general | |
- e.g. with dispensing means | |
- e.g. for ampoules | |
Clinical contact thermometers for use with humans or animals | |
For optical fibres | |
For X-ray films |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For MIS instruments | |
For suture anchors | |
For MIS suturing instruments | |
For surgical stapler | |
For bone screw or threaded wires |
This place does not cover:
For suture needles | |
For wound clamps | |
For scalpel-blades | |
For used sharps | |
For syringes or for hypodermic or infusion needles | |
Packages for needles in general |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For retaining suture needles or sutures |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Bactericidal products in casings for used articles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Flexible multi-pouches |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Swingable locking handles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For prostheses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For surgical instruments or accessories | |
For prostheses |
This place does not cover:
Bags for midwives | |
Bags in general | |
First-aid kits |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Carried on clothing or back |
This place does not cover:
For sutures | |
Accessories for operating tables, e.g. for collecting body wastes | |
Combustible sputum cups | |
Sterilising refuse | |
For destroying hypodermic or infusion needles or syringes | |
Disposal of medical waste by destroying it or transforming it into something useful or harmless | |
For domestic refuse or the like |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Refuse receptacles in general |
This place does not cover:
For suture needles | |
For scalpel-blades | |
For syringes or for hypodermic or infusion needles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For destroying used hypodermic needles or infusion needles or syringes |
This place does not cover:
Devices for determining blood loss |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Counting means |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Preservative liquid in packages or dispensers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical masks, gowns or dresses | |
Devices for carrying off, treatment, or carrying over body liquids |
Surgical or diagnostic instruments, implements and accessories not covered by A61B 1/00 - A61B 17/00.
The breakdown symbols (i.e. the non "parallel" or non "mirror" symbols) are to be used for classifying the invention information in case the invention is insufficiently classified by an invention information symbol. They are also to be used for classifying the additional information. They are stored in the additional information field.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surgical tractors | |
Implantable mammary prosthesis | |
Dilators |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Dental torque limiters |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For implantable prosthetic joints | |
For prostheses |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protection of eyes against laser radiation |
This place does not cover:
Garments with protection |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring/detecting at the treatment site for control purposes | |
For implanting artificial joints | |
For non-implantable prostheses |
This place does not cover:
Measuring penetration depth |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Measuring of cardiac valve or valve annulus |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Protective suturing devices | |
Blunt suture needles | |
Blunt dissectors | |
For trocars | |
Means for protection against accidental injuries by used needles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Orientation indicators for gripping |
This place covers:
Also used for tools having design features for easy sterilising such as features for taking a tool apart easily.
This place does not cover:
Bone joint inserts | |
Implantable mesh grafts |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Plugging wall openings | |
Retractors | |
Tissue expanders |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopes with cleaning features | |
For vein removal: | |
For ultrasonic devices: | |
Cleaning of dental devices | |
Cleaning of fluid or tube connectors | |
Cleaning by methods involving presence of liquid or steam |
This place covers:
for surgery of small targets, mainly inside the brain but also in the breast or other soft tissue.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radio-opaque marker |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Access ports for other organs | |
Access sites for bone |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Needle guiding or locating |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Tables with compression means for mammography | |
Tables with patient immobilising means for radiation diagnosis | |
Bone screws or pins |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Breast surgery | |
Breast tissue markers |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Ophthalmoscopes: | |
Surgical microscopes |
If the invention is more linked to surgical aspects or in combination with other surgical devices it should be classified in A61B 90/20. If it deals mainly with technical aspects concerning for instance the optics, it should be classified in G02B 21/0012.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopes for respiratory tract with illuminating arrangements | |
Bronchoscopes with illuminating arrangements | |
Instruments for performing medical examinations of vagina with illuminating arrangements | |
Wall mounted illumination of surgical working place | |
Lighting operating theatres |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Light guides |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand grips for operation or dentist lamps |
This place does not cover:
Surgical microscopes: | |
Systems with images on a monitor: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Capsule endoscopes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Detecting body movement for diagnosis | |
Modelling using patient body |
If only a trajectory is overlaid on the image, classify in A61B 2034/107 only;
If only the tool i.e. a representation of the tool is overlaid, this is not enough to classify with this code.
If only virtual haptic boundary is present: classify in A61B 34/76.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Stereo radiography |
This place covers:
Hardware details of viewing device, e.g. viewing sensor; determining that a viewer is viewing.
Illustrative example of subject matter classified in this group:
This place covers:
Includes laser scanners i.e. for surface registration.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Surface scanners in dental field | |
Projecting of images/ contour detection | |
Scanning devices in general |
If a model is built upon the information, A61B 2034/105 should also be given.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Instruments specially adapted for MRI | |
Tracking using the electric effect of the MRI RF coils on a coil by evaluating the induced system: | |
Automatic image recognition used for the tracking | |
Tracking using MRI imaging | |
Invasive instruments for MRI |
This place covers:
including multislice CT
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Needle guides with ultrasound guidance |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Mechanical markers for eye keratomy | |
Markers in surgical tampons or sponges | |
Sponges/dressings with markers | |
Markers for catheters | |
Calibration of imaging systems, e.g. using test probes | |
Testing of X-ray installation, e.g. by phantoms |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Radium seeds |
This place covers:
Includes laser marks (e.g. a laser point guiding for a laparoscope)
This place does not cover:
Identification means coded with symbols |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Visible markers on catheters | |
Optical identification markers of media introduction devices |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Magnetic markers on catheters |
This place covers:
Radiopaque, having particular properties, not just leaving a shadow on the x-ray.
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for implanting pellets, radium seeds or the like |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Drapes |
This place does not cover:
Surgical manipulators | |
Holders for articles |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscope positioning articulated arms | |
Accessories for operation tables | |
Stands as supports for apparatus or articles in general | |
Stands with ball joints | |
Supports for lighting | |
Supports for optical elements |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Counterbalancing structure (e.g. surgical microscope) |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Lockable arms (mostly of the tension cable lock-type) are common in cardiac retractors: |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Wrist support platforms | |
Chairs in general | |
Ergonomic chairs | |
Operating chairs |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Endoscopes with cleaning features | |
Cleaning of dental devices | |
Disinfecting | |
Cleaning of fluid or tube connectors | |
Cleaning in General | |
Cleaning by methods involving presence of liquid or steam |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For cleaning features on endoscopes |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Devices for testing effectiveness of sterilisation |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Hand held absorbent pads containing cleaning liquid |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
For scanning devices | |
RFID tags |
This place covers:
Particular types of patients or of subject under examination using apparatus and methods according to A61B 5/00
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Transmission of foetal data | |
Measuring heart rate of foetus | |
Pregnancy / labour monitoring | |
Sensor adapted to attachment to the uterus |
This place covers:
Infants up to around 1 year old
This place covers:
Older children
This place covers:
Evaluation of subjects, usually healthy, while practicing sports.
This place covers:
E.g., evaluate responses of the public to stimuli such as advertisements for marketing purposes
This place covers:
Evaluation of subjects while conducting means of transport
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Evaluate vehicle drivers, e.g. for sleepiness | |
Sensors mounted on cars |
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
Electrodes for electrosurgery | |
Electrodes for stimulation |